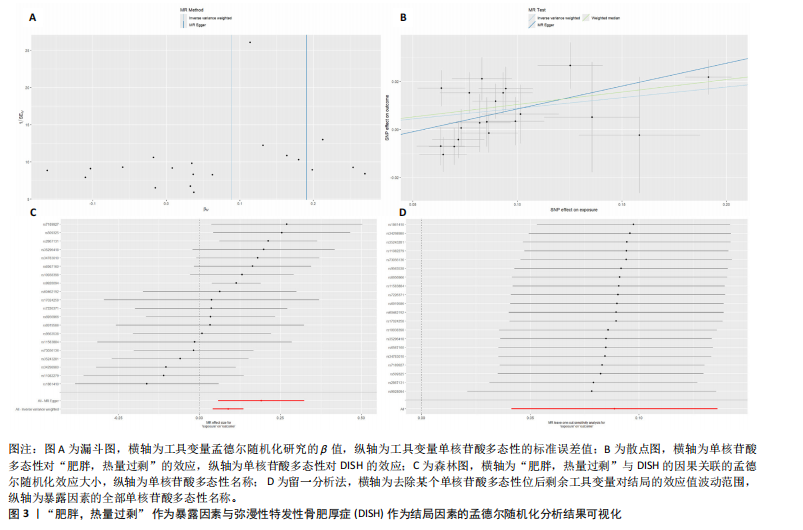
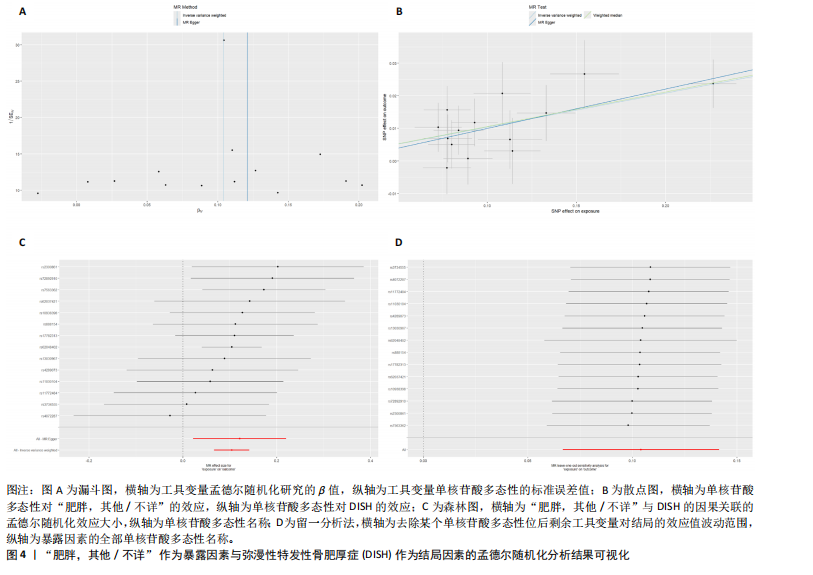
[1] MADER R, VERLAAN JJ, BUSKILA D. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: clinical features and pathogenic mechanisms. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013;9(12):741-750.
[2] FORESTIER J, ROTES-QUEROL J. Senile ankylosing hyperostosis of the spine. Ann Rheum Dis. 1950;9(4):321-330.
[3] RESNICK D, NIWAYAMA G. Radiographic and pathologic features of spinal involvement in diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). Radiology. 1976;119(3):559-568.
[4] TERZI R. Extraskeletal symptoms and comorbidities of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. World J Clin Cases. 2014; 2(9):422-425.
[5] MADER R, NOVOFESTOVSKI I, ADAWI M, et al. Metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk in patients with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2009;38(5):361-365.
[6] OKADA E, ISHIHARA S, AZUMA K, et al. Metabolic Syndrome is a Predisposing Factor for Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis. Neurospine. 2021;18(1):109-116.
[7] SETHI A, RUBY JG, VERAS MA, et al. Genetics implicates overactive osteogenesis in the development of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Nat Commun. 2023; 14(1):2644.
[8] WEIR CB, JAN A. BMI Classification Percentile And Cut Off Points. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2024.
[9] MOHAMMED MS, SENDRA S, LLORET J, et al. Systems and WBANs for Controlling Obesity. J Healthc Eng. 2018;2018:1564748.
[10] SAKLAYEN MG. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2018;20(2):12.
[11] COACCIOLI S, FATATI G, DI CATO L, et al. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in diabetes mellitus, impaired glucose tolerance and obesity. Panminerva Med. 2000;42(4):247-251.
[12] 刘小康,郭海龙,鲍丰,等.弥漫性特发性骨肥厚症的危险因素分析[J].临床骨科杂志,2024,27(1):20-24.
[13] EMDIN CA, KHERA AV, KATHIRESAN S. Mendelian Randomization. JAMA. 2017; 318(19):1925-1926.
