中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (17): 3713-3723.doi: 10.12307/2025.646
• 组织构建相关数据分析 Date analysis of organization construction • 上一篇 下一篇
海洋中药治疗骨质疏松的用药规律及作用机制
赖 越1,林 轩2,徐 淼3,刘 欢4,沈剑粦5,黄文华1,6
- 1广东医科大学第一临床医学院,广东省湛江市 524023;2莆田学院环境与生物工程学院,福建省莆田市 351100;3福建医科大学基础医学院,福建省福州市 350100;4西南医科大学附属中医医院骨科,四川省泸州市 646000;5莆田学院附属医院中心实验室,福建省莆田市 351100;6南方医科大学基础医学院人体解剖学国家重点学科,广东省数字医学与生物力学重点实验室,广东省医学3D打印应用转化工程技术研究中心,广东省广州市 510515
Medication pattern and mechanism of marine traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of osteoporosis
Lai Yue1, Lin Xuan2, Xu Miao3, Liu Huan4, Shen Jianlin5, Huang Wenhua1, 6
- 1The First Clinical Medical School, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524023, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Environmental and Biological Engineering, Putian University, Putian 351100, Fujian Province, China; 3School of Basic Medicine, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350100, Fujian Province, China; 4Department of Orthopaedics, The Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 5Central Laboratory, the Affiliated Hospital of Putian University, Putian 351100, Fujian Province, China; 6Guangdong Engineering Research Center for Translation of Medical 3D Printing Application, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Digital Medicine and Biomechanics, National Key Discipline of Human Anatomy, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
分子对接:是通过受体的特征以及受体和药物分子之间的相互作用方式来进行药物设计的方法,主要研究分子间(如配体和受体)相互作用并预测其结合模式和亲合力的一种理论模拟方法。近年来,分子对接方法已成为计算机辅助药物研究领域的一项重要技术。
