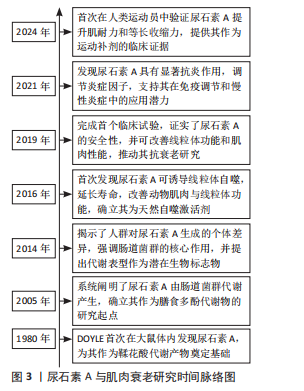
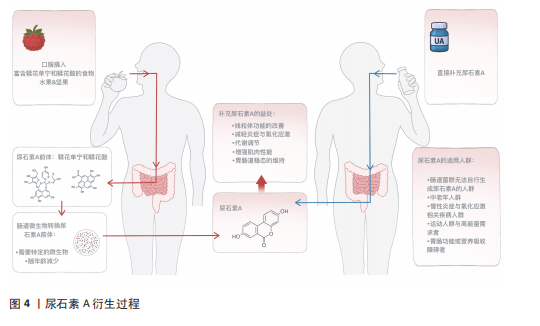
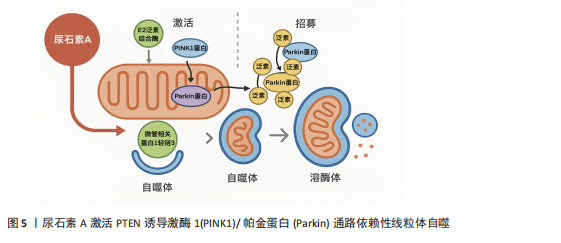
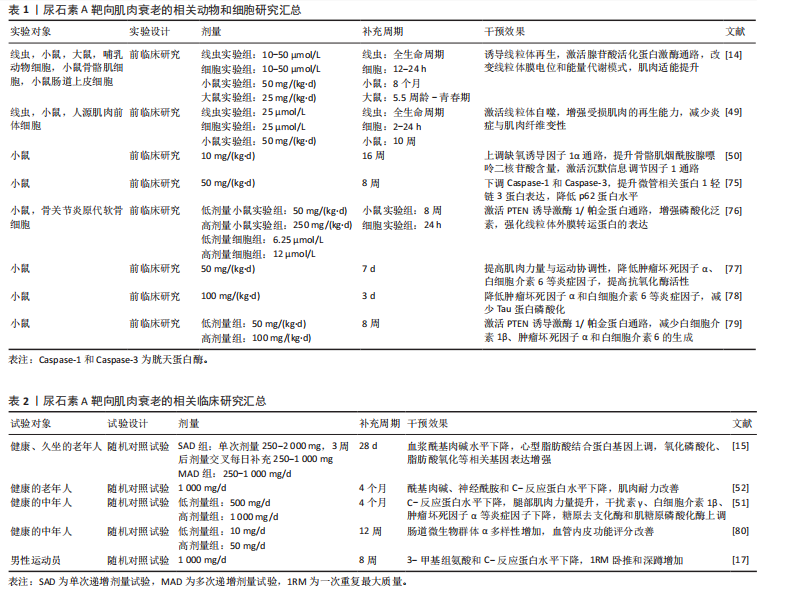
[1] LÓPEZ-OTÍN C, BLASCO MA, PARTRIDGE L, et al. Hallmarks of aging: An expanding universe. Cell. 2023;186(2):243-278.
[2] LI Y, TIAN X, LUO J, et al. Molecular mechanisms of aging and anti-aging strategies. Cell Commun Signal. 2024; 22(1):285.
[3] MARCANGELI V, YOUSSEF L, DULAC M, et al. Impact of high-intensity interval training with or without l-citrulline on physical performance, skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue in obese older adults. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(3):1526-1540.
[4] HOU Y, CHU X, PARK JH, et al. Urolithin A improves Alzheimer’s disease cognition and restores mitophagy and lysosomal functions. Alzheimers Dement. 2024;20(6):4212-4233.
[5] HUANG JR, ZHANG MH, CHEN YJ, et al. Urolithin A ameliorates obesity-induced metabolic cardiomyopathy in mice via mitophagy activation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023;44(2):321-331.
[6] KARIM S, MADANI B, BURZANGI AS, et al. Urolithin A’s Antioxidative, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antiapoptotic Activities Mitigate Doxorubicin-Induced Liver Injury in Wistar Rats. Biomedicines. 2023;11(4):1125.
[7] 乌里盼·托乎达阿里,孙媛,丁宛婷,等.基于miRNA155-5p介导的MAPK/NF-κB通路探讨尿石素A的抗炎机制[J].中国药理学通报,2024,40(6):1066-1074.
[8] ZHAO H, SONG G, ZHU H, et al. Pharmacological Effects of Urolithin A and Its Role in Muscle Health and Performance: Current Knowledge and Prospects. Nutrients. 2023;15(20):4441.
[9] RIBEIRO M, ALVARENGA L, CARDOZO LFMF, et al. Urolithin as a Metabolite of Ellagitannins and Ellagic Acid from Fruits and Nuts Produced by the Gut Microbiota: Its Role on Non-Communicable Diseases. Curr Nutr Rep. 2025;14(1):55.
[10] PIDGEON R, MITCHELL S, SHAMASH M, et al. Diet-derived urolithin A is produced by a dehydroxylase encoded by human gut Enterocloster species. Nat Commun. 2025;16(1):999.
[11] D’AMICO D, ANDREUX PA, VALDÉS P, et al. Impact of the Natural Compound Urolithin A on Health, Disease, and Aging. Trends Mol Med. 2021;27(7):687-699.
[12] GARCÍA-VILLALBA R, GIMÉNEZ-BASTIDA JA, CORTÉS-MARTÍN A, et al. Urolithins: a Comprehensive Update on their Metabolism, Bioactivity, and Associated Gut Microbiota. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2022; 66(21):e2101019.
[13] TOMÁS-BARBERÁN FA, GARCÍA-VILLALBA R, GONZÁLEZ-SARRÍAS A, et al. Ellagic acid metabolism by human gut microbiota: consistent observation of three urolithin phenotypes in intervention trials, independent of food source, age, and health status. J Agric Food Chem. 2014; 62(28):6535-6538.
[14] RYU D, MOUCHIROUD L, ANDREUX PA, et al. Urolithin A induces mitophagy and prolongs lifespan in C. elegans and increases muscle function in rodents. Nat Med. 2016; 22(8):879-888.
[15] ANDREUX PA, BLANCO-BOSE W, RYU D, et al. The mitophagy activator urolithin A is safe and induces a molecular signature of improved mitochondrial and cellular health in humans. Nat Metab. 2019;1(6):595-603.
[16] BOBOWSKA A, GRANICA S, FILIPEK A, et al. Comparative studies of urolithins and their phase II metabolites on macrophage and neutrophil functions. Eur J Nutr. 2021;60(4):1957-1972.
[17] ZHAO H, ZHU H, YUN H, et al. Assessment of Urolithin A effects on muscle endurance, strength, inflammation, oxidative stress, and protein metabolism in male athletes with resistance training: an 8-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2024;21(1):2419388.
[18] 邓宇,杨诗颖,冼文妍,等.鞣花酸在UM-A型人肠道菌群中体外转化及对肠道菌群的影响[J].食品与发酵工业,2023, 49(2):34-40.
[19] HASHEMINEZHAD SH, BOOZARI M, IRANSHAHI M, et al. A mechanistic insight into the biological activities of urolithins as gut microbial metabolites of ellagitannins. Phytother Res. 2022;36(1):112-146.
[20] ZHANG M, CUI S, MAO B, et al. Ellagic acid and intestinal microflora metabolite urolithin A: A review on its sources, metabolic distribution, health benefits, and biotransformation. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(24):6900-6922.
[21] TOMÁS-BARBERÁN FA, GONZÁLEZ-SARRÍAS A, GARCÍA-VILLALBA R, et al. Urolithins, the rescue of “old” metabolites to understand a “new” concept: Metabotypes as a nexus among phenolic metabolism, microbiota dysbiosis, and host health status. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017;61(1):1-36.
[22] ROMO-VAQUERO M, FERNÁNDEZ-VILLALBA E, GIL-MARTINEZ AL, et al. Urolithins: potential biomarkers of gut dysbiosis and disease stage in Parkinson’s patients. Food Funct. 2022;13(11):6306-6316.
[23] HU Y, ZHANG L, WEI LF, et al. Liposomes encapsulation by pH driven improves the stability, bioaccessibility and bioavailability of urolithin A: A comparative study. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;253(Pt 7):127554.
[24] XIAN W, YANG S, DENG Y, et al. Distribution of Urolithins Metabotypes in Healthy Chinese Youth: Difference in Gut Microbiota and Predicted Metabolic Pathways. J Agric Food Chem. 2021;69(44):13055-13065.
[25] MEMBREZ M, MIGLIAVACCA E, CHRISTEN S, et al. Trigonelline is an NAD+ precursor that improves muscle function during ageing and is reduced in human sarcopenia. Nat Metab. 2024;6(3):433-447.
[26] AL AMIR DACHE Z, THIERRY AR. Mitochondria-derived cell-to-cell communication. Cell Rep. 2023;42(7):112728.
[27] CAI X, NG CP, JONES O, et al. Lactate activates the mitochondrial electron transport chain independently of its metabolism. Mol Cell. 2023;83(21):3904-3920.e7.
[28] LIANG R, ZHU L, HUANG Y, et al. Mitochondria: fundamental characteristics, challenges, and impact on aging. Biogerontology. 2024;25(6):923-941.
[29] CESARE MM, FELICE F, SANTINI V, et al. Antioxidants in Sport Sarcopenia. Nutrients. 2020;12(9):2869.
[30] OKOYE CN, KOREN SA, WOJTOVICH AP. Mitochondrial complex I ROS production and redox signaling in hypoxia. Redox Biol. 2023;67:102926.
[31] 肖玉欣,王楠,王婧,等.鞣花酸和尿石素类代谢产物的生物活性及其对肠道健康的作用研究进展[J].食品科学,2022, 43(9):275-284.
[32] HARPER C, GOPALAN V, GOH J. Exercise rescues mitochondrial coupling in aged skeletal muscle: a comparison of different modalities in preventing sarcopenia. J Transl Med. 2021;19(1):71.
[33] PARRY HA, ROBERTS MD, KAVAZIS AN. Human Skeletal Muscle Mitochondrial Adaptations Following Resistance Exercise Training. Int J Sports Med. 2020;41(6):349-359.
[34] LI X, LI C, ZHANG W, et al. Inflammation and aging: signaling pathways and intervention therapies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):239.
[35] TYLUTKA A, WALAS Ł, ZEMBRON-LACNY A. Level of IL-6, TNF, and IL-1β and age-related diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1330386.
[36] AGNIHOTRI P, DEKA H, CHAKRABORTY D, et al. Anti-inflammatory potential of selective small compounds by targeting TNF-α & NF-kB signaling: a comprehensive molecular docking and simulation study. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023;41(23):13815-13828.
[37] GUO Q, JIN Y, CHEN X, et al. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: new insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):53.
[38] FU W, WU G. Targeting mTOR for Anti-Aging and Anti-Cancer Therapy. Molecules. 2023;28(7):3157.
[39] KUNZ HE, LANZA IR. Age-associated inflammation and implications for skeletal muscle responses to exercise. Exp Gerontol. 2023;177:112177.
[40] ARNOLD WD, CLARK BC. Neuromuscular junction transmission failure in aging and sarcopenia: The nexus of the neurological and muscular systems. Ageing Res Rev. 2023;89:101966.
[41] SO HK, KIM H, LEE J, et al. Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 1 Ablation in Motor Neurons Causes Mitochondrial Dysfunction Leading to Age-related Motor Neuron Degeneration with Muscle Loss. Research (Wash D C). 2023;6:0158.
[42] HASTINGS RL, AVILA MF, SUNEBY E, et al. Cellular and molecular evidence that synaptic Schwann cells contribute to aging of mouse neuromuscular junctions. Aging Cell. 2023;22(11):e13981.
[43] PADILLA CJ, HARRIGAN ME, HARRIS H, et al. Profiling age-related muscle weakness and wasting: neuromuscular junction transmission as a driver of age-related physical decline. Geroscience. 2021;43(3):1265-1281.
