中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (38): 6104-6108.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.38.007
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
羟基磷灰石表面修饰人工角膜钛支架的体内生物相容性
汪雪梅1,赵秋芳1,吴晓蓉2
- 1陕西中医药大学附属医院眼科,陕西省咸阳市 712000; 2南昌大学第一附属医院眼科,江西省南昌市 330006)
Hydroxyapatite surface modification of artificial cornea titanium scaffold: in vivo biocompatibility
- 1Department of Ophtalmology, Affiliated Hospital of Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China;
2Department of Ophtalmology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China
摘要:
背景:纯钛人工角膜支架在临床应用中的并发症发生率较高,因此寻找一种生物相容性高的人工角膜支架材料一直是国内外研究的重点和热点。
目的:观察羟基磷灰石表面修饰人工角膜钛支架的体内生物相容性。
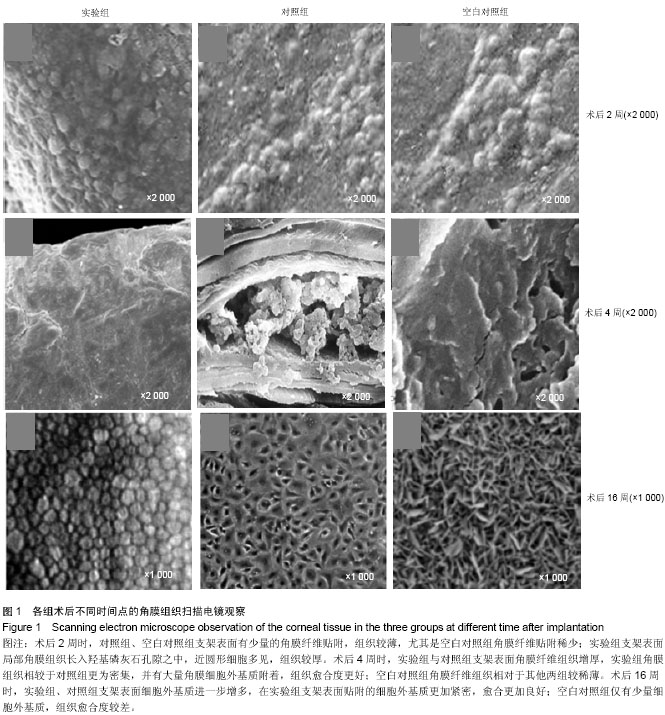
方法:取新西兰白兔27只,制作右眼角膜碱烧伤模型,造模后立即均分为3组,实验组右眼植入经过羟基磷灰石表面修饰的人工角膜钛支架,对照组右眼植入人工角膜钛支架,空白对照组右眼仅制备囊袋而不植入支架。术后2,4,16周取兔右眼角膜组织,进行病理组织学观察及扫描电镜观察。
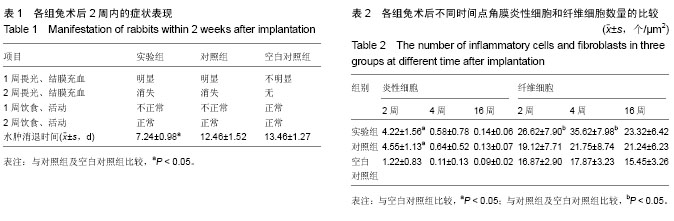
结果与结论:术后16周,3组间炎性细胞与纤维细胞数量比较差异均无显著性意义。随着时间的延长,实验组角膜组织逐渐增多,纤维组织逐渐增厚,细胞外基质附着逐渐增加,角膜组织贴附密集度、细胞外基质附着密集度及组织愈合度均优于对照组及空白对照组。表明羟基磷灰石表面修饰人工角膜钛支架具有良好的生物相容性,可有效促进角膜细胞增生,有利于角膜血管化。
中图分类号: