中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (13): 3412-3423.doi: 10.12307/2026.326
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
运动诱导细胞外囊泡:在胰岛素抵抗发生发展中的作用与机制
要俪娟,王印凤,马震南,陈乐琴
- 山西师范大学体育学院,山西省太原市 030031
-
接受日期:2025-07-10出版日期:2026-05-08发布日期:2025-12-26 -
通讯作者:陈乐琴,教授,山西师范大学体育学院,山西省太原市 030031 -
作者简介:要俪娟,女,2000年生,山西省晋中市人,汉族,硕士,主要从事运动人体科学研究。
Exercise-induced extracellular vesicles: action and mechanisms in occurrence and development of insulin resistance
Yao Lijuan, Wang Yinfeng, Ma Zhennan, Chen Leqin
- School of Physical Education, Shanxi Normal University, Taiyuan 030031, Shanxi Province, China
-
Accepted:2025-07-10Online:2026-05-08Published:2025-12-26 -
Contact:Chen Leqin, Professor, School of Physical Education, Shanxi Normal University, Taiyuan 030031, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Yao Lijuan, MS, School of Physical Education, Shanxi Normal University, Taiyuan 030031, Shanxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
细胞外囊泡:是作为细胞间信息传递的关键递质,不同来源的细胞外囊泡在胰岛素抵抗中呈现截然相反的作用,脂肪源性细胞外囊泡可通过单靶点加重代谢紊乱,而运动诱导的细胞外囊泡则通过抗炎、促葡萄糖转运、增强线粒体功能等来改善胰岛素抵抗,是在代谢性疾病干预中具有前景的治疗靶点。胰岛素抵抗:是指胰岛素靶组织对胰岛素介导的葡萄糖摄取和利用效能降低的病理生理状态,运动通过调控细胞外囊泡的分泌和内含物,形成多器官协同的代谢网络,可改善胰岛素抵抗,不同细胞分泌的细胞外囊泡携带特定信号分子影响胰岛素信号通路、炎症反应等,参与胰岛素抵抗的发生发展过程。
摘要
背景:细胞外囊泡作为细胞间信息交流的新兴关键递质,通过传递miRNA、蛋白质及脂质分子,在骨骼肌、脂肪组织和肝脏等胰岛素靶器官中发挥关键调控作用,而运动诱导的细胞外囊泡在胰岛素抵抗发生发展进程中的作用机制成为代谢领域的热点前沿。
目的:梳理运动诱导的细胞外囊泡在胰岛素抵抗中的最新研究进展。
方法:应用计算机检索PubMed、MedReading、Web of Science、中国知网、万方、维普数据库,文献检索时限为2012-01-01/2025-03-03,搜集相关运动干预后细胞外囊泡对疾病影响的研究,中文检索词为“细胞外囊泡,运动,胰岛素抵抗,疾病”等,英文检索词为“extracellular vesicle,physicalexercise,insulin resistance,disease”等。通过纳入与排除标准,最终纳入107篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:文章系统梳理了细胞外囊泡、运动和胰岛素抵抗的关系,结果表明,细胞外囊泡作为关键递质,通过传递miRNA、蛋白质等分子,在多器官代谢调控中发挥重要作用,并且不同的运动形式对细胞外囊泡的影响不同,有氧运动、力量训练、单次及高强度运动产生的细胞外囊泡在胰岛素抵抗中显现差异化疗效。运动诱导的细胞外囊泡通过多靶点、多通路协同改善胰岛素抵抗,以及对胰岛素信号通路、炎症反应和整体代谢调节具有深远影响,成为连接运动干预与代谢健康的核心桥梁;不同运动模式通过重塑细胞外囊泡分子谱,为精准运动处方设计提供了理论依据。然而,需深入剖析运动-细胞外囊泡-胰岛素抵抗三者之间的复杂关系,为运动改善代谢健康的科学原理提供系统性理论支撑,并为肥胖、糖尿病等相关代谢性疾病的预防与治疗开辟全新的思路与方向。
中图分类号:
引用本文
要俪娟, 王印凤, 马震南, 陈乐琴. 运动诱导细胞外囊泡:在胰岛素抵抗发生发展中的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(13): 3412-3423.
Yao Lijuan, Wang Yinfeng, Ma Zhennan, Chen Leqin. Exercise-induced extracellular vesicles: action and mechanisms in occurrence and development of insulin resistance[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3412-3423.

2.2 细胞外囊泡的分类 细胞外囊泡是指从细胞膜上脱落或者由细胞分泌的双层膜结构组成的囊泡状小体,主要有3类:微囊泡、外泌体和凋亡小体。微囊泡是细胞激活、损伤或凋亡后从细胞膜脱溶的小囊泡,直径为100-1 000 nm;外泌体由细胞内的多泡小体与细胞膜融合后,以外分泌的形式释放到细胞外,直径为30-150 nm;凋亡小体是胞膜皱缩内陷将染色质碎片、细胞器碎片等细胞成分包裹形成的泡状小体,其直径大于1 000 nm。细胞外囊泡在细胞内发生过程可分为通过质膜向外出芽(即微囊泡)以及通过内体膜向内出芽(即外泌体)。由于无法准确定义生物发生途径,因此文章使用了国际细胞外囊泡学会命名法。
2.3 细胞外囊泡在胰岛素抵抗中的作用机制
2.3.1 细胞外囊泡参与主要靶器官的作用机制
(1)骨骼肌:骨骼肌作为体内最大的葡萄糖储存和消耗器官,是胰岛素的主要靶组织[21]。经证实,来自骨骼肌细胞的细胞外囊泡可以引起胰岛素抵抗。当胰岛素抵抗发生在骨骼肌时,骨骼肌的收缩和舒张功能受损,从而导致血糖升高。在胰岛素抵抗发生发展过程中,不同细胞分泌的细胞外囊泡携带特定的miRNA靶向骨骼肌调节血糖,脂肪细胞来源细胞外囊泡分泌miR-27a会抑制骨骼肌中过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ的表达,从而导致胰岛素抵抗[22]、胰腺癌细胞来源细胞外囊泡分泌miR-151-3p和miR-450b-3p抑制磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B/叉头框蛋白O1信号通路促进骨骼肌胰岛素抵抗[23]、骨骼肌来源细胞外囊泡通过上调miR-143、miR-145与胰岛素受体底物1的3’非翻译区互补配对结合[24],阻断了胰岛素信号向下游的正常传递,促进胰岛素抵抗。细胞外囊泡也能携带蛋白质分子直接作用于胰岛素受体底物1,抑制磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶的激活,进而减少葡萄糖转运蛋白4向细胞膜的转位,降低骨骼肌对葡萄糖的摄取能力,加重胰岛素抵抗[25]。有研究证实,2型糖尿病患者的血清细胞外囊泡中含有miR-20b-5p,可以减少骨骼肌细胞中的糖原积累,导致骨骼肌胰岛素抵抗[26]。
在胰岛素抵抗的发生发展过程中,骨骼肌来源细胞外囊泡对线粒体功能产生了重要的调节作用。线粒体作为骨骼肌细胞内的能量代谢核心枢纽,其功能状态与胰岛素敏感性密切相关[27]。骨骼肌来源细胞外囊泡通过调控miRNA等分子机制影响转录共激活因子及其下游基因的表达来影响线粒体的功能和数量,最终导致胰岛素抵抗的恶化[28]。最新研究发现,线粒体自噬在胰岛素抵抗中的作用是通过清除受损和功能失调的线粒体,以维持正常的线粒体功能和能量代谢,从而改善胰岛素抵抗[29],但其在环境和饮食中的具体机制暂不明确。
总之,骨骼肌来源细胞外囊泡通过miRNA、蛋白质分子和线粒体功能参与调控胰岛素抵抗的发生和发展,这些机制为研究胰岛素抵抗的病理生理学提供了重要线索。
(2)脂肪组织:脂肪细胞释放的细胞外囊泡通过细胞间的交流在2型糖尿病等代谢性疾病的发生过程中发挥重要作用[30]。①携带miR-155抑制巨噬细胞中的基因表达来激活信号通路,导致巨噬细胞向促炎性M1型极化,影响脂肪细胞的代谢和功能,从而加剧炎症反应并促进胰岛素抵抗[31];②增强sonic hedgehog基因通过信号通路介导M1巨噬细胞极化来促进脂肪组织胰岛素抵抗[32];③miR-122、miR-192、miR-27a-3p和miR-27b-3p直接参与发展胰岛素抵抗的早期阶段[33];此外,miR-223升高可调节巨噬细胞表型和激活状态[34];④miR-802-5p下调热休克蛋白60导致氧化应激和胰岛素抵抗[35]。反之,胰岛素抵抗引起的肥胖促进脂肪组织中促炎性巨噬细胞浸润增加,分泌大量炎症因子,通过Toll样受体4依赖途径干扰胰岛素信号通路,导致脂肪细胞对胰岛素不敏感。进一步研究发现,肝细胞来源细胞外囊泡通过携带miR-3075抑制脂肪组织的胰岛素敏感性和携带miR-130a-3p进入脂肪细胞来抑制PH结构域基因的表达来激活脂肪细胞中的信号通路[36-37],从而改善葡萄糖耐量并恢复脂肪组织的胰岛素抵抗。
大量实验证实,细胞外囊泡可以通过调节葡萄糖转运蛋白4表达影响胰岛素敏感性。细胞外囊泡能够抑制过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ及其下游靶基因葡萄糖转运蛋白4的表达,导致胰岛素抵抗和葡萄糖不耐受[38]。巨噬细胞衍生的细胞外囊泡干扰人类脂肪细胞中的葡萄糖转运蛋白4易位而诱导胰岛素抵抗[39];同时在血糖异常患者中发现,细胞外囊泡中的miR-652和miR-146b在调节胰岛素敏感性方面具有重要作用[40];外泌体中的长链非编码RNA调节胰岛β细胞功能为葡萄糖稳态提供了一种新的机制,为2型糖尿病的预防提供了一种新的思路[41]。
在2型糖尿病等代谢性疾病的发生中,脂肪细胞释放的细胞外囊泡通过携带特定的miRNA和葡萄糖转运蛋白4的表达来促进炎症反应、调节胰岛素信号通路以及影响脂肪组织和巨噬细胞的功能。这些发现为代谢性疾病的治疗提供了新的潜在靶点。
(3)肝脏组织:肝脏在维持血糖稳态中起着至关重要的作用,细胞外囊泡在肝脏糖异生和脂质代谢中的作用也具有复杂性,不同来源的细胞外囊泡通过向肝细胞递送miRNA来改善肝脏胰岛素抵抗[42]。在动物模型中发现,M2巨噬细胞分泌的外泌体通过递送miR-690至肝细胞,显著改善肝脏胰岛素抵抗[43];脂肪干细胞来源细胞外囊泡携带miR-21-5p进入肝细胞来促进糖异生和提高胰岛素敏感性[44];相反,细胞外囊泡通过携带肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和miR-122,增强糖异生来加重胰岛素抵抗[45]。细胞外囊泡对肝脏的脂质代谢也产生显著的影响,在胰岛素抵抗相关的肝脏脂质代谢紊乱过程中,细胞外囊泡通过抑制和促进相关基因的表达导致肝脏脂肪酸的合成增加和氧化减少,从而加重脂质代谢紊乱,最终异常的细胞外囊泡可能导致脂肪肝的发生,并与胰岛素抵抗形成恶性循环[46]。
细胞外囊泡在肝脏糖异生和脂质代谢中的作用复杂多样,既可以通过递送特定miRNA改善胰岛素抵抗,也可能通过其他机制加重代谢紊乱。这些发现为肝脏代谢调控提供了新的视角,并为开发相关治疗策略提供理论基础。
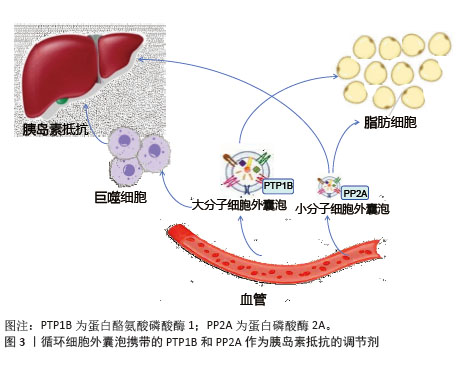
2.3.2 胰岛素信号通路调节 脂肪细胞来源细胞外囊泡可以通过转移脂肪因子含量来干扰肝脏和骨骼肌中的胰岛素信号传导[47-48],从而诱导胰岛素抵抗[49];巨噬细胞分泌白细胞介素6和白细胞介素16来减少肝细胞中的胰岛素信号传导[18]。胰岛素抵抗下的细胞外囊泡携带的蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶1和蛋白磷酸酶2A相互作用,削弱脱磷酸化胰岛素受体的活性[50],减少脂肪和肝脏等靶组织中的胰岛素信号激活,影响胰岛素抵抗[18],见图3。实验证实来自胰岛素抵抗小鼠的细胞外囊泡可调节骨骼肌和胰腺β细胞中的胰岛素信号转导功能[51],外泌体在靶组织中引发功能变化并调节其他组织中的胰岛素信号转导,使得胰岛素抵抗状态下参与信号转导的活化蛋白水平降低[52]。
综上所述,脂肪细胞、巨噬细胞和其他组织来源的细胞外囊泡通过携带特定的蛋白质、miRNA或脂质来显著影响胰岛素信号传导,从而在胰岛素抵抗的发生和发展中发挥重要作用。
2.3.3 细胞外囊泡通过其他机制作用于胰岛素抵抗 近年来,胰岛素分泌已被证明不仅受血糖水平和炎症因子的调节,还受细胞外囊泡的调节。细胞外囊泡可以通过内容物靶向胰岛细胞,直接影响胰岛细胞的分泌水平或间接影响胰岛细胞的增殖或凋亡,从而参与胰岛素分泌的调节。在相关代谢性疾病的动物模型中发现,细胞外囊泡通过运输靶向胰岛细胞的非编码RNA来增强胰岛素分泌,循环系统中的循环细胞外囊泡能够触发胰岛素分泌受损,高胰岛素血症会导致细胞外囊泡分泌增加从而诱导皮质神经元的胰岛素抵抗。在人类研究中发现,胰岛素抵抗导致糖尿病相关细胞外囊泡浓度升高,胰岛素信号蛋白水平发生变化,增强胰岛素抵抗[15]。细胞外囊泡在2型糖尿病中通过多维度机制和多种炎症相关分子驱动炎症与免疫失衡,并通过血液循环实现远端器官的炎症传播。局部组织释放的细胞外囊泡可以激活转录因子和炎症小体来招募免疫细胞浸润,循环系统中的细胞外囊泡可以扩散炎症至全身,加重胰岛素抵抗。
综上所述,目前研究人员针对细胞外囊泡的干预策略为2型糖尿病治疗提供新思路,为运动防治代谢疾病提供了多层次的理论支持和技术路径。随着精准医学和生物工程技术的发展,细胞外囊泡的相关研究未来有望实现从机制探索到临床转化的重大突破。
2.4 运动诱导的细胞外囊泡的生理功能调节机制 运动对人类具有多系统益处,包括降低心血管风险、改善糖代谢稳态、促进体质量减轻、刺激合成代谢激素和预防肌肉减少症[53]。目前,运动已被证明会改变细胞外囊泡的miRNA表达和蛋白质含量[54],耐力训练和阻力训练等不同类型的运动都会影响细胞外囊泡的变化,有助于改善氧化应激反应、减少炎症和调节代谢。
2.4.1 代谢调节机制 运动诱导的细胞外囊泡通过调节胰岛素信号通路,显著提升胰岛素敏感性[55-57]。8周运动训练增强了大脑胰岛素敏感性,细胞外囊泡携带特定的miRNA抑制胰岛素受体底物的负调节因子,增强胰岛素介导的葡萄糖摄取和代谢,提高胰岛素敏感性,对预防和治疗2型糖尿病等代谢性疾病具有重要意义。经过研究发现,患者在炎症或高糖环境下缺乏运动[58],巨噬细胞分泌的细胞外囊泡携带miR-29抑制胰岛素分泌相关基因的转录或翻译,导致胰岛素分泌不足。
在脂肪组织微环境中,巨噬细胞衍生的细胞外囊泡通过转移特定miRNA,参与胰岛素抵抗的调节,而运动干预可重塑这一过程,改善脂肪组织代谢功能。哈佛大学的一组研究人员报告显示,运动会增加骨骼肌分泌小分子肽“鸢尾素”的含量[59],鸢尾素与整合素αV受体结合激活腺苷酸激活蛋白激酶信号通路,上调脂肪褐变基因,促进白色脂肪向棕色脂肪转化,加速能量消耗,导致体质量减轻。单次抗阻运动后骨骼肌释放的细胞外囊泡富含miR-1,抑制脂肪细胞分化相关基因过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ,提高脂肪分解酶活性,降低体脂率[60]。
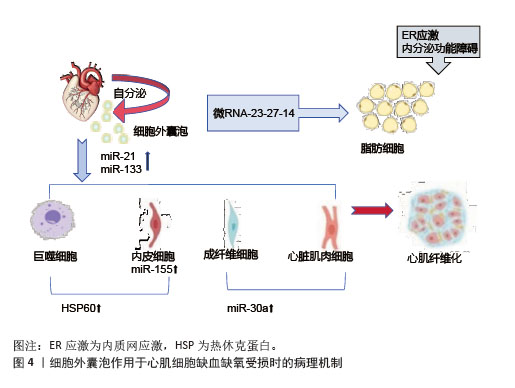
2.4.2 组织修复与保护机制 运动诱导的细胞外囊泡对肌肉和心血管组织具有保护与修复作用[61]。细胞外囊泡携带的miR-133b、miR-181a-5之间存在显著相关性,促进线粒体生物合成,提升肌肉有氧代谢能力。阻力训练后,细胞外囊泡释放miR-486-5、miR-215-5p分子,通过靶向负调控因子,刺激肌肉肥大[62] 。在心血管系统中,细胞外囊泡携带的血管内皮生长因子和miR-182-5p升高,激活内皮细胞信号通路,促进血管内皮增殖、迁移及血管生成。在缺血缺氧状态下,运动诱导的细胞外囊泡在心肌细胞中携带miR-21、miR-133,抑制细胞凋亡、调节纤维化进程和促进血管新生,发挥心肌保护作用[63]。在心肌缺血再灌注损伤模型中发现,细胞外囊泡能够抑制心肌细胞凋亡,减少活性氧的产生,减轻心肌损伤,促进心肌修复,见图4。
细胞外囊泡携带脑源性神经营养因子通过激活神经营养酪氨酸受体B,对神经元存活、突触可塑性及认知功能产生显著影响,有助于改善学习和记忆能力,对阿尔茨海默病和帕金森病的防治可能具有潜在价值[64]。在神经退行性疾病防治方面,运动诱导的细胞外囊泡通过上调脑源性神经营养因子水平,延缓阿尔茨海默病进展[65]。运动增加细胞外囊泡中线粒体衍生的肽,抑制神经元凋亡、保留突触、减少炎症并支持葡萄糖和氧化代谢[66],为帕金森病等神经疾病的治疗提供新方向。
2.4.3 炎症与疾病调控机制 运动诱导的细胞外囊泡通过多种途径发挥抗炎作用[67]。细胞外囊泡携带miR-146a靶向Toll样受体4和白细胞介素1受体信号通路,降低白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α促炎细胞因子水平;miR-155抑制细胞因子信号传导抑制蛋白1,增强抗炎信号传导;miR-486和miR-29通过调节过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ和高迁移率族蛋白B1,抑制巨噬细胞M1极化,促进调节性T细胞分化[68]。运动上调细胞外囊泡中的过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激活因子1α,实现线粒体生物发生与脂代谢的协同调控[69]。细胞外囊泡在运动后可以释放促炎细胞因子,减少炎症来预防炎症相关疾病,在大脑水平产生有益影响[70]。细胞外囊泡中的白细胞介素10通过阻断核因子κB核转位和调节胶质细胞表型,有效抑制神经炎症[71]。
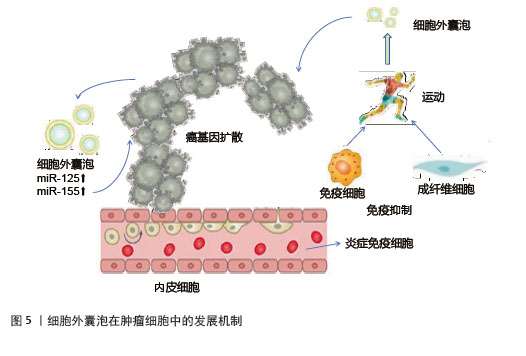
运动诱导的细胞外囊泡在肿瘤调控中具有双重作用。一方面,运动可以增加骨骼肌来源细胞外囊泡释放肌源性miRNA和鸢尾素,抑制癌细胞增殖、侵袭和转移,发挥抑制肿瘤作用[72]。细胞外囊泡携带的糖酵解酶可竞争性抑制肿瘤细胞代谢,发挥抗癌作用[73]。另一方面,细胞外囊泡中的miR-125b和miR-155致癌性miRNA,抑制抑癌基因表达或激活相关信号通路,使细胞获得迁移和侵袭能力,从而促进肿瘤细胞的转移[74],见图5。然而,目前缺乏直接检查骨骼肌来源细胞外囊泡对癌细胞影响的临床前研究,这限制了对运动诱导的骨骼肌来源细胞外囊泡的确切作用的理解[75],深入探究骨骼肌来源细胞外囊泡与癌细胞相互作用的分子机制,将为运动抗癌策略提供更坚实的理论基础。
2.4.4 运动特异性效应与衰老机制 运动强度显著影响细胞外囊泡的蛋白质组成和功能,高强度运动后细胞外囊泡分泌己糖激酶来适应能量需求[54]。然而,过度训练可能导致细胞外囊泡传递促纤维化信号,提示需平衡运动强度[76]。运动类型对细胞外囊泡成分的强度依赖性也至关重要。耐力训练促使细胞外囊泡富集脂肪酸转运蛋白及miR-206,增强肌肉氧化能力[77];阻力训练诱导细胞外囊泡释放肌肉合成相关分子,促进肌纤维肥大[78]。细胞外囊泡通过抗氧化应激与调控衰老相关分泌表型来抑制细胞衰老,运动过程中减少细胞外囊泡中促炎因子的分泌,阻断衰老相关分泌表型的旁分泌效应[79-80]。衰老的脂肪细胞通过细胞外囊泡传递内质网应激信号,促进周围细胞衰老[81]。因此,细胞外囊泡中内质网应激相关蛋白或miRNA可作为肥胖相关代谢疾病的早期诊断标志物[82]。
总之,运动诱导的细胞外囊泡通过多靶点、多通路调节,整合代谢、抗炎、抗氧化及组织再生功能,在神经保护、抗炎及肿瘤抑制中展现广阔的应用前景。
2.5 运动诱导的细胞外囊泡在胰岛素抵抗中的作用机制 胰岛素抵抗是2型糖尿病、肥胖等代谢性疾病的核心病理特征,而运动具有强大的抗炎作用,能够有效打破胰岛素抵抗与慢性炎症之间的恶性循环。近年来,研究表明,运动诱导的细胞外囊泡作为细胞间通讯的关键递质[83],通过调节靶器官代谢、胰岛素信号通路及炎症反应,在打破这一恶性循环中发挥重要作用。
2.5.1 在主要靶器官中的作用机制
