中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (34): 5433-5437.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.34.005
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
崩瓷修补的临床试验及体外材料学拉伸强度实验
王 星1,齐 鲁2,顾振宇3,何惠宇1
- 1新疆医科大学第一附属医院口腔修复科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054; 2新疆医科大学第二附属医院口腔科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830063;3新疆兵团医院口腔科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830011
Clinical trial of collapsed repair and in vitro tensile strength test
Wang Xing1, Qi Lu2, Gu Zhen-yu3, He Hui-yu1
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; Department of Stomatology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3Department of Stomatology, Hospital of Xinjiang Production & Construction Corps, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
背景:目前对瓷类修复体后崩瓷修补的研究较多,但缺乏系统性、横向的比较。
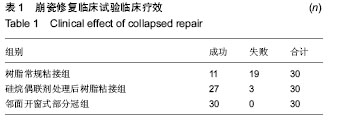
目的:通过临床试验及体外实验比较树脂常规粘接、硅烷偶联剂处理后树脂粘接及邻面开口式部分冠3种崩瓷修补方法的效果。
方法:①临床试验:将90例崩瓷患者随机均分为3组修补,分别采用树脂常规粘接、硅烷偶联剂处理后树脂粘接及邻面开口式部分冠3种崩瓷修补方法,对比3组1年后的修补成功率。②体外实验:将20个瓷试件均分为2组,分别进行树脂常规粘接及硅烷偶联剂处理后树脂粘接处理,检测两组剪切强度;将20个双层瓷试件均分为4组,其中3组黏结面分别进行喷砂、硅烷偶联剂、喷砂联合硅烷偶联剂处理,另1组不做任何处理(对照组),黏结后检测各组试件拉伸强度。
结果与结论:树脂常规粘接组、硅烷偶联剂处理后树脂粘接组及邻面开口式部分冠组修复成功率分别为37%,90%,100%。树脂常规粘接组与硅烷偶联剂处理后粘接组剪切强度分别为(13.978±0.343),(10.058±0.64) MPa,组间比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01)。对照组、喷砂组、硅烷偶联剂组、联合处理组的拉伸强度分别为(0.68±0.04),(1.00±0.02),(1.31±0.08),(1.09±0.04) kN,组间两两比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01)。表明硅烷偶联剂处理后树脂粘接及邻面开口式部分冠崩瓷修补效果优于树脂常规粘接。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)