| [1]祖波,刘立明.闭合复位交锁髓内钉固定治疗股骨干骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2014,17(1):81-82.
[2]Bienkowski P,Harvey EJ,Reindl R, et al.The locked flexible intramedullary humerus nail in pediatric femur and tibia shaft fractures: a feasibility study. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004; 24(6): 634-637.
[3]郑松,刘明,陈斌,等.交锁髓内钉与微创锁定加压钢板治疗股骨干骨折疗效分析[J].中国基层医药,2013,20(9):1313-1315.
[4]Perez A,Mahar A,Negus C, et al.A computational evaluation of the effect of intramedullary nail material properties on the stabilization of simulated femoral shaft fractures. Med Eng Phys. 2008;30(6):755-760.
[5]Lee YS, Lo TY, Huang HL, et al.Intramedullary fixation of tibial shaft fractures: a comparison of the unlocked and interlocked nail. Int Orthop. 2008;32(1):69-74.
[6]刘桂发,王晖.带锁髓内钉与动力加压钢板治疗股骨干骨折骨不连疗效观察[J].吉林医学,2011,32(19):3922-3923.
[7]Keeler KA,Dart B,Luhmann SJ, et al.Antegrade intramedullary nailing of pediatric femoral fractures using an interlocking pediatric femoral nail and a lateral trochanteric entry point. J Pediatr Orthop. 2009;29(4): 345-351.
[8]Jencikova-Celerin L,Phillips JH,Werk LN, et al.Flexible interlocked nailing of pediatric femoral fractures: experience with a new flexible interlocking intramedullary nail compared with other fixation procedures. J Pediatr Orthop. 2008;28(8): 864-873.
[9]王文岳,杨天府,刘雷,等.加长型PFNA治疗股骨干骨折伴同侧髋部骨折的临床观察[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(4):300-302.
[10]吕增华.普通髓内钉、加压钢板与交锁髓内钉治疗股骨干骨折临床疗效观察[J].中国医药导刊,2013,31(6):56-57.
[11]Steinberg EL,Geller DS,Yacoubian SV, et al.Intramedullary fixation of tibial shaft fractures using an expandable nail: early results of 54 acute tibial shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(5):303-309.
[12]Heiner DE,Meyer MH,Frick SL, et al.Gene expression during fracture healing in rats comparing intramedullary fixation to plate fixation by DNA microarray. J Orthop Trauma. 2006; 20(1):27-38.
[13]马雪海,郑进,郑圣鼐,等.扩张自锁髓内钉与锁定钢板置入治疗胫骨干闭合骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(35):6522-6526.
[14]李栋,丁彬,赵一贫,等.钢板结合髓内钉治疗胫骨单髁伴同侧胫骨干中、远段骨折效果观察[J].中国乡村医药,2013,20(20):15-16.
[15]赵大治.胫骨单髁伴同侧胫骨干中、远段骨折应用钢板结合髓内钉治疗的临床观察[J].中外医疗,2013,32(20):75-76.
[16]Klein P,Opitz M,Schell H, et al.Comparison of unreamed nailing and external fixation of tibial diastases--mechanical conditions during healing and biological outcome. J Orthop Res. 2004;22(5):1072-1078.
[17]孙克明,季泽娟,姚满叶,等.弹性髓内针与钢板内固定治疗大年龄儿童前臂双骨干骨折的疗效比较[J].中国实用医药,2012,7(3): 58-59.
[18]陈庆雄,蒋家正,李雄杰,等.钢板与髓内钉固定治疗股骨干骨折术后钢板内固定失败的效果比较[J].广东医学,2013,34(20): 3133-3135.
[19]倪杰,姚琦,袁晓明,等.带锁髓内钉固定和钢板螺钉固定治疗胫骨干骨折的对比研究[J].东南大学学报(医学版),2010,29(2): 172-175.
[20]黎俪莎.老年性重度骨质疏松性骨干骨折髓内钉和锁定钢板固定疗效的对比分析[J].中国伤残医学,2014,22(11):48-49.