(1)骨骼肌细胞:运动诱导的骨骼肌来源细胞外囊泡改善线粒体能量代谢效率,参与代谢调节、信号传导、基因表达调控以及促进骨形成。一方面,运动作为干预手段,能增加骨骼肌对葡萄糖的摄取,激活信号通路,促进葡萄糖转运蛋白4转位[84],减少内脏脂肪,改善身体成分,降低炎症水平,提高胰岛素敏感性。另一方面,运动诱导的骨骼肌来源细胞外囊泡转运乳酸脱氢酶A至骨髓基质细胞,激活糖酵解途径促进成骨分化,间接增强骨骼肌的代谢活性。在糖原代谢方面,骨骼肌来源细胞外囊泡携带的miR-378通过靶向抑制糖原合成酶激酶3β,恢复肌糖原代谢平衡,维持胰岛素敏感性[84],而萎缩骨骼肌分泌的骨骼肌来源细胞外囊泡减少,促骨形成能力下降,运动通过恢复骨骼肌来源细胞外囊泡的正常分泌,改善骨骼肌与骨骼的协同代谢功能[85]。
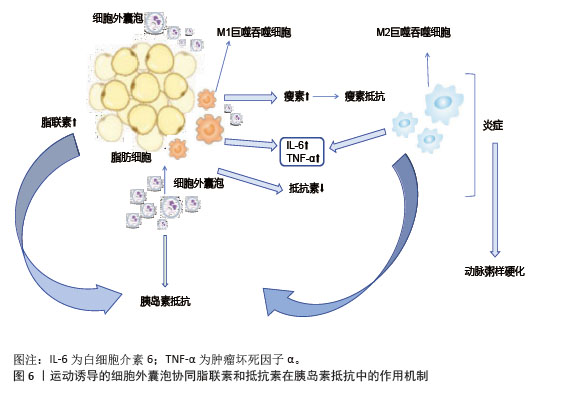
(2)脂肪细胞:运动诱导的细胞外囊泡对脂肪细胞分化和功能具有显著调控作用。长期运动通过调节循环细胞外囊泡,促进脂肪组织褐变,提高胰岛素敏感性[86],减少肝脂肪变性。运动后脂肪组织中的miR-652-3p表达增加,提高肥胖女性皮下脂肪组织中的胰岛素敏感性[87],miR-27a抑制脂肪细胞分化关键转录因子过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ的表达,减少脂肪细胞体积和数量,从而改善代谢健康[88]。细胞外囊泡中的miR-330、miR-133a通过过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ促进白色脂肪向棕色脂肪转化,增强产热和脂质氧化能力[89]。运动诱导的细胞外囊泡通过增加脂联素的分泌及减少抵抗素的分泌,激活腺苷酸激活蛋白激酶通路,促进骨骼肌葡萄糖摄取和脂肪酸氧化,缓解胰岛素抵抗[89],见图6。
(3)肝脏细胞:运动诱导的细胞外囊泡调控肝脏糖异生和脂代谢改善胰岛素抵抗。肝源性细胞外囊泡中的miR-122在运动后表达上调,靶向抑制葡萄糖-6-磷酸酶和磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸羧激酶,减少肝脏葡萄糖输出[90]。骨骼肌来源细胞外囊泡携带的有机阳离子转运蛋白2促进肝脏细胞摄取肉碱,增强脂肪酸β-氧化能力,减少肝内脂肪堆积,预防脂肪肝的发生,维持肝脏的代谢功能稳态[91]。运动减少肝细胞来源细胞外囊泡分泌促炎因子,抑制肝窦内皮细胞的炎症信号传导,缓解肝脏炎症和胰岛素抵抗[92]。
2.5.2 对胰岛素信号通路的调节 运动诱导的细胞外囊泡通过miRNA和蛋白质成分精细调控胰岛素信号通路。骨骼肌来源细胞外囊泡中的miR-221/222靶向抑制脂肪细胞第10号染色体缺失的磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源基因,激活磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B通路,促进葡萄糖转运蛋白4转位和葡萄糖摄取[93];脂肪细胞来源细胞外囊泡中的miR-143抑制胰岛素受体底物1丝氨酸位点的异常磷酸化,恢复胰岛素受体信号传导,增强骨骼肌对胰岛素的响应[94]。细胞外囊泡中的蛋白质成分积极参与胰岛素信号通路的调节,运动诱导的骨骼肌细胞外囊泡携带的胰岛素受体底物2蛋白补充肝脏细胞内的胰岛素受体底物蛋白池,增强胰岛素信号传递,抑制糖异生[95];脂肪细胞来源细胞外囊泡中的热休克蛋白70通过与胰岛素受体底物1结合,维持胰岛素信号通路的完整性,提高骨骼肌细胞对胰岛素的敏感性[95]。
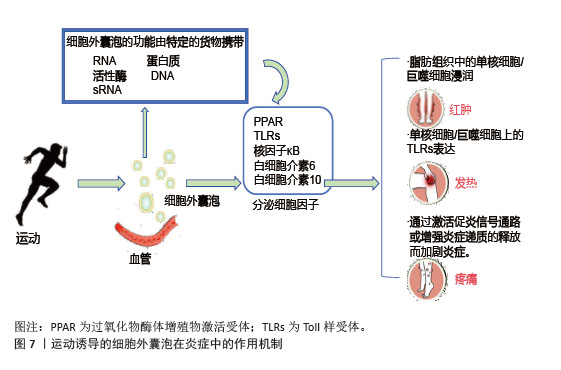
2.5.3 对炎症相关信号通路的靶向干预 运动诱导的细胞外囊泡靶向核因子κB信号通路抑制炎症反应,改善胰岛素抵抗,高表达miR-181a;靶向抑制核因子κB,抑制蛋白激酶β,阻断核因子κB核转位,减少肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6促炎因子释放。脂肪组织中的细胞外囊泡与核因子κB相互作用抑制其活性,促进胰岛素信号通路基因的表达,改善骨骼肌胰岛素敏感性[96],见图7。在肝脏中,细胞外囊泡通过调节Toll样受体4/核因子κB通路,抑制炎症性细胞因子分泌,有效改善胰岛素抵抗和炎症反应[97]。
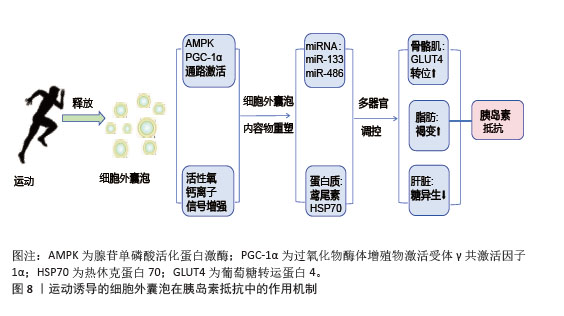
综上所述,运动诱导的细胞外囊泡通过多靶点、多通路协同作用,改善骨骼肌、脂肪组织和肝脏的代谢功能,增强胰岛素敏感性,并抑制慢性炎症,见图8。这些机制为代谢性疾病的治疗提供了新的生物学策略。
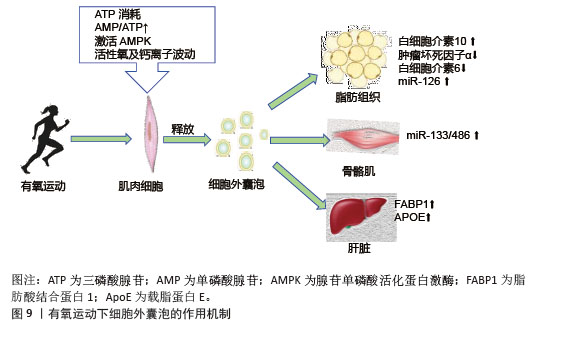
2.6 不同类型运动诱导的细胞外囊泡与胰岛素抵抗 有氧运动通过激活能量代谢核心调节因子腺苷单磷酸活化蛋白激酶促进细胞外囊泡的生成与释放,运动引起的肌肉收缩导致ATP消耗,使得细胞内腺苷单磷酸和腺苷三磷酸比例显著升高,进而激活腺苷单磷酸活化蛋白激酶[98]。运动诱导的氧化应激产生的活性氧和钙离子波动进一步刺激了细胞外囊泡释放。有氧运动诱导的细胞外囊泡靶向作用于多个胰岛素敏感组织,包括肝脏、脂肪组织以及骨骼肌等,携带miR-133和miR-486靶向胰岛素信号通路关键分子发挥作用,见图9。运动后循环细胞外囊泡的蛋白质组学分析显示,肝脏相关蛋白显著富集,证实了运动可能通过血流动力学改变或表面整合素介导细胞外囊泡向肝脏富集[99]。
力量训练诱导的细胞外囊泡在改善胰岛素抵抗方面同样发挥着重要作用,能够调节骨骼肌代谢和糖脂代谢平衡。力量训练诱导的细胞外囊泡在蛋白质和miRNA组成上具有特异性,肌球蛋白重链和线粒体生物合成相关蛋白细胞色素c氧化酶亚基4的富集,促进肌肉代谢[100]。力量训练诱导的细胞外囊泡通过骨骼肌、肝脏、脂肪细胞协同作用改善代谢[101],骨骼肌中高表达的miR-1和miR-206促进骨骼肌细胞的增殖与分化,加速肌纤维修复,增强线粒体功能,优化葡萄糖氧化能力,提高骨骼肌对胰岛素的响应能力;在肝脏中细胞外囊泡调节相关信号通路抑制糖异生关键酶的活性,减少肝脏葡萄糖输出;在脂肪细胞中,影响脂肪代谢相关基因的表达,调节脂肪细胞分化与脂质代谢,从而改善全身胰岛素抵抗状态。
高强度间歇训练是降低胰岛素抵抗和2型糖尿病个体心脏代谢标志物的有效策略。高强度间歇训练通过双重机制调控细胞外囊泡释放,在短时间高强度运动阶段,可迅速激活肌肉细胞内的能量应激反应和腺苷单磷酸活化蛋白激酶/过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激活因子1α通路,从而促进细胞外囊泡的释放。高强度间歇训练诱导的细胞外囊泡携带miR-133a/b,靶向叉头框蛋白O1抑制其核转位,减少肝脏糖异生关键酶磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸羧激酶、葡萄糖-6-磷酸酶的表达[102]。高强度间歇训练诱导的细胞外囊泡对胰岛素抵抗的改善作用主要通过增强骨骼肌的代谢实现,携带的 miRNA 可调节骨骼肌细胞内不同能量底物代谢相关基因的表达。在运动及恢复阶段,高强度间歇训练诱导的细胞外囊泡能提高骨骼肌对胰岛素的敏感性,改善心血管功能,增强血管舒张能力,间接对全身胰岛素抵抗发挥积极作用。临床研究表明,2型糖尿病患者在12周高强度间歇训练中,通过下调蛋白激酶A和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路蛋白,减少炎症反应。动物实验进一步证实,将高强度间歇训练小鼠的细胞外囊泡注射至久坐小鼠后,可使后者肝脏叉头框蛋白O1水平降低40%,糖耐量显著改善[103]。
单次运动后循环细胞外囊泡呈现动态变化,减少空腹状态下细胞外囊泡的浓度,增强胰岛敏感性。高胰岛素血症会增加细胞外囊泡分泌,减少胰岛素信号传导[98]。在健康人群中,骑自行车后细胞外囊泡浓度短暂升高,CD81、热休克蛋白70等标志物增加,加速肝脏摄取速度[6],而在代谢异常人群中,糖尿病前期个体小细胞外囊泡释放受阻,但单次高强度间歇训练仍可提高miR-133a水平,改善糖代谢[104]。单次运动减少血小板来源的CD41+细胞外囊泡,降低高胰岛素血症对胰岛素信号的抑制[104]。临床数据显示,单次中等强度运动使肥胖成人胰岛素敏感性提高35%,高强度运动效果维持更久[105]。不同运动类型可以通过特异性调控细胞外囊泡的miRNA和蛋白质组来多维度改善胰岛素抵抗,见表2[104,106-107]。

综上所述,各类研究均表明不同类型运动诱导的细胞外囊泡对胰岛素抵抗具有改善作用,主要通过调节胰岛素信号通路、影响靶组织代谢以及减轻炎症反应等途径实现。有氧运动、高强度间歇训练和单次运动都涉及到对胰岛素信号通路中关键分子的调节;力量训练和有氧运动均关注到对骨骼肌代谢的促进作用。然而,不同运动类型诱导的细胞外囊泡在关键分子、靶组织侧重以及具体作用机制上存在差异。有氧运动更侧重于抗炎及对脂肪组织炎症微环境的调节;力量训练着重于促进骨骼肌合成代谢;高强度间歇训练则在抑制肝脏糖异生和增强骨骼肌代谢灵活性方面表现突出;单次运动主要体现在对循环系统中细胞外囊泡的快速调节以改善胰岛素敏感性。由于物种差异和个体代谢状态不同,运动诱导细胞外囊泡改善胰岛素抵抗的具体效果和机制也有所不同。