[14] KURKI MI, KARJALAINEN J, PALTA P, et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature. 2023;613(7944):508-518.
[15] DAVIES NM, HOLMES MV, DAVEY SMITH G. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: a guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ. 2018;362:k601.
[16] PRITCHARD JK, PRZEWORSKI M. Linkage disequilibrium in humans: models and data. Am J Hum Genet. 2001;69(1):1-14.
[17] PARK JH, WACHOLDER S, GAIL MH, et al. Estimation of effect size distribution from genome-wide association studies and implications for future discoveries. Nat Genet. 2010;42(7):570-575.
[18] BRION MJ, SHAKHBAZOV K, VISSCHER PM. Calculating statistical power in Mendelian randomization studies. Int J Epidemiol. 2013;42(5):1497-1501.
[19] BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur J Epidemiol. 2017;32(5):377-389.
[20] BOWDEN J, DEL GRECO MF, MINELLI C, et al. A framework for the investigation of pleiotropy in two-sample summary data Mendelian randomization. Stat Med. 2017;36(11):1783-1802.
[21] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512-525.
[22] VERBANCK M, CHEN CY, NEALE B, et al. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet. 2018;50(5):693-698.
[23] HARTWIG FP, DAVEY SMITH G, BOWDEN J. Robust inference in summary data Mendelian randomization via the zero modal pleiotropy assumption. Int J Epidemiol. 2017;46(6):1985-1998.
[24] BRIKMAN S, LUBANI Y, MADER R, et al. High prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) among obese young patients - A retrospective observational study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2024;65:152356.
[25] HARLIANTO NI, WESTERINK J, FOPPEN W, et al. Visceral Adipose Tissue and Different Measures of Adiposity in Different Severities of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis. J Pers Med. 2021;11(7):663.
[26] CHAPUT CD, SIDDIQUI M, RAHM MD. Obesity and calcification of the ligaments of the spine: a comprehensive CT analysis of the entire spine in a random trauma population. Spine J. 2019;19(8):1346-1353.
[27] FURUKAWA S, FUJITA T, SHIMABUKURO M, et al. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2004;114(12):1752-1761.
[28] DAN LANTSMAN C, HERMAN A, VERLAAN JJ, et al. Abdominal fat distribution in diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis and ankylosing spondylitis patients compared to controls. Clin Radiol. 2018;73(10):910.e15-910.e20.
[29] AHMED O, RAMACHANDRAN K, PATEL Y, et al. Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis Prevalence, Characteristics, and Associated Comorbidities: A Cross-Sectional Study of 1815 Whole Spine CT Scans. Global Spine J. 2024;14(4):1201-1209.
[30] HIROTA R, TERAMOTO A, YOSHIMOTO M, et al. Osteophyte Bridge Formation Correlates with Vascular Calcification and Cardiovascular Disease in Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis. J Clin Med. 2023;12(16):5412.
[31] ZINCARELLI C, IERVOLINO S, DI MINNO MN, et al. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis prevalence in subjects with severe atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012;64(11):1765-1769.
[32] OUDKERK SF, MOHAMED HOESEIN FAA, PTHM MALI W, et al. Subjects with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis have an increased burden of coronary artery disease: An evaluation in the COPDGene cohort. Atherosclerosis. 2019;287:24-29.
[33] ORDEN AO, DAVID JM, DÍAZ RP, et al. Association of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis and aortic valve sclerosis. Medicina (B Aires). 2014;74(3):205-209.
[34] JULKUNEN H, AROMAA A, KNEKT P. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) and spondylosis deformans as predictors of cardiovascular diseases and cancer. Scand J Rheumatol. 1981;10(3):241-248.
[35] MADER R, LAVI I. Diabetes mellitus and hypertension as risk factors for early diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(6):825-828.
[36] DENKO CW, MALEMUD CJ. Body mass index and blood glucose: correlations with serum insulin, growth hormone, and insulin-like growth factor-1 levels in patients with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). Rheumatol Int. 2006;26(4):292-297.
[37] FASSIO A, ADAMI G, IDOLAZZI L, et al. Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) in Type 2 Diabetes: A New Imaging Possibility and a New Biomarker. Calcif Tissue Int. 2021;108(2):231-239.
[38] PARIENTE E, PINI SF, OLMOS JM, et al. Early stages of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) and chronic inflammation: the Camargo Cohort Study. Clin Rheumatol. 2023;42(7):1931-1942.
[39] DĄBROWSKI M, KUBASZEWSKI Ł. Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis of Cervical Spine with Dysphagia-Molecular and Clinical Aspects. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(8):4255.
[40] MADER R, PAPPONE N, BARALIAKOS X, et al. Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) and a Possible Inflammatory Component. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021;23(1):6.
[41] MADER R, NOVOFASTOVSKI I, SCHWARTZ N, et al. Serum adiponectin levels in patients with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37(10):2839-2845. |