Rap1/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路:Rap1/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路中的细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)分支对骨发育和维持至关重要,这一途径的中断可能影响骨代谢进而导致骨质疏松。抑制Rap1可导致破骨细胞活性增加。成骨细胞中Rap1/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路被激活以实现成骨细胞的增殖分化。
背景:海洋中药为治疗骨质疏松提供了一种潜在有效且不易产生不良反应的方法。
目的:应用数据挖掘和网络药理学方法分析并探讨中医临床治疗骨质疏松的用药规律及作用机制。
方法:采用数据挖掘和网络药理学方法,对国家知识产权局批准的治疗骨质疏松的海洋中药专利处方进行用药模式和作用机制研究,并特别关注这些处方中的核心中药成分,利用超高效液相色谱串联质谱对牡蛎-续断-淫羊藿组成的复方药组核心成分进行全面的鉴定分析。
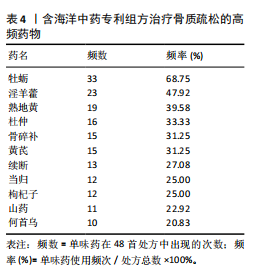
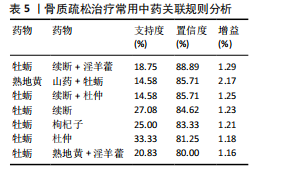
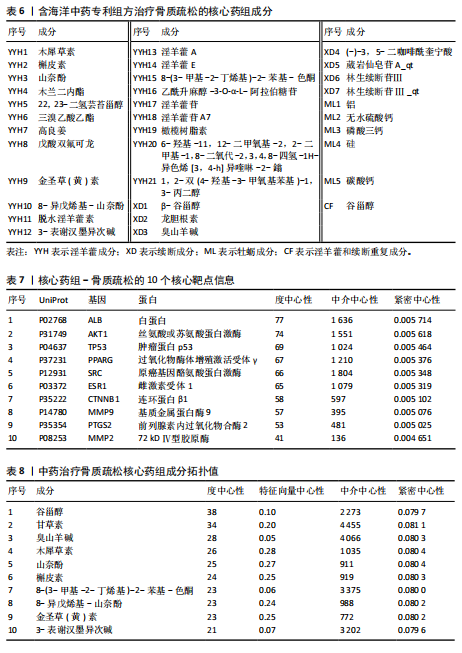
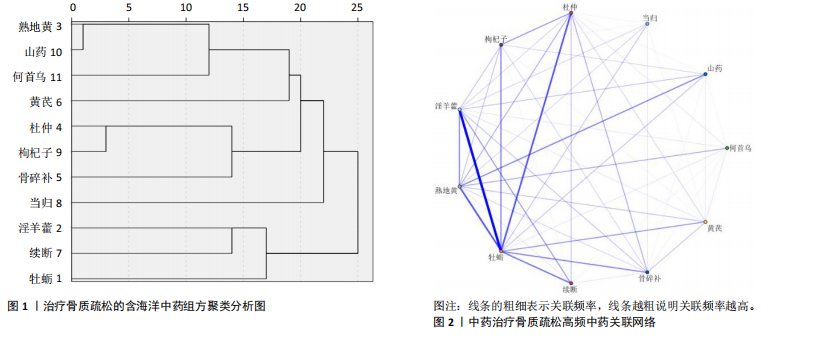
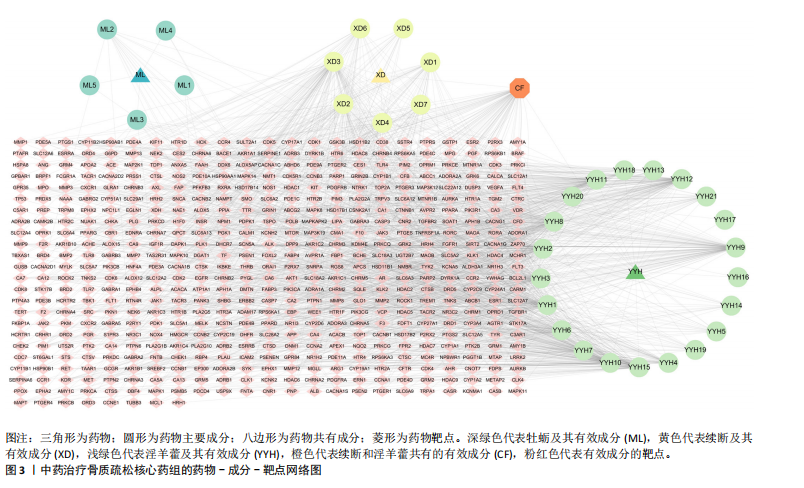
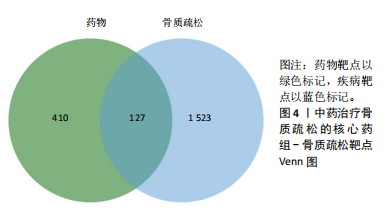
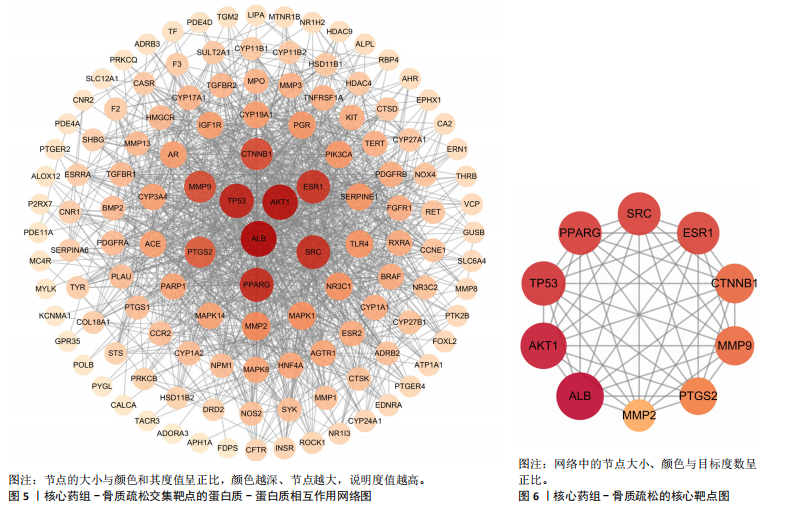