| [1] SWINBURN BA, KRAAK VI, ALLENDER S, et al. The Global Syndemic of Obesity, Undernutrition, and Climate Change: The Lancet Commission report. Lancet. 2019;393(10173):791-846. [2] AHMAD HAIRI H, IBRAHIM NI, SADIKAN MZ, et al. Deciphering the role of classical oestrogen receptor in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus: From molecular mechanism to clinical evidence. Bioimpacts. 2024;15:30378. [3] CARNEY RP, MIZENKO RR, BOZKURT BT, et al. Harnessing extracellular vesicle heterogeneity for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Nat Nanotechnol. 2025;20(1):14-25. [4] 车开萱,路明月,邱俊强.有氧运动防治肥胖相关胰岛素抵抗:以靶向炎症为视角[J].中国慢性病预防与控制,2024, 32(10):790-795. [5] GURUNATHAN S, KANG MH, JEYARAJ M, et al. Review of the Isolation, Characterization, Biological Function, and Multifarious Therapeutic Approaches of Exosomes. Cells. 2019;8(4):307. [6] LIEM M, ANG CS, MATHIVANAN S. Insulin Mediated Activation of PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Modifies the Proteomic Cargo of Extracellular Vesicles. Proteomics. 2017; 17(23-24):17. [7] LI B, LI W, LIU T, et al. Extracellular vesicles regulate the transmission of insulin resistance and redefine noncommunicable diseases. Front Mol Biosci. 2023;9:1024786. [8] SÁEZ T, TOLEDO F, SOBREVIA L. Extracellular Vesicles and Insulin Resistance: A Potential Interaction in Vascular Dysfunction. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2019;17(5):491-497. [9] DE MATOS MA, OTTONE VDE O, DUARTE TC, et al. Exercise reduces cellular stress related to skeletal muscle insulin resistance. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2014;19(2):263-270. [10] EICHNER NZM, ERDBRÜGGER U, MALIN SK. Extracellular Vesicles: A Novel Target for Exercise-Mediated Reductions in Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Risk. J Diabetes Res. 2018;2018:7807245. [11] APOSTOLOPOULOU M, MASTROTOTARO L, HARTWIG S, et al. Metabolic responsiveness to training depends on insulin sensitivity and protein content of exosomes in insulin-resistant males. Sci Adv. 2021;7(41):eabi9551. [12] DENG ZB, POLIAKOV A, HARDY RW, et al. Adipose tissue exosome-like vesicles mediate activation of macrophage-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2009;58(11): 2498-2505. [13] ZHAO H, SHANG Q, PAN Z, et al. Exosomes From Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Attenuate Adipose Inflammation and Obesity Through Polarizing M2 Macrophages and Beiging in White Adipose Tissue. Diabetes. 2018;67(2):235-247. [14] CREWE C, JOFFIN N, RUTKOWSKI JM, et al. An Endothelial-to-Adipocyte Extracellular Vesicle Axis Governed by Metabolic State. Cell. 2018;175(3):695-708.e13. [15] 蒋和敏,付麒,杨涛.细胞外囊泡在胰岛功能调控中的作用[J].中华糖尿病杂志, 2018,10(8):557-559. [16] LI CJ, FANG QH, LIU ML, et al. Current understanding of the role of Adipose-derived Extracellular Vesicles in Metabolic Homeostasis and Diseases: Communication from the distance between cells/tissues. Theranostics. 2020;10(16):7422-7435. [17] XU H, DU X, XU J, et al. Pancreatic β cell microRNA-26a alleviates type 2 diabetes by improving peripheral insulin sensitivity and preserving β cell function. PLoS Biol. 2020;18(2):e3000603. [18] 邢正,郭兰兰,张靓.运动调控胞外囊泡生物发生的研究进展[J].生命科学, 2024,36(2):245-257. [19] 武汉体育学院.空军军医大学张星教授应邀在运动与健康科学前沿论坛作学术报告[EB/OL](2024-06-01). https://xljk.whsu.edu.cn/info/1123/1833.htm [20] ALI S, VIDAL-GÓMEZ X, PIQUET M, et al. Circulating extracellular vesicle-carried PTP1B and PP2A phosphatases as regulators of insulin resistance. Diabetologia. 2025; 68(1):231-242. [21] CHOW L, FROM A, SEAQUIST E. Skeletal muscle insulin resistance: the interplay of local lipid excess and mitochondrial dysfunction. Metabolism. 2010;59(1):70-85. [22] YU Y, DU H, WEI S, et al. Adipocyte-Derived Exosomal MiR-27a Induces Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle Through Repression of PPARγ. Theranostics. 2018; 8(8):2171-2188. [23] WANG L, ZHANG B, ZHENG W, et al. Exosomes derived from pancreatic cancer cells induce insulin resistance in C2C12 myotube cells through the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 pathway. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):5384. [24] SU J, LIANG H, YAO W, et al. MiR-143 and MiR-145 regulate IGF1R to suppress cell proliferation in colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e114420. [25] MA S, XING X, HUANG H, et al. Skeletal muscle-derived extracellular vesicles transport glycolytic enzymes to mediate muscle-to-bone crosstalk. Cell Metab. 2023;35(11):2028-2043.e7. [26] KATAYAMA M, WIKLANDER OPB, FRITZ T, et al. Circulating Exosomal miR-20b-5p Is Elevated in Type 2 Diabetes and Could Impair Insulin Action in Human Skeletal Muscle. Diabetes. 2019;68(3):515-526. [27] 张好好,陈璐璐.骨骼肌线粒体异常在胰岛素抵抗形成中的作用[J].国际内分泌代谢杂志,2011,31(1):35-38. [28] HALLING JF, PILEGAARD H. PGC-1α-mediated regulation of mitochondrial function and physiological implications. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2020;45(9):927-936. [29] 陈玉华,郑标,成迪,等.线粒体自噬影响胰岛素抵抗的作用及机制[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2024,51(4):772-784. [30] WANG J, LI L, ZHANG Z, et al. Extracellular vesicles mediate the communication of adipose tissue with brain and promote cognitive impairment associated with insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2022;34(9): 1264-1279.e8. [31] 王柯,吕君君,刘冬梅,等.