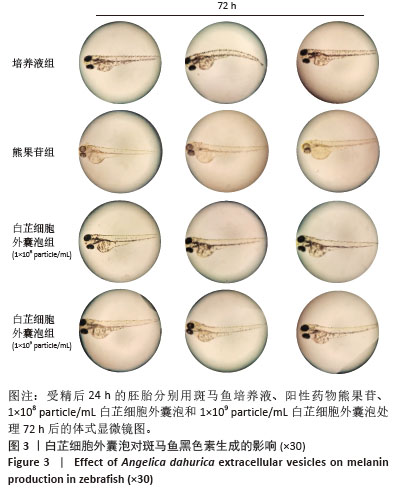
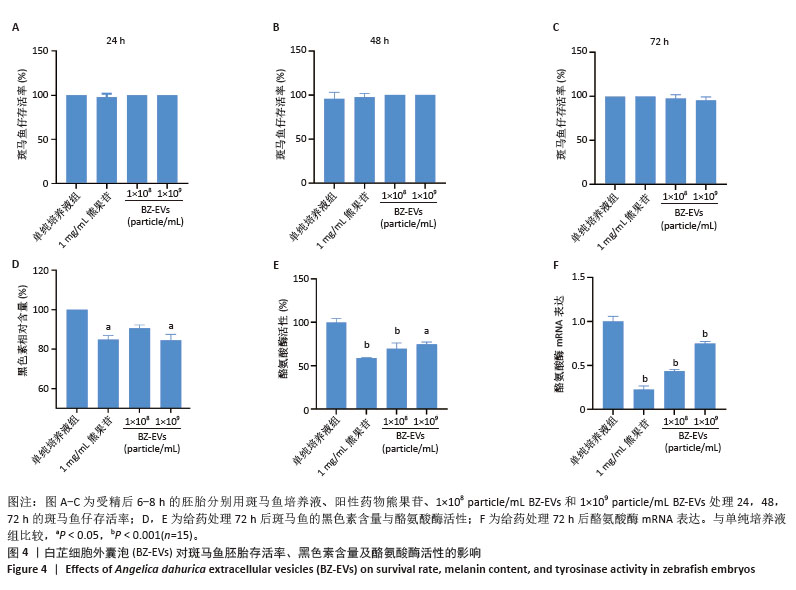
[1] LI Y, XIAO Q, TANG J, et al. Extracellular Vesicles: Emerging Therapeutics in Cutaneous Lesions. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:6183-6202.
[2] HUMPHREY S, MANSON BROWN S, CROSS SJ, et al. Defining Skin Quality: Clinical Relevance, Terminology, and Assessment. Dermatol Surg. 2021;47(7):974-981.
[3] BELLU E, MEDICI S, CORADDUZZA D, et al. Nanomaterials in Skin Regeneration and Rejuvenation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(13):7095.
[4] 何毅帆,龙芸鸾,李征,等.天然植物美白成分作用机理的研究进展[J].日用化学品科学,2022,45(10):37-43.
[5] PROSPÉRI MT, GIORDANO C, GOMEZ-DURO M, et al. Extracellular vesicles released by keratinocytes regulate melanosome maturation, melanocyte dendricity, and pigment transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024;121(16):e2321323121.
[6] JIANG X, YANG C, WANG Z, et al. Loss-of-function variants in GLMN are associated with generalized skin hyperpigmentation with or without glomuvenous malformation. Br J Dermatol. 2024;191(1):107-116.
[7] SAMPEDRO-GUERRERO J, VIVES-PERIS V, GOMEZ-CADENAS A, et al. Encapsulation Reduces the Deleterious Effects of Salicylic Acid Treatments on Root Growth and Gravitropic Response. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(22):14019.
[8] CHENG Y, ZHANG L, YOU Y. The effects of supramolecular nicotinamide combined with supramolecular salicylic acid on chloasma. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2024;23(2):681-686.
[9] SEARLE T, AL-NIAIMI F, ALI FR. The top 10 cosmeceuticals for facial hyperpigmentation. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33(6):e14095.
[10] PHILIPP-DORMSTON WG. Melasma: A Step-by-Step Approach Towards a Multimodal Combination Therapy. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024;17:1203-1216.
[11] 郭聪颖.富硒绿豆发酵液面膜的研发和富硒黑茶的活性初探[D].上海:上海师范大学,2020.
[12] 李薄薄,马洁,朱士强,等.抑制黑色素合成信号通路的植物美白原料的研究与开发[J].日用化学品科学,2023,46(3):21-28.
[13] 马畅,李妍.白芷、白芍水和乙醇提取物对酪氨酸酶的抑制效应[J].香料香精化妆品,2023(2):54-58.
[14] 鹿发展,刘平平,刘娟.白芨花提取物的美白、抗氧化和抗衰老功效研究[J].云南化工,2024,51(10):100-104.
[15] 付媛媛,顾玲,何艳,等.洋甘菊提取物在化妆品中的应用研究进展[J].香料香精化妆品,2023(2):132-137.
