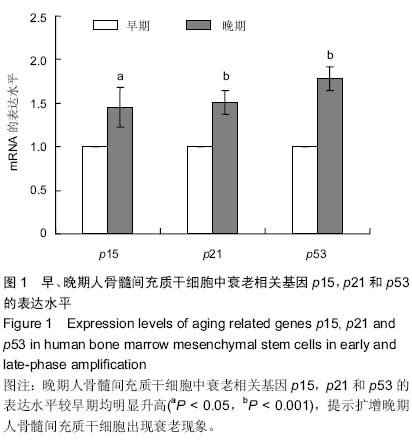
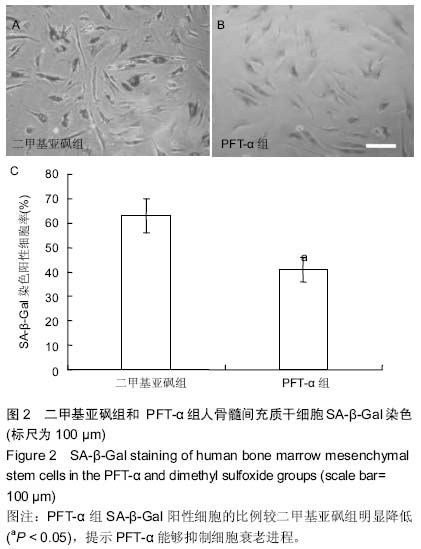
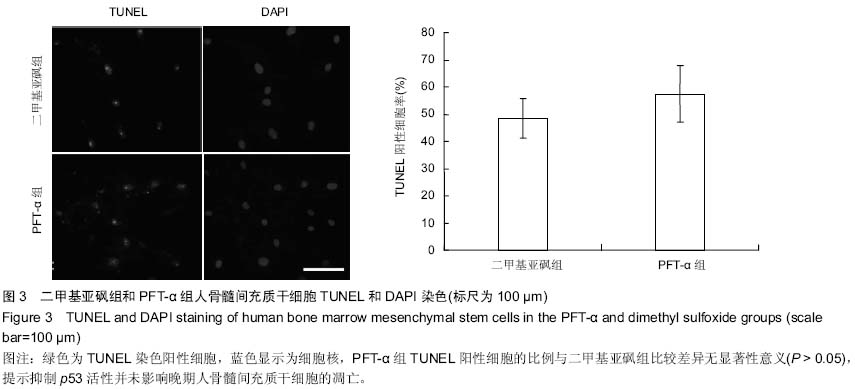
| [1] Prockop DJ. Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 1997;276(5309):71-74.
[2] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.
[3] Krebsbach PH, Kuznetsov SA, Bianco P, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells: characterization and clinical application. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1999;10(2):165-181.
[4] Park JS, Kim HY, Kim HW, et al. Increased caveolin-1, a cause for the declined adipogenic potential of senescent human mesenchymal stem cells. Mech Ageing Dev. 2005; 126(5):551-559.
[5] Kang JY, Kim JJ, Jang SY, et al. The p53-p21(Cip1/WAF1) pathway is necessary for cellular senescence induced by the inhibition of protein kinase CKII in human colon cancer cells. Mol Cells. 2009;28(5):489-494.
[6] Sakaguchi Y, Sekiya I, Yagishita K, et al. Comparison of human stem cells derived from various mesenchymal tissues: superiority of synovium as a cell source. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(8):2521-2529.
[7] Minguell JJ, Erices A, Conget P. Mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2001;226(6):507-520.
[8] Zhou Y, Yu D, Zhu H. Optimization of culture condition of human bone marrow stromal cells in terms of purification, proliferation, and pluripotency. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2014;50(9):822-830.
[9] Friedenstein AJ, Latzinik NW, Grosheva AG, et al. Marrow microenvironment transfer by heterotopic transplantation of freshly isolated and cultured cells in porous sponges. Exp Hematol. 1982;10(2):217-227.
[10] Cheng FJ, Zou P, Zhong ZD, et al. The growth characteristics of mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells in human umbilical cord blood. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2003; 11(6):565-568.
[11] Izadpanah R, Kaushal D, Kriedt C, et al. Long-term in vitro expansion alters the biology of adult mesenchymal stem cells. Cancer Res. 2008;68(11):4229-4238.
[12] Sethe S, Scutt A, Stolzing A. Aging of mesenchymal stem cells. Ageing Res Rev. 2006;5(1):91-116.
[13] Mareschi K, Ferrero I, Rustichelli D, et al. Expansion of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from pediatric and adult donor bone marrow. J Cell Biochem. 2006;97(4):744-754.
[14] Minieri V, Saviozzi S, Gambarotta G, et al. Persistent DNA damage-induced premature senescence alters the functional features of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(4):734-743.
[15] Pant V, Lozano G. Limiting the power of p53 through the ubiquitin proteasome pathway. Genes Dev. 2014;28(16): 1739-1751.
[16] Liu TM, Ng WM, Tan HS, et al. Molecular basis of immortalization of human mesenchymal stem cells by combination of p53 knockdown and human telomerase reverse transcriptase overexpression. Stem Cells Dev. 2013; 22(2):268-278.
[17] Mowla SN, Lam EW, Jat PS. Cellular senescence and aging: the role of B-MYB. Aging Cell. 2014;13(5):773-779.
[18] Mantovani C, Terenghi G, Magnaghi V. Senescence in adipose-derived stem cells and its implications in nerve regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(1):10-15.
[19] Peng Y, Xuan M, Leung VY, et al. Stem cells and aberrant signaling of molecular systems in skin aging. Ageing Res Rev. 2015;19:8-21.
[20] Yew TL, Chiu FY, Tsai CC, et al. Knockdown of p21(Cip1/Waf1) enhances proliferation, the expression of stemness markers, and osteogenic potential in human mesenchymal stem cells. Aging Cell. 2011;10(2):349-361.
[21] Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, et al. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(1):44-84.
[22] Dröge W. Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiol Rev. 2002;82(1):47-95.
[23] Calabrese V, Lodi R, Tonon C, et al. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and cellular stress response in Friedreich's ataxia. J Neurol Sci. 2005;233(1-2):145-162.
[24] Yan LJ. Positive oxidative stress in aging and aging-related disease tolerance. Redox Biol. 2014;2C:165-169.
[25] Wei X, Yin H. Covalent Modification of DNA by α, β-Unsaturated Aldehydes Derived from Lipid Peroxidation:Recent Progress and Challenges. Free Radic Res. 2015;12:1-36.
[26] Lu K, Zhang C, Wu W, et al. Rhubarb extract has a protective role against radiation-induced brain injury and neuronal cell apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 2015 Apr 28. [Epub ahead of print]
[27] Asikin Y, Takahashi M, Mizu M, et al. DNA damage protection against free radicals of two antioxidant neolignan glucosides from sugarcane molasses.J Sci Food Agric. 2015 Apr 10. [Epub ahead of print]
[28] Li Y, Feng H, Gu H, et al. The p53-PUMA axis suppresses iPSC generation. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2174.
[29] Hong H, Takahashi K, Ichisaka T, et al. Suppression of induced pluripotent stem cell generation by the p53-p21 pathway. Nature. 2009;460(7259):1132-1135.
[30] Gu Z, Jiang J, Xia Y, et al. p21 is associated with the proliferation and apoptosis of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells from non-obese diabetic mice. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2013;121(10):607-613. |