脂肪组织细胞外基质与胰岛素抵抗[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2017,33(10):993-998. [32] SONG M, HAN L, CHEN FF. et al. Adipocyte-Derived Exosomes Carrying Sonic Hedgehog Mediate M1 Macrophage Polarization-Induced Insulin Resistance via Ptch and PI3K Pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018; 48(4):1416-1432. [33] CASTAÑO C, KALKO S, NOVIALS A, et al. Obesity-associated exosomal miRNAs modulate glucose and lipid metabolism in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018; 115(48):12158-12163. [34] DEIULIIS JA, SYED R, DUGGINENI D, et al. Visceral Adipose MicroRNA 223 Is Upregulated in Human and Murine Obesity and Modulates the Inflammatory Phenotype of Macrophages. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e0165962. [35] KWAN HY, CHEN M, XU K, et al. The impact of obesity on adipocyte-derived extracellular vesicles. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78(23):7275-7288. [36] JI Y, LUO Z, GAO H. et al. Hepatocyte-derived exosomes from early onset obese mice promote insulin sensitivity through miR-3075. Nat Metab. 2021;3(9):1163-1174. [37] WU J, DONG T, CHEN T, et al. Hepatic exosome-derived miR-130a-3p attenuates glucose intolerance via suppressing PHLPP2 gene in adipocyte. Metabolism. 2020;103:154006. [38] YING W, RIOPEL M, BANDYOPADHYAY G, et al. Adipose Tissue Macrophage-Derived Exosomal miRNAs Can Modulate In Vivo and In Vitro Insulin Sensitivity. Cell. 2017;171(2):372-384.e12. [39] ZHANG Y, SHI L, MEI H, et al. Inflamed macrophage microvesicles induce insulin resistance in human adipocytes. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2015;12:21. [40] WIESER V, ADOLPH TE, GRANDER C, et al. Adipose type I interferon signalling protects against metabolic dysfunction. Gut. 2018;67(1):157-165. [41] 邓文艺,屈顺林.细胞外囊泡在肥胖引起的胰岛素抵抗中的作用[J].生命的化学, 2019,39(2):373-381. [42] ZHAO Y, ZHAO MF, JIANG S, et al. Liver governs adipose remodelling via extracellular vesicles in response to lipid overload. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):719. [43] YING W, GAO H, DOS REIS FCG, et al. MiR-690, an exosomal-derived miRNA from M2-polarized macrophages, improves insulin sensitivity in obese mice. Cell Metab. 2021; 33(4):781-790.e5. [44] CAO M, ZHAO Y, CHEN T, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNAs ameliorate polycystic ovary syndrome by protecting against metabolic disturbances. Biomaterials. 2022;288:121739. [45] KRANENDONK ME, VISSEREN FL, VAN HERWAARDEN JA, et al. Effect of extracellular vesicles of human adipose tissue on insulin signaling in liver and muscle cells. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014; 22(10):2216-2223. [46] 贺亚婕,杜丽坤,任那,等.中药调控内质网应激相关通路改善肝脏脂质代谢紊乱的机制研究进展[J].天津中医药大学学报,2024,43(11):1046-1052. [47] KRANENDONK ME, DE KLEIJN DP, KALKHOVEN E, et al. Extracellular vesicle markers in relation to obesity and metabolic complications in patients with manifest cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014;13:37. [48] PENNA F, GARCIA-CASTILLO L, COSTELLI P. Extracellular Vesicles and Exosomes in the Control of the Musculoskeletal Health. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2024;22(2):257-265. [49] MLECZKO J, ORTEGA FJ, FALCON-PEREZ JM, et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Hypoxic Adipocytes and Obese Subjects Reduce Insulin-Stimulated Glucose Uptake. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2018;62(5):1700917. [50] URASAKI Y, LE TT. Cinnamaldehyde and Curcumin Prime Akt2 for Insulin-Stimulated Activation. Nutrients. 2022; 14(16):3301. [51] ASWAD H, FORTERRE A, WIKLANDER OP, et al. Exosomes participate in the alteration of muscle homeostasis during lipid-induced insulin resistance in mice. Diabetologia. 2014;57(10):2155-2164. [52] KIM B, SULLIVAN KA, BACKUS C, et al. Cortical neurons develop insulin resistance and blunted Akt signaling: a potential mechanism contributing to enhanced ischemic injury in diabetes. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;14(10):1829-1839. [53] ANDERSON E, DURSTINE JL. Physical activity, exercise, and chronic diseases: A brief review. Sports Med Health Sci. 2019;1(1):3-10. [54] WHITHAM M, PARKER BL, FRIEDRICHSEN M, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Provide a Means for Tissue Crosstalk during Exercise. Cell Metab. 2018;27(1):237-251.e4. [55] JENKINS NT, LANDERS RQ, THAKKAR SR, et al. Prior endurance exercise prevents postprandial lipaemia-induced increases in reactive oxygen species in circulating CD31+ cells. J Physiol. 