[21]Fogagnolo F,Kfuri M Jr,Paccola CA, et al.Intramedullary fixation of pertrochanteric hip fractures with the short AO-ASIF proximal femoral nail. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004;124(1):31-37.
[22]罗宇,谭家昌.弹性钉与钢板内固定治疗儿童前臂双骨折的对比研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(11):1025-1027.
[23]McConnell A,Zdero R,Syed,K, et al.The biomechanics of ipsilateral intertrochanteric and femoral shaft fractures: a comparison of 5 fracture fixation techniques. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(8):517-524.
[24]王华明,陈志龙,李卫平,等.弹性髓内钉治疗儿童股骨干骨折钢板固定失效病例[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(26):4819-4825.
[25]蔡贤华,王威,王志华,等.不同前路内固定方式治疗枢椎椎体横行骨折合并Hangman骨折稳定性的有限元分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,24(3):257-265.
[26]翁鉴,曾晖,肖德明,等.扩髓髓内钉与锁定接骨板治疗股骨干骨折的疗效比较[J].临床骨科杂志,2013,16(5):517-519.
[27]黄雷,朱彦昭,张峰,等.钢板结合髓内钉治疗胫骨单髁伴同侧胫骨干中、远段骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(8):739-744.
[28]张大鹏,孙大辉,谷贵山,等.髓内针固定与钢板固定治疗成人肱骨干骨折疗效的Meta分析[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2008,34(6): 1054-1059.
[29]蒋光明,蒋正帅,熊克晓,等.钢板内固定与髓内钉治疗肱骨干骨折的比较[J].实用预防医学,2008,15(1):202-203.
[30]胡杨华,陈继良,王晓露,等.弹性髓内针与锁定钢板内固定治疗儿童股骨干骨折临床评估[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2012,33(16): 2156-2157.
[31]张弩,张春,刘世清,等.骨形态发生蛋白植入长骨干粉碎性骨折周围:预防骨折内固定后的不愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(43):6902-6906.
[32]李卓伟,王志远.弹性髓内钉治疗儿童股骨干骨折的临床疗效观察[J].现代诊断与治疗,2013,24(13):2896-2897.
[33]许峰,倪江东.微创经皮钢板与膨胀髓内钉治疗胫骨干骨折的比较分析[J].医学临床研究,2011,28(10):1936-1938.
[34]Kawano Y, Okazaki M, Ikegami H, et al. The "Docking" Method for Periprosthetic Humeral Fracture After Total Elbow Arthroplasty A Case Report. J Bone Joint Surg. 2010;92-A (10):1988-1991.
[35]苏全,黎颖,林民贵,等.两种不同方法治疗肱骨干骨折的疗效观察[J].现代医药卫生,2009,25(5):707-708.
[36]邢丹,马信龙,马剑雄,等.大鼠股骨干开放骨折愈合模型的建立及生物力学性能评价[J].中国骨伤,2013,26(8):676-680.
[37]刘昌海,王占朝,陆骅,等.经皮锁定钢板与传统解剖钢板内固定治疗胫骨下段骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(17): 2703-2708.
[38]Oh JK, Oh CW, Jeon IH, et al. Percutaneous Plate Stabilization of Proximal Tibial Fractures. J Trauma. 2005; 59(2):431-437.
[39]邱功名.交锁髓内钉与加压钢板内固定治疗肱骨干骨折的疗效对比[J].中国伤残医学,2013,21(1):23-24.
[40]郑振鑫.弹性髓内针与钢板内固定治疗儿童尺桡骨双骨折的临床评估[J].健康必读(中旬刊),2013,12(6):225-226 |
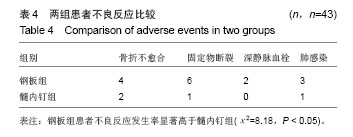
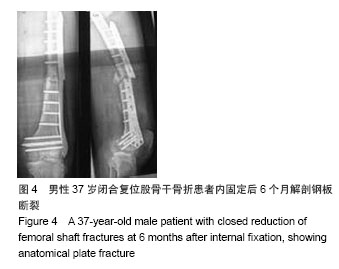
.jpg)
.jpg)