[16] ALBUQUERQUE PBS, DE OLIVEIRA WF, DOS SANTOS SILVA PM, et al. Skincare application of medicinal plant polysaccharides - A review. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;277:118824.
[17] NG SY, EH SUK VR, GEW LT. Plant polyphenols as green sunscreen ingredients: A systematic review. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022;21(11): 5409-5444.
[18] POLERÀ N, BADOLATO M, PERRI F, et al. Quercetin and its Natural Sources in Wound Healing Management. Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(31): 5825-5848.
[19] LAN J, SUN L, XU F, et al. M2 Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Promote Cell Migration and Invasion in Colon Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019;79(1): 146-158.
[20] CHUNG CC, CHAN L, CHEN JH, et al. Plasma extracellular vesicles tau and β-amyloid as biomarkers of cognitive dysfunction of Parkinson’s disease. FASEB J. 2021;35(10):e21895.
[21] KESHTKAR S, AZARPIRA N, GHAHREMANI MH. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: novel frontiers in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):63.
[22] 鲍少杰.虾青素对肠道炎症的影响及西兰花胞外囊泡载虾青素体系构建[D].扬州:扬州大学,2021.
[23] LI C, SONG Q, YIN X, et al. Preparation, Characterization, and In Vitro Anticancer Activity Evaluation of Broccoli-Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Coated Astaxanthin Nanoparticles. Molecules. 2022;27(12):3955.
[24] CONG L, MA J, ZHANG Y, et al. Effect of anti-skin disorders of ginsenosides- A Systematic Review. J Ginseng Res. 2023;47(5):605-614.
[25] GABRIELLI M, BATTISTA N, RIGANTI L, et al. Active endocannabinoids are secreted on extracellular membrane vesicles. EMBO Rep. 2015; 16(2):213-220.
[26] COSSETTI C, IRACI N, MERCER TR, et al. Extracellular vesicles from neural stem cells transfer IFN-γ via Ifngr1 to activate Stat1 signaling in target cells. Mol Cell. 2014;56(2):193-204.
[27] PARK JJ, HWANG SJ, KANG YS, et al. Synthesis of arbutin-gold nanoparticle complexes and their enhanced performance for whitening. Arch Pharm Res. 2019;42(11):977-989.
[28] DING Y, JIANG Y, IM ST, et al. Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol inhibits melanogenesis via protein kinase A/cAMP response element-binding protein and extracellular signal-regulated kinase-mediated microphthalmia-associated transcription factor downregulation in α-melanocyte stimulating hormone-stimulated B16F10 melanoma cells and zebrafish. Cell Biochem Funct. 2021;39(4):546-554.
[29] SHI G, FENG Y, TONISSEN KF. Development of a human tyrosinase activity inhibition assay using human melanoma cell lysate. Biotechniques. 2024;76(11):547-551.
[30] 朱翠翠.调节黑色素生成的主要信号通路[J].日用化学品科学, 2023,46(7):61-70.
[31] WANG Z, ZHANG D, SHUI M, et al. Investigation of the whitening activity of ginsenosides from Panax notoginseng and optimization of the dosage form. J Ginseng Res. 2024;48(6):543-551.
[32] SANJAYA SS, PARK MH, KARUNARATHNE WAHM, et al. Inhibition of α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-induced melanogenesis and molecular mechanisms by polyphenol-enriched fraction of Tagetes erecta L. flower. Phytomedicine. 2024;126:155442.
[33] CHO J, JUNG H, KANG DY, et al. The Skin-Whitening and Antioxidant Effects of Protocatechuic Acid (PCA) Derivatives in Melanoma and Fibroblast Cell Lines. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023;45(3):2157-2169.
[34] TUNG XY, YIP JQ, GEW LT. Searching for Natural Plants with Antimelanogenesis and Antityrosinase Properties for Cosmeceutical or Nutricosmetics Applications: A Systematic Review. ACS Omega. 2023;8(37):33115-33201.
[35] CAI CS, HE GJ, XU FW. Advances in the Applications of Extracellular Vesicle for the Treatment of Skin Photoaging: A Comprehensive Review. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:6411-6423.
[36] JANG B, CHUNG H, JUNG H, et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Korean Codium fragile and Sargassum fusiforme Negatively Regulate Melanin Synthesis. Mol Cells. 2021;44(10):736-745.
[37] CHAMBERS ES, VUKMANOVIC-STEJIC M. Skin barrier immunity and ageing. Immunology. 2020;160(2):116-125.
[38] ZHAO B, LIN H, JIANG X, et al. Exosome-like nanoparticles derived from fruits, vegetables, and herbs: innovative strategies of therapeutic and drug delivery. Theranostics. 2024;14(12):4598-4621.
[39] WOITH E, GUERRIERO G, HAUSMAN JF, et al. Plant Extracellular Vesicles and Nanovesicles: Focus on Secondary Metabolites, Proteins and Lipids with Perspectives on Their Potential and Sources. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(7):3719.
[40] NATANIA F, IRIAWATI I, AYUNINGTYAS FD,et al. Potential of Plant-derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles from Physalis peruviana Fruit for Human Dermal Fibroblast Regeneration and Remodeling. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2025;13(2):358-371.
|