2011;589(Pt 22): 5539-5553. [56] STROHACKER K, BRESLIN WL, CARPENTER KC, et al. Moderate-intensity, premeal cycling blunts postprandial increases in monocyte cell surface CD18 and CD11a and endothelial microparticles following a high-fat meal in young adults. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2012;37(3):530-539. [57] ADAMS BD, AREM H, HUBAL MJ, et al. Exercise and weight loss interventions and miRNA expression in women with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018;170(1):55-67. [58] LI J, ZHANG Y, YE Y, et al. Pancreatic β cells control glucose homeostasis via the secretion of exosomal miR-29 family. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(3):e12055. [59] BOSTRÖM P, WU J, JEDRYCHOWSKI MP, et al. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012; 481(7382):463-468. [60] VECHETTI IJ JR, PECK BD, WEN Y, et al. Mechanical overload-induced muscle-derived extracellular vesicles promote adipose tissue lipolysis. FASEB J. 2021;35(6):e21644. [61] GUESCINI M, CANONICO B, LUCERTINI F, et al. Muscle Releases Alpha-Sarcoglycan Positive Extracellular Vesicles Carrying miRNAs in the Bloodstream. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0125094. [62] NAIR VD, GE Y, LI S, et al. Sedentary and Trained Older Men Have Distinct Circulating Exosomal microRNA Profiles at Baseline and in Response to Acute Exercise. Front Physiol. 2020;11:605. [63] NIE Y, SATO Y, GARNER RT, et al. Skeletal muscle-derived exosomes regulate endothelial cell functions via reactive oxygen species-activated nuclear factor-κB signalling. Exp Physiol. 2019;104(8): 1262-1273. [64] CARVALHO AL, CALDEIRA MV, SANTOS SD, et al. Role of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor at glutamatergic synapses. Br J Pharmacol. 2008;153 Suppl 1(Suppl 1): S310-324. [65] DELGADO-PERAZA F, NOGUERAS-ORTIZ C, SIMONSEN AH, et al. Neuron-derived extracellular vesicles in blood reveal effects of exercise in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023;15(1):156. [66] HASHIMOTO Y, NIIKURA T, TAJIMA H, et al. A rescue factor abolishing neuronal cell death by a wide spectrum of familial Alzheimer’s disease genes and Abeta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(11):6336-6341. [67] CATITTI G, DE BELLIS D, VESPA S, et al. Extracellular Vesicles as Players in the Anti-Inflammatory Inter-Cellular Crosstalk Induced by Exercise Training. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(22):14098. [68] FINICELLI M, DIGILIO FA, GALDERISI U, et al. The Emerging Role of Macrophages in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: The Potential Impact of Oxidative Stress and Extracellular Vesicle on Macrophage Polarization and Function. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(3):464. [69] SULLIVAN BP, NIE Y, EVANS S, et al. Obesity and exercise training alter inflammatory pathway skeletal muscle small extracellular vesicle microRNAs. Exp Physiol. 2022;107(5): 462-475. [70] KINNEY JW, BEMILLER SM, MURTISHAW AS, et al. Inflammation as a central mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2018;4:575-590. [71] TAGANOV KD, BOLDIN MP, CHANG KJ, et al. NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103(33):12481-12486. [72] WANG Z, KIM SY, TU W, et al. Extracellular vesicles in fatty liver promote a metastatic tumor microenvironment. Cell Metab. 2023;35(7):1209-1226.e13. [73] KRESBACH C, HOLST L, SCHOOF M, et al. Intraventricular SHH inhibition proves efficient in SHH medulloblastoma mouse model and prevents systemic side effects. Neuro Oncol. 2024;26(4):609-622. [74] DHONDT B, ROUSSEAU Q, DE WEVER O, et al. Function of extracellular vesicle-associated miRNAs in metastasis. Cell Tissue Res. 2016;365(3):621-641. [75] SILVESTRI M, GRAZIOLI E, DURANTI G, et al. Exploring the Impact of Exercise-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer Biology. Biology (Basel). 2024;13(9):701. [76] DESHMUKH AS, STEENBERG DE, HOSTRUP M, et al. Author Correction: Deep muscle-proteomic analysis of freeze-dried human muscle biopsies reveals fiber type-specific adaptations to exercise training. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):1600. [77] LIU Y, ZHOU R, GUO Y, et al. Muscle-derived small extracellular vesicles induce liver fibrosis during overtraining. Cell Metab. 2025;37(4):824-841.e8. [78] KYRIAKIDOU Y, COOPER I, KRAEV I, et al. Preliminary Investigations Into the Effect of Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage on Systemic Extracellular Vesicle Release in Trained Younger and Older Men. Front Physiol. 2021;12:723931. [79] MEI R, QIN W, ZHENG Y, et al. Role of Adipose Tissue Derived Exosomes in Metabolic Disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:873865. [80] GARCIA-MARTIN R, WANG G, BRANDÃO BB, et al. MicroRNA sequence codes for small extracellular vesicle release and cellular retention. Nature. 2022;601(7893):446-451. [81] FANG J, LI L, CAO X, et al. Transmissible Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Mediated by Extracellular Vesicles from Adipocyte Promoting the Senescence of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Hypertrophic Obesity. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:7175027. [82] 王珊,曹玉林,吴迪,等.细胞外囊泡表面蛋白冠的研究进展[J].中国生物工程杂志,2024,44(Z1):134-141. [83] 陈子扬,蒲锐,邓爽,等.外泌体对运动介导胰岛素抵抗类疾病的调控作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(25):4089-4094 [84] 沈文清,何标,丁树哲.AMPK:运动调控骨骼肌糖脂代谢的重要激酶[J].生命科学,2022,34(6):631-643. [85] 李涛.运动调节骨骼肌细胞葡萄糖摄取的研究进展[J].中国科技论文在线精品论文,2024,17(3):388-392. [86] DI W, AMDANEE N, ZHANG W, et al. Long-term exercise-secreted extracellular vesicles promote browning of white adipocytes by suppressing miR-191a-5p. Life Sci. 2020; 263:118464. [87] STEVENS MT, SAUNDERS BM. Targets and regulation of microRNA-652-3p in homoeostasis and disease. J Mol Med. 2021;99(6):755-769. [88] LIU G, WANG Y, PAN Y, et al. Hypertonicity induces mitochondrial extracellular vesicles (MEVs) that activate TNF-α and β-catenin signaling to promote adipocyte dedifferentiation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023; 14(1):333. [89] CREWE C, FUNCKE JB, LI S, et al. Extracellular vesicle-based interorgan transport of mitochondria from energetically stressed adipocytes. Cell Metab. 2021;33(9):1853-1868.e11. [90] CASTAÑO C, NOVIALS A, PÁRRIZAS M. An Overview of Inter-Tissue and Inter-Kingdom Communication Mediated by Extracellular Vesicles in the Regulation of Mammalian Metabolism. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(3):2071. [91] 郭项英,彭子富,何亦敏,等.MiRNA-122在运动改善非酒精性脂肪肝中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(2): 272-279. [92] 陈光文,蔡晓波,陆伦根.肝窦内皮细胞在非酒精性脂肪性肝炎中的作用[J].肝脏,2024,29(8):998-1001. [93] 邓群,包芸.微小RNA通过靶向PI3K/AKT信号通路改善2型糖尿病胰岛素抵抗的机制研究[J].临床医学进展,2023, 13(2):1886-1892. [94] FENG J, XING W, XIE L. Regulatory Roles of MicroRNAs in Diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(10):1729. [95] NIGI L, GRIECO GE, VENTRIGLIA G, et al. MicroRNAs as Regulators of Insulin Signaling: Research Updates and Potential Therapeutic Perspectives in Type 2 Diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(12):3705. [96] 李楠,史海燕,周越.运动介导microRNAs改善慢性炎症及骨骼肌胰岛素抵抗的研究进展[J].生命科学,2022, 34(3):324-331. [97] 杜杰.有氧运动通过抑制肝脏IKKβ/NF-κB信号通路改善胰岛素抵抗小鼠炎症反应[J].中国体育科技,2017,53(6):101-107. [98] 程永芳,林珍梅,张玲,等.NLRP3炎症小体在代谢性疾病中的研究进展[J].中国免疫学杂志,2024,40(2):445-448. [99] VANDERBOOM PM, DASARI S, RUEGSEGGER GN, et al. A size-exclusion-based approach for purifying extracellular vesicles from human plasma. Cell Rep Methods. 2021; 1(3):100055. [100] GARCIA-MARTIN R, BRANDAO BB, THOMOU T, et al. Tissue differences in the exosomal/small extracellular vesicle proteome and their potential as indicators of altered tissue metabolism. Cell Rep. 2022;38(3):110277. [101] MUELLER M, BREIL FA, LURMAN G, et al. Different molecular and structural adaptations with eccentric and conventional strength training in elderly men and women. Gerontology. 2011;57(6):528-538. [102] YAN C, CHEN J, LI M, et al. A decrease in hepatic microRNA-9 expression impairs gluconeogenesis by targeting FOXO1 in obese mice. Diabetologia. 2016;59(7): 1524-1532. [103] 韩思婕,潘翔,朱芊芊,等.茯苓多糖调节2型糖尿病模型大鼠肝脏糖异生的机制研究[J].中国药房,2022,33(13): 1581-1587. [104] HEISTON EM, BALLANTYNE A, LA SALVIA S, et al. Acute exercise decreases insulin-stimulated extracellular vesicles in conjunction with augmentation index in adults with obesity. J Physiol. 2023; 601(22):5033-5050. [105] BALKAU B, MHAMDI L, OPPERT JM, et al. Physical activity and insulin sensitivity: the RISC study. Diabetes. 2008;57(10):2613-2618. [106] WANG X, YI X, TANG D. Aerobic Exercise Improves Pulmonary Fibrosis by Improving Insulin Resistance and Inflammation in Obese Mice. Front Physiol. 2022;12:785117. [107] KIDO K, ATO S, YOKOKAWA T, et al. Resistance training recovers attenuated APPL1 expression and improves insulin-induced Akt signal activation in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2018;314(6):E564-E571. |