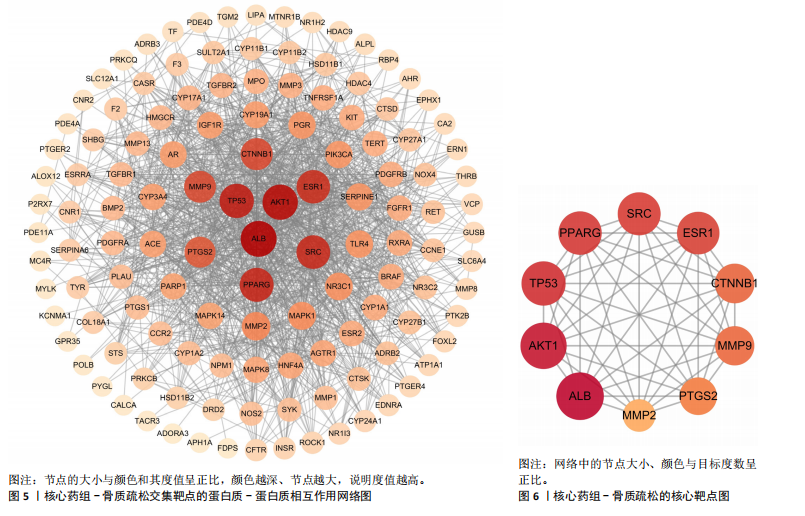
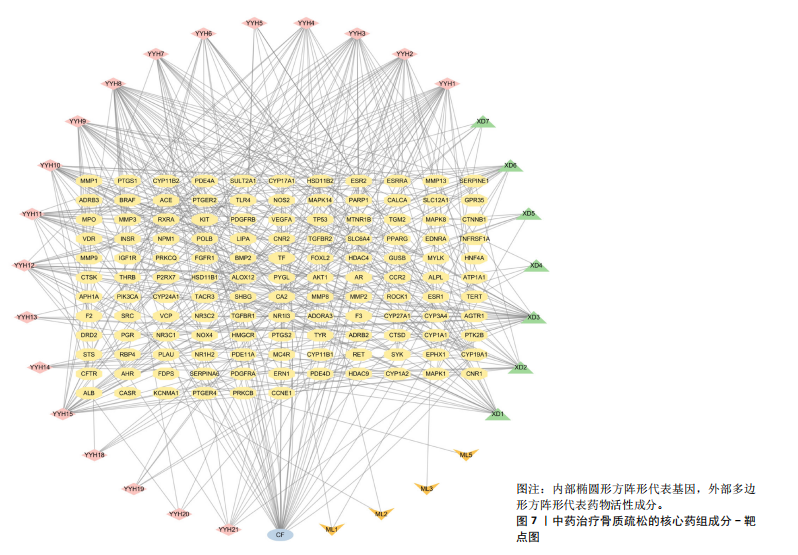
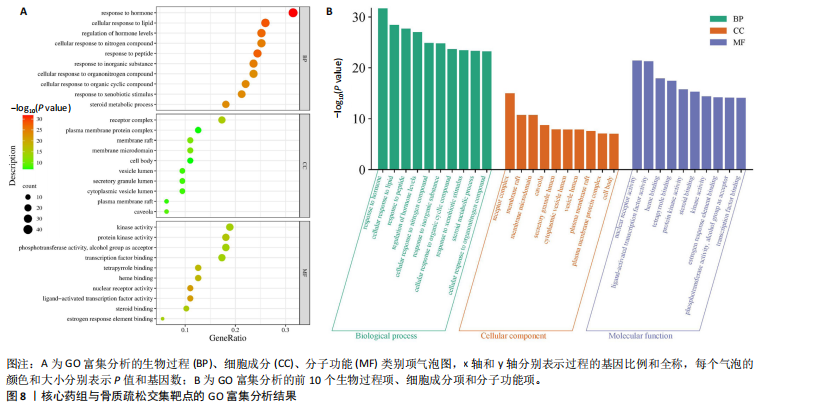
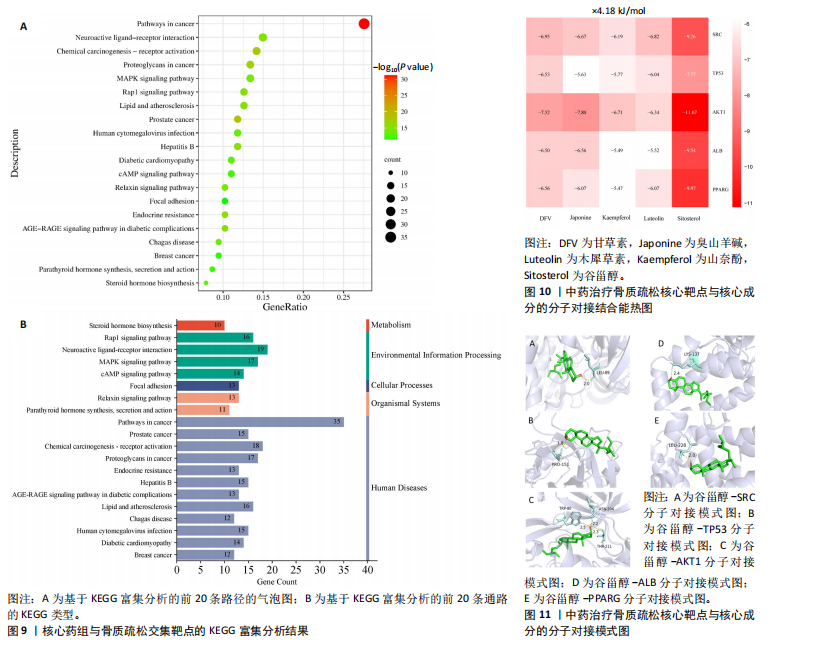
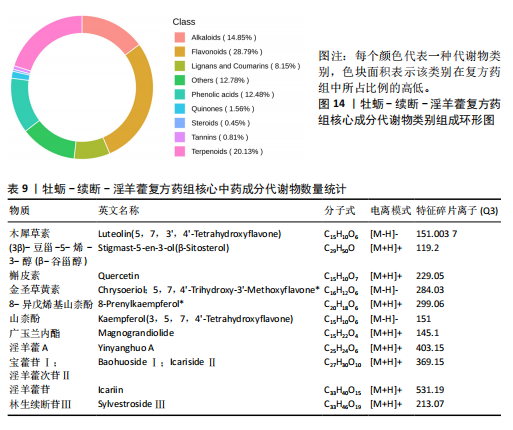
结果与结论:①从国家知识产权局(SIPO)网站建立到2024-04-01,检索发现381项骨质疏松治疗的授权专利,共鉴定出48首含有海洋中药的中成药处方,这些处方包含183味中药,其中13种海洋中药用药频次共574次,单首专利组方中用药味数2-41种不等;②牡蛎是最常用的海洋中药,续断、淫羊藿、地黄、杜仲是最常用的非海洋中药;关联规则分析确定了牡蛎、续断和淫羊藿为核心药物群;网络药理学分析显示该核心药组治疗骨质疏松的核心靶点包括ALB、AKT1、TP53、PPARG和SRC;核心药组发挥疗效的核心成分为谷甾醇、甘草素、臭山羊碱、木犀草素、山奈酚;③GO与KEGG富集分析显示,Rap1/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路在核心药物组的骨质疏松作用机制中起着重要作用;④分子对接结果显示核心成分与核心靶点之间存在良好的相互作用;⑤超高效液相色谱串联质谱检测复方药组核心成分为木犀草素、谷甾醇、山奈酚等,与网络药理学鉴定的药物成分相符合;对复方药组成分进行定量分析得出,黄酮类化合物、萜类化合物以及生物碱这3类物质在药物成分占比中较大。
https://orcid.org/0009-0007-5888-0150(赖越)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: