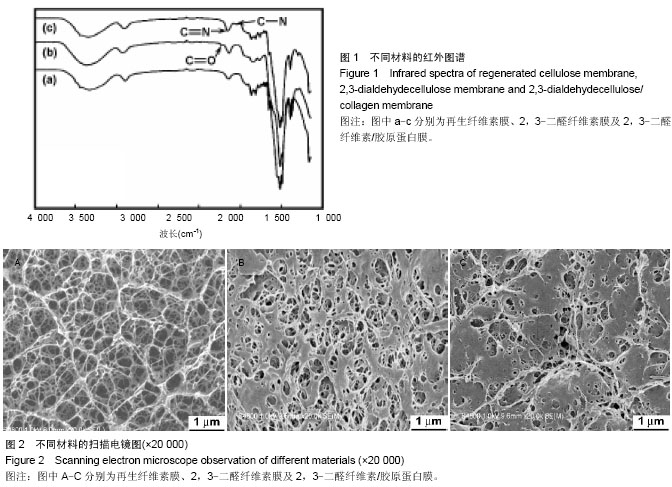
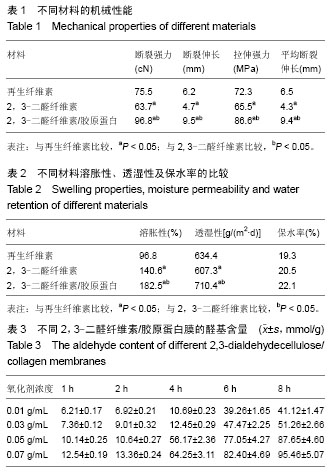
| [1] 杨建义,张国李,刘文松,等.自体椎板骨块作为椎体间融合材料在椎弓根钉内固定治疗椎体滑脱症中的应用[J].中国实用医刊, 2010,37(19):75-76.
[2] 檀臻炜,姚一民,匡红,等.经椎弓根植入生物人工材料骨诱导人工骨加内固定治疗骨质疏松性胸腰段骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2012, 28(6):505-508.
[3] 袁振超,陈远明,陈锋,等.腰椎滑脱症椎间植骨融合中3种植骨材料的远期效果对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(16): 3033-3040.
[4] 贺欣,郝定均,贺宝荣,等.两种植骨方式及材料治疗腰椎滑脱的疗效比较[C].//中华医学会第十二届骨科学术会议暨第五届COA学术大会论文集,2010:6-10.
[5] 莫楚鸿,谭建基,唐灿锐,等.钛金属后路椎弓根钉棒内固定系统联合椎间植骨治疗腰椎滑脱:5年同一科室36例随访[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(13):2429-2432.
[6] 李健,张振山,杨波,等.腰椎后路椎弓根钉置入并自体颗粒骨打压植骨治疗下腰椎结核[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(39): 7315-7318.
[7] 闫景龙,奚春阳,张志鹏,等.新型腰椎后路植骨方法的临床应用及近期疗效观察[J].中华外科杂志,2014,52(10):750-753.
[8] 张宏其,王昱翔,郭超峰,等.分期后路融合内固定前路病灶清除椎间植骨治疗儿童腰椎结核伴后凸畸形[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2010, 20(10):820-824.
[9] 王诗军,李钰婷,李淳德,等.腰椎椎弓根钉内固定植骨融合术中伤口周围注射罗哌卡因复合液的镇痛效应[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(48):7769-7774.
[10] 张莹,初同伟,张超,等.一期后路椎管减压、椎间植骨内固定术治疗胸、腰椎爆裂性骨折的临床观察[J].重庆医学,2012,41(20): 2038-2040.
[11] 叶青,黄武,贺云松,等.后路复位结合“H”形植骨棘突回植重建椎管结构治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2014,30(6): 530-534.
[12] 孙君超,肖荣驰,欧俊,等.不同植骨材料诱导兔腰椎横突间的融合[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(25):4586-4590.
[13] 王磊磊,金格勒,任龙龙,等.不同植骨材料在腰椎融合过程中的应用及转化生长因子β的表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(16):2885-2888.
[14] 羊明智,彭立军,胡文凯,等.一期后路病灶清除植骨选择性病椎置钉内固定术在相邻多个胸腰椎结核中的应用[J].现代医药卫生,2013, 29(15):2287-2288,2290.
[15] 宋楹卓.三种植骨材料在脊柱后侧融合中作用的实验研究及自体髂骨植骨在枕颈融合中的临床研究[D].第四军医大学,2012.
[16] 杨曦,宋跃明,刘浩,等.前路减压n-HA/PA66支撑植骨内固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折的近期临床效果[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011, 21(11): 885-889.
[17] Wang Y,Owoc JS,Boyd SK,et al.Regional variations in trabecular architecture of the lumbar vertebra: Associations with age, disc degeneration and disc space narrowing.Bone. 2013;56(2):249-254.
[18] 陈勇忠,王剑火,张朋,等.含链霉素医用硫酸钙人工骨修复胸腰椎结核骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(21):3287-3292.
[19] 李健,钟志宏,张平,等.椎弓根螺钉置入内固定联合自体颗粒骨移植治疗退行性腰椎病变[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(13):2421-2424.
[20] Wegrzyn J,Roux JP,Farlay D,et al.The role of bone intrinsic properties measured by infrared spectroscopy in whole lumbar vertebra mechanics: Organic rather than inorganic bone matrix?Bone.2013;56(2):229-233.
[21] 刘晓晨,贾文霄,邓伟,等.MR动态增强扫描对兔腰椎植骨融合术后的血管化监测[J].临床放射学杂志,2011,30(5):738-741.
[22] 朱泽章,毛赛虎,赵清华,等.纳米人工骨椎间融合术在前路内固定治疗特发性胸腰椎或腰椎侧凸中的应用[J].中华外科杂志,2012, 50(8):709-713.
[23] Li H,Na W,Jiang Y,et al.Percutaneous nephrolithotomy versus ureteroscopic lithotomy for large (>15 mm) impacted upper ureteral stones in different locations: Is the upper border of the fourth lumbar vertebra a good indication for choice of management method?J Endourol.2013;27(9):1120-1125.
[24] 陈波,刘云华,张宏斌,等.前路病灶清除植骨内固定术治疗胸、腰椎结核[J].临床骨科杂志,2011,14(1):11-11,14.
[25] 钟志宏.后路自体颗粒骨打压植骨腰椎椎体间融合内固定的生物力学及临床研究[D].广州医学院,2010.
[26] 万标林,梁伟国,王斌,等.自体椎板关节突柱状植骨融合治疗腰椎退行性疾病的疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(11):964-967.
[27] Wang Y,Bünger CE,Zhang Y,et al.Lowest instrumented vertebra selection in Lenke 3C and 6C scoliosis: What if we choose lumbar apical vertebra as distal fusion end?Eur Spine J.2012; 21(6):1053-1061.
[28] 朱瑜琪,王金荣.腰椎融合及植入物内固定后滑脱腰椎的椎体稳定性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(35):6339-6344.
[29] 罗军,肖荣驰.复合人工骨用于兔腰椎横突间植骨的生物学评价[J].中国基层医药,2011,18(1):1-3.
[30] 孟新文,边江,禹晓东,等.两种不同内固定材料和植骨材料治疗胸腰椎椎体骨折的疗效分析[J].西北国防医学杂志,2011,32(2): 118-119.
[31] Garo A,Arnoux PJ,Wagnac E,et al.Calibration of the mechanical properties in a finite element model of a lumbar vertebra under dynamic compression up to failure.Med Biol Eng Comput.2011;49(12):1371-1379.
[32] 肖荣驰,李强,唐志宏,等.三种椎间植骨材料治疗腰椎滑脱的比较研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2007,21(5):453-456.
[33] 史晓林,刘清阁,张昊,等.不同植骨材料重建伤椎修复胸腰椎爆裂骨折:验证植骨愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(39):6233-6239.
[34] 任东林,林飞,胡天翼,等.三种腰椎后路椎间融合植骨材料的临床对比研究[J].脊柱外科杂志,2013,11(1):13-18.
[35] 李洪彬,范剑波,向登,等.腰椎后路钉棒系统结合椎间植骨融合治疗腰椎滑脱62例[J].重庆医学,2009,38(16):2069-2070.
[36] 许峰,韦江波.后路椎间环锯加盖植骨融合法治疗腰椎管狭窄症[J].实用骨科杂志,2010,16(9):674-676.
[37] 傅万有,闫占明,吕福润,等.不同术式治疗腰椎间滑脱症的疗效分析[J].颈腰痛杂志,2002,23(4):312-314.
[38] 张正丰,周跃,王建,等.后路椎体切除减压椎间植骨融合椎弓根螺钉内固定术治疗严重胸腰椎旋转骨折脱位[J].中华创伤杂志, 2010, 26(1):32-35.
[39] 山富彦.不同植骨材料联合钉棒系统在胸腰椎结核植骨融合术的应用和比较[J].实用医学杂志,2012,28(14):2416-2418.
[40] 张平德.不同自体植骨材料在不同植骨融合术腰椎滑脱患者中的对比分析[J].检验医学与临床,2013,10(15):1957-1958,1960. |