[44] 周友,朱小艳,黄建荣,等.尿石素A通过促进线粒体自噬保护糖尿病小鼠心脏损伤的作用研究[J].中国药理学通报, 2020,36(10):1385-1390.
[45] MORADI N, CHAMPSI S, HOOD DA. Sulforaphane, Urolithin A, and ZLN005 induce time-dependent alterations in antioxidant capacity, mitophagy, and mitochondrial biogenesis in muscle cells. Sports Med Health Sci. 2024;7(1):16-27.
[46] LU Y, LI Z, ZHANG S, et al. Cellular mitophagy: Mechanism, roles in diseases and small molecule pharmacological regulation. Theranostics. 2023;13(2):736-766.
[47] DONG Y, ZHANG X. Targeting cellular mitophagy as a strategy for human cancers. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024;12:1431968.
[48] WANG S, LONG H, HOU L, et al. The mitophagy pathway and its implications in human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):304.
[49] LUAN P, D’AMICO D, ANDREUX PA, et al. Urolithin A improves muscle function by inducing mitophagy in muscular dystrophy. Sci Transl Med. 2021;13(588):eabb0319.
[50] GHOSH N, DAS A, BISWAS N, et al. Urolithin A augments angiogenic pathways in skeletal muscle by bolstering NAD+ and SIRT1. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):20184.
[51] SINGH A, D’AMICO D, ANDREUX PA, et al. Urolithin A improves muscle strength, exercise performance, and biomarkers of mitochondrial health in a randomized trial in middle-aged adults. Cell Rep Med. 2022;3(5):100633.
[52] LIU S, D’AMICO D, SHANKLAND E, et al. Effect of Urolithin A Supplementation on Muscle Endurance and Mitochondrial Health in Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(1):e2144279.
[53] DENK D, SINGH A, KASLER H, et al. Impact of urolithin A supplementation, a mitophagy activator on mitochondrial health of immune cells (MitoIMMUNE): A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in healthy adults. J Clin Oncol. 2024;42(16):1-10.
[54] TONEY AM, FOX D, CHAIDEZ V, et al. Immunomodulatory Role of Urolithin A on Metabolic Diseases. Biomedicines. 2021;9(2):192.
[55] KUEREC AH, LIM XK, KHOO AL, et al. Targeting aging with urolithin A in humans: A systematic review. Ageing Res Rev. 2024; 100:102406.
[56] TUOHETAERBAIKE B, ZHANG Y, TIAN Y, et al. Pancreas protective effects of Urolithin A on type 2 diabetic mice induced by high fat and streptozotocin via regulating autophagy and AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;250:112479.
[57] DING SL, PANG ZY, CHEN XM, et al. Urolithin a attenuates IL-1β-induced inflammatory responses and cartilage degradation via inhibiting the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways in rat articular chondrocytes. J Inflamm (Lond). 2020;17:13.
[58] LARROSA M, GONZÁLEZ-SARRÍAS A, YÁÑEZ-GASCÓN MJ, et al. Anti-inflammatory properties of a pomegranate extract and its metabolite urolithin-A in a colitis rat model and the effect of colon inflammation on phenolic metabolism. J Nutr Biochem. 2010;21(8):717-725.
[59] GUADA M, GANUGULA R, VADHANAM M, et al. Urolithin A Mitigates Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity by Inhibiting Renal Inflammation and Apoptosis in an Experimental Rat Model. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2017;363(1):58-65.
[60] BROOME SC, WHITFIELD J, KARAGOUNIS LG, et al. Mitochondria as Nutritional Targets to Maintain Muscle Health and Physical Function During Ageing. Sports Med. 2024; 54(9):2291-2309.
[61] KUJAWSKA M, JOURDES M, KURPIK M, et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Pomegranate Juice against Parkinson’s Disease and Presence of Ellagitannins-Derived Metabolite-Urolithin A-In the Brain. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;21(1):202.
[62] JING T, LIAO J, SHEN K, et al. Protective effect of urolithin a on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice via modulation of inflammation and oxidative stress. Food Chem Toxicol. 2019;129:108-114.
[63] TONEY AM, FAN R, XIAN Y, et al. Urolithin A, a Gut Metabolite, Improves Insulin Sensitivity Through Augmentation of Mitochondrial Function and Biogenesis. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2019;27(4):612-620.
[64] CÁSEDAS G, LES F, CHOYA-FOCES C, et al. The Metabolite Urolithin-A Ameliorates Oxidative Stress in Neuro-2a Cells, Becoming a Potential Neuroprotective Agent. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(2):177.
[65] WOJCIECHOWSKA O, KUJAWSKA M. Urolithin A in Health and Diseases: Prospects for Parkinson’s Disease Management. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(7):1479.
[66] JAMIALAHMADI T, HASANPOUR M, VAKILIAN F, et al. Evaluation of Urolithin A Efficacy in Heart Failure Patients with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Randomized, Double-blind, Crossover, Placebo-controlled Clinical Trial. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2024;19(3):221-228.
[67] KONDO S, ADACHI SI, KOMATSU W, et al. Antidiabetic Effect of Urolithin A in Cultured L6 Myotubes and Type 2 Diabetic Model KK-Ay/Ta Mice with Glucose Intolerance. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024;46(2):1078-1090.
[68] LIU X, GUO B, LI Q, et al. mTOR in metabolic homeostasis and disease. Exp Cell Res. 2024;441(2):114173.
[69] CHEN P, CHEN F, LEI J, et al. Activation of the miR-34a-Mediated SIRT1/mTOR Signaling Pathway by Urolithin A Attenuates D-Galactose-Induced Brain Aging in Mice. Neurotherapeutics. 2019;16(4):1269-1282.
[70] RODRIGUEZ J, CAILLE O, FERREIRA D, et al. Pomegranate extract prevents skeletal muscle of mice against wasting induced by acute TNF-α injection. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017;61(4):1-12.
[71] TOTIGER TM, SRINIVASAN S, JALA VR, et al. Urolithin A, a Novel Natural Compound to Target PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019; 18(2):301-311.
[72] BI J, SONG L, GUO Q, et al. Effect of urolithin A on intracellular survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by regulating AKT-FOXO1-mediated autophagy. mSphere. 2025;10(5): e0006125.
[73] FAITG J, D’AMICO D, RINSCH C, et al. Mitophagy Activation by Urolithin A to Target Muscle Aging. Calcif Tissue Int. 2024; 114(1):53-59.
[74] XIA B, SHI XC, XIE BC, et al. Urolithin A exerts antiobesity effects through enhancing adipose tissue thermogenesis in mice. PLoS Biol. 2020;18(3):e3000688.
[75] NISHIMOTO Y, FUJISAWA K, UKAWA Y, et al. Effect of urolithin A on the improvement of vascular endothelial function depends on the gut microbiota. Front Nutr. 2023;9: 1077534.
[76] ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y, HALEMAHEBAI G, et al. Urolithin A, a pomegranate metabolite, protects pancreatic β cells from apoptosis by activating autophagy. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;272:113628.
[77] D’AMICO D, OLMER M, FOUASSIER AM, et al. Urolithin A improves mitochondrial health, reduces cartilage degeneration, and alleviates pain in osteoarthritis. Aging Cell. 2022;21(8):e13662.
[78] ZHU H, ZHAO H, QIAN H, et al. Urolithin A Ameliorates Athletic Ability and Intestinal Microbiota in Sleep Deprivation from the Perspective of the Gut-Muscle Axis. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2024;68(7):e2300599.
[79] TU HJ, SU CJ, PENG CS, et al. Urolithin A exhibits a neuroprotective effect against Alzheimer’s disease by inhibiting DYRK1A activity. J Food Drug Anal. 2023;31(2):358-370.
[80] ZHANG C, SONG Y, CHEN L, et al. Urolithin A Attenuates Hyperuricemic Nephropathy in Fructose-Fed Mice by Impairing STING-NLRP3 Axis-Mediated Inflammatory Response via Restoration of Parkin-Dependent Mitophagy. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:907209.
|