| [1] | 张庆彤, 陈乐琴, 刘昶, 陈昱廷, 郭睿武. 内源性大麻素系统调控运动动机的神经机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [2] | 李智斐, 韩 斌, 柳秋丽, 张展鸣, 韦浩凯, 左匡时, 张翼升. 基于动作捕捉技术分析神经根型颈椎病患者的颈椎运动特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2286-2293. |
| [3] | 刘金龙, 阿卜杜吾普尔•海比尔, 白 臻, 苏丹阳, 苗 鑫, 李 菲, 杨晓鹏. 不同非手术方法治疗青少年特发性脊柱侧凸效果的系统综述与网状Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2370-2379. |
| [4] | 陈豪杰, 王 黛, 沈 山. 种植体周围炎中的免疫炎症微环境机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2054-2062. |
| [5] | 王 峥, 程 吉, 于金龙, 刘文红, 王召红, 周鲁星. 水凝胶材料在脑卒中治疗中的应用进展与未来展望[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2081-2090. |
| [6] | 蔡子鸣, 于庆贺, 马鹏飞, 张 鑫, 周龙千, 张崇阳, 林文平. 血红素氧合酶1减轻脂多糖诱导髓核间充质干细胞的炎症反应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1624-1631. |
| [7] | 何家乐, 黄 茜, 董鸿斐, 陈 朗, 钟方宇, 李先慧. 脱细胞真皮基质联合脂肪干细胞外泌体促进烧伤创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1699-1710. |
| [8] | 夏林枫, 王 露, 龙乾发, 唐荣武, 罗浩东, 汤 轶, 钟 俊, 刘 阳. 人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体减轻脓毒症脑病小鼠血脑屏障损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1711-1719. |
| [9] | 崔连旭, 李昊旻, 许峻荣, 谭宝东, 陆大鸿, 彭四维, 王进辉. 脐带间充质干细胞条件培养基对小型猪创伤性颅脑损伤组织修复的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1730-1735. |
| [10] | 潘 冬, 杨加玲, 田 卫, 王东济, 朱 政, 马文超, 刘 娜, 付常喜. 抗阻运动激活衰老大鼠骨骼肌卫星细胞:脂联素受体1途径的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1736-1746. |
| [11] | 陈钰璘, 何莹莹, 胡 凯, 陈枝凡, 聂 莎, 蒙衍慧, 李闰珍, 张小朵, 李宇稀, 唐耀平. 瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡防治动脉粥样硬化的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1768-1781. |
| [12] | 周思瑞, 徐玉坤, 赵可伟. 白芷细胞外囊泡对抗黑色素的思路和方法[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1747-1754. |
| [13] | 曹 涌, 滕虹良, 邰鹏飞, 李骏达, 朱腾旗, 李兆进. 细胞因子和卫星细胞在肌肉再生中的相互作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1808-1817. |
| [14] | 黄嘉雯, 潘之怡, 薛文君, 廉源沛, 徐建达. 植物源性囊泡与恶性肿瘤治疗:跨物种交流并调节宿主细胞反应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1828-1838. |
| [15] | 潘鸿飞, 庄圳冰, 徐白云, 杨章阳, 林恺瑞, 詹冰晴, 蓝靖涵, 高 恒, 张南波, 林家煜. 不同浓度金诺芬抑制M1型巨噬细胞功能及修复糖尿病小鼠伤口的价值[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1390-1397. |
此综述系统梳理了运动诱导细胞外囊泡在胰岛素抵抗中的最新研究进展,为基于细胞外囊泡的运动疗法的开发提供理论支撑,揭示了细胞外囊泡介导的信号通路(胰岛素信号传导、炎症通路、线粒体功能调控等),填补运动干预与代谢调节之间的机制空白,明确细胞外囊泡在不同运动模式(有氧运动、力量训练、高强度间歇训练等)下对靶器官的特异性调控作用,为临床设计精准运动处方提供分子靶点,弥补现有药物治疗的不良反应与个体差异性缺陷,深入挖掘细胞外囊泡在炎症-代谢轴中的双向调节作用,有望开发以细胞外囊泡为载体的新型生物疗法,为疾病防治及运动疗法的研究与应用提供坚实的理论依据与新思路。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2024年9月至2025年3月进行检索。
1.1.2 文献检索时限 2012-01-01/ 2025-03-03。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、MedReading、Web of Science、中国知网、万方、维普数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“细胞外囊泡,运动,胰岛素抵抗,疾病”等,英文检索词为“EVs,physical exercise,exosomes,microvesicles,apoptotic bod,oncosomes,insulin resistance,disease”等。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 综述性论文及研究性论文。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
1.1.8 检索文献量 中文文献185篇,英文文献583篇。
1.2 入选标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 优先选择近5年发表的与研究主题相关的高影响因子杂志的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 内容相似、研究结果不完善、重复发表的文献。
1.3 数据的提取 共检索到文献768篇,排除内容相似、研究结果不完善、重复发表的文献660篇,共纳入107篇符合标准的文献进行综述,见图2。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
目前研究多基于细胞外囊泡混合群体分析,忽视外泌体、微囊泡等亚型的功能差异,对特定组织来源细胞外囊泡在胰岛素抵抗中的作用机制研究不足,研究多聚焦单一靶器官调控,代谢器官间通过细胞外囊泡形成的交互网络尚未明确,且运动与临床药物的协同效应机制缺乏探索,细胞外囊泡分离与表征的标准化体系也尚未建立,严重制约其临床转化应用。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 已有研究对细胞外囊泡在运动改善胰岛素抵抗中的机制进行综述,但目前尚未有不同运动模式下特异性调控细胞外囊泡,导致胰岛素抵抗改善效果差异化的相关应用系统性综述。文章阐述细胞外囊泡在胰岛素抵抗中的双向调控机制,病理状态下细胞外囊泡促进代谢紊乱的分子路径,运动干预如何通过重塑细胞外囊泡内含物组成,实现多器官代谢协同改善,构建完整的“病理-干预”机制链条,结合当前医学研究热点,为个性化运动处方设计提供了理论支撑,临床上涵盖基础机制解析、干预策略优化、技术创新、临床转化及产业应用等多个维度,构建了“运动-细胞外囊泡-代谢稳态”的系统性研究框架。
3.3 综述的局限性 ①目前细胞外囊泡介导的器官间动态通讯网络的描述不够详尽,缺乏对特定组织来源细胞外囊泡复杂调控机制的深入挖掘,难以全面揭示作用于胰岛素抵抗的病理全貌;②关于外泌体、微囊泡等亚型在粒径、表面标志物及内含物组成上的功能差异还是一片空白,需要更多的研究去填补;③在动物实验中证实运动诱导的细胞外囊泡改善胰岛素抵抗的潜力,但运动与临床药物的协同效应机制不明;④细胞外囊泡分离纯化的标准化方法及质量控制体系尚未建立,限制了其作为治疗剂或生物标志物的临床应用。
3.4 综述的重要意义 此综述突破传统单一器官研究框架,建立细胞外囊泡介导器官间通讯的胰岛素抵抗病理新模型。总结运动调控细胞外囊泡改善胰岛素抵抗的分子机制,为糖尿病、肥胖等疾病防治提供了跨学科研究靶点。鉴于目前研究的局限性,结合当前医学对炎症与代谢关联机制的热点研究,后续探索运动精准调控细胞外囊泡的策略,推动代谢性疾病管理从“经验式治疗”向“精准预防-个性化诊疗”模式转型,实现个性化运动处方与细胞外囊泡靶向治疗的有机结合,为代谢健康管理开辟全新路径。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
文题释义:
细胞外囊泡:是作为细胞间信息传递的关键递质,不同来源的细胞外囊泡在胰岛素抵抗中呈现截然相反的作用,脂肪源性细胞外囊泡可通过单靶点加重代谢紊乱,而运动诱导的细胞外囊泡则通过抗炎、促葡萄糖转运、增强线粒体功能等来改善胰岛素抵抗,是在代谢性疾病干预中具有前景的治疗靶点。
胰岛素抵抗:是指胰岛素靶组织对胰岛素介导的葡萄糖摄取和利用效能降低的病理生理状态,运动通过调控细胞外囊泡的分泌和内含物,形成多器官协同的代谢网络,可改善胰岛素抵抗,不同细胞分泌的细胞外囊泡携带特定信号分子影响胰岛素信号通路、炎症反应等,参与胰岛素抵抗的发生发展过程。
#br#
文章系统梳理了细胞外囊泡在运动改善胰岛素抵抗中的核心机制,首次整合多运动模式、多靶器官及多层次分子通路,填补了现有综述在“运动类型特异性”和“器官间交互作用”的空白,研究提出的细胞外囊泡双向调控理论及运动诱导细胞外囊泡的精准干预策略,为后续临床转化(如细胞外囊泡作为药物递送载体、运动效果评估生物标志物)奠定了理论基础,助推从“经验性运动处方”向“机制驱动型精准干预”的范式转变。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||