| [1] Li M, Cai DH, Zhang H, et al. Jiefangjun Yixue Zazhi.2008; 33(3):269-272.李明,蔡德鸿,张桦,等.间充质干细胞联合骨髓细胞输注诱导胰岛移植免疫耐受的研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2008,33(3):269-272.[2] Zhang H, Cai DH, Han JL, et al.Nanfang Yikedaxue Xuebao. 2007;27(6):824-826.张桦,蔡德鸿,韩钧凌,等.半自动消化法分离纯化人胰岛细胞的实验研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报.2007,27(6):824-826.[3] Zhang H, Chen H, Sun J,et al.Guangdong Yixue.2007; 28(3): 349-351.张桦,陈宏,孙嘉,等.推进式离心管结合单密度梯度法快速纯化大鼠胰岛[J].广东医学,2007,28(3):349-351.[4] Guo Z,Wu T,Sozen H,et al.A substantial level of donor hematopoietic chimerism is requiredto protect donor-specific islet grafts in diabetic NOD mice. Transplantation. 2003;75(7): 909-915.[5] Masak K,Yoshinori I,Shin M, et al.An irradiation-free nonmyeloablative bone marrow transplantation model : important of the balance between donor T-cell number and the intensity of conditioning.Transplantation. 2005;80(9): 1145-1152. [6] Zhang J, Zhang Q, Zhang YC, et al. Qiguan Yizhi. 2011;6(2): 350-353.张剑,张琪,张英才,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对异种胰岛移植排斥反应的影响[J].器官移植,2011,6(2):350-353.[7] Ding Y, Xu D, Feng G, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells prevent the rejection of fully allogenic islet grafts by the immunosuppressive activity of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9. Diabetes.2009;58: 1797-1806.[8] Zhao Y, Lin B, Darfl inger R, Zhang Y, et al. Human cord blood stem cellmodulated regulatory T lymphocytes reverse the autoimmune-caused type 1 diabetes in nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice.PLoS One.2009;4(1):e4226.[9] Bartholomew A, Sturgeon C, Siatskas M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells suppress lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and prolong skin graft survival in vivo. Exp Hematol.2002;30(1): 42-48.[10] Krampera M,Glennie S,Dyson J ,et al .Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the responses of naïve antigen specific T-cells to their cognate peptide.Blood. 2003; 101(9):3722-3729.[11] Aggarwal S, Pittenger F. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005; 105(4): 1815-1822.[12] Park MJ, Shin JS, Kim YH,et al. Murine mesenchymal stem cells suppress T lymphocyte activation through IL-2 receptor α (CD25) cleavage by producing matrix metalloproteinases. Stem Cell Rev.2011;7:381-393. [13] Sioud M,Mobergslien A,Boudabous A,et al. Evidence for the involvement of galectin-3 in mesenchymal stem cell suppression of allogeneic T-cell proliferation. Scand J Immunol. 2010;71(4): 267-274.[14] Deng WM, Han Q, You SG, et al. Zhonghua Jianyanyixue Zazhi.2003;26(8):466-469.邓为民,韩钦,尤胜国,等.异基因骨髓源间充质干细胞移植形成稳定的嵌合体并诱导免疫耐受的研究[J].中华检验医学杂志,2003, 26(8):466-469.[15] Zhang J,Li H,Jiang N,et al. Inhibition of rejection in murine islet xenografts by CTLA4Ig and CD40LIg gene transfer.Chin Med J(Engl).2010;123(21):3106-3109.[16] Wang Y,Zhang A,Ye Z,et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit acute rejection of rat liver allografts in association with regulatory T-cell expansion. Transplant Proc.2009;41(8):4352-4356. |
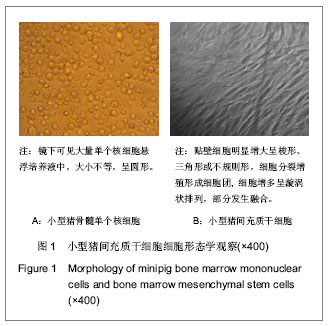
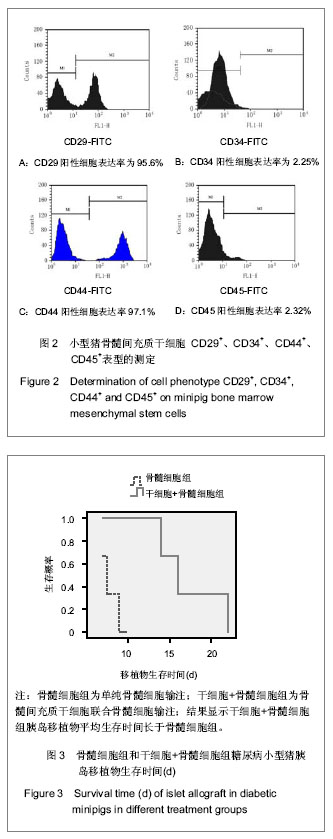
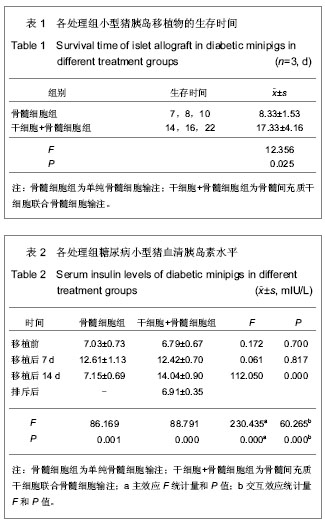
.jpg)