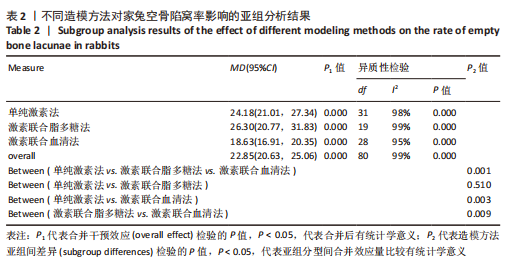
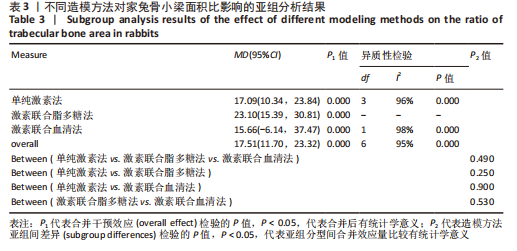
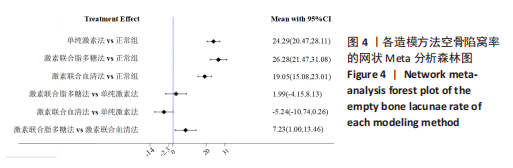
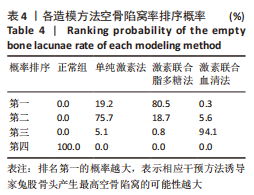
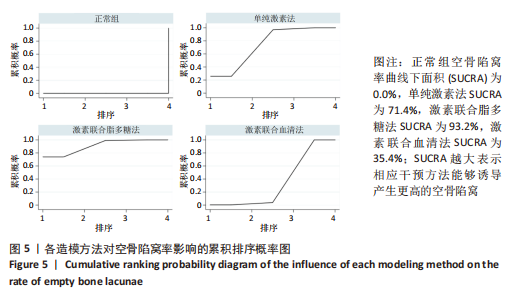
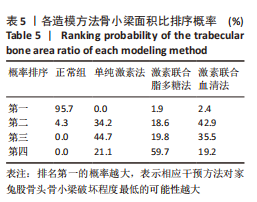
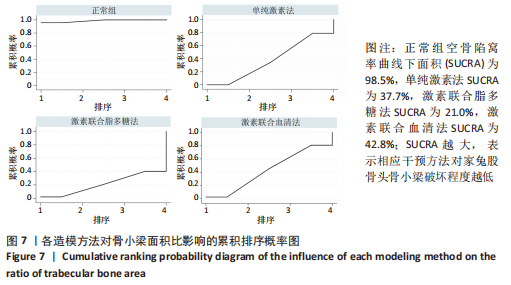
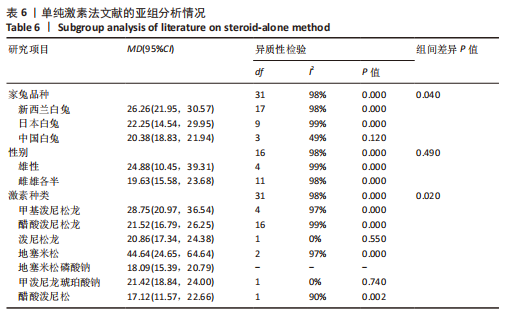
[1] CHAO PC, CUI MY, LI XA, et al. Correlation between miR-1207-5p expression with steroid-induced necrosis of femoral head and VEGF expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(7):2710-2718.
[2] 章建华, 张成龙, 尹华. 激素类型对大鼠股骨头坏死模型的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2014,29(12):3969-3973.
[3] 陈匡阳, 马彬, 王亚楠, 等. SYRCLE动物实验偏倚风险评估工具简介[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2014,14(10):1281-1285.
[4] 陈杰, 张堃, 孔令俊, 等. 三七总皂苷通过调控Wnt/β-catenin通路减轻家兔股骨头坏死[J]. 中药药理与临床,2019, 35(4):95-99.
[5] 龚梅芳,徐传毅,唐志芳,等. 活血健骨汤对兔缺血性股骨头坏死的血液流变性和血脂的作用[J]. 微循环学杂志, 1999(2):31-33.
[6] 李宝林, 胡勇. 川芎嗪对激素性股骨头缺血坏死模型兔血管新生因子的影响及促成骨作用的研究[J]. 中国生化药物杂志, 2014,34(6):69-70.
[7] 李玉彬, 谢利民, 李理, 等. 健脾补肾方对家兔激素性股骨头坏死模型脂质代谢的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2010, 16(2):90-93.
[8] 刘伟, 赵劲民, 苏伟, 等. 低剂量激素诱导股骨头缺血性坏死模型的建立[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(43):8050-8054.
[9] 欧阳铭, 王涛, 张少春. 普伐他汀对激素性股骨头坏死兔脂联素表达的影响[J]. 广东医学,2011,32(19):2517-2519.
[10] 孙亮, 刘万林, 娜日松, 等. 3-甲基腺嘌呤调控自噬基因Beclin1可降低模型兔激素性股骨头缺血坏死的发生与发展[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(15):2391-2396.
[11] 瓦庆德, 张天宏, 刘毅. 丹参骨髓腔内注射预防激素性股骨头坏死的可能性[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(50): 9884-9888.
[12] 王萧枫, 吴银生, 王利明, 等. 激素法与液氮法在兔股骨头坏死造模中的应用比较研究[J]. 中国现代医生,2012,50(25):18-20.
[13] 肖鹏, 江蓉星, 贾敏. 活血通络汤治疗激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的空骨陷窝率及病理形态学观察[J]. 四川中医,2015, 33(4):51-53.
[14] 徐国华, 田伟明, 柴仪. 骨复活汤对兔激素性股骨头坏死血浆ET-1、NO的影响[J]. 河北中医药学报,2008,23(4):3-4.
[15] 许杰, 刘飞, 王新民, 等. 加味肾气丸联合髓芯减压术、人牙髓基质干细胞移植对兔早期激素性股骨头坏死的治疗作用研究[J]. 河北中医,2021,43(10):1674-1680.
[16] 张弛, 杨志伟, 段小英. 活血通络法治疗激素性股骨头坏死兔胰岛素样生长因子1的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(52): 9787-9791.
[17] 蔡万翔, 江蓉星, 王敏, 等. 活血通络汤在家兔激素性股骨头缺血性坏死模型中对Notch1、DLL3和HERP1的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2018,33(1):300-303.
[18] 瓦庆德, 张天宏, 李振威, 等. 丹参骨髓腔内注射对兔股骨头坏死破骨细胞数量的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2010, 16(18): 176-178.
[19] 郑曙光, 戎志斌, 施文甫, 等. 苗医熏蒸验方对兔早期肾上腺皮质激素性股骨头坏死的预防[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2011,17(13): 202-204.
[20] 周李学, 李志敏, 段璋, 等. 补肾活血汤对激素性股骨头缺血坏死骨材料力学的影响[J]. 福建中医药,2016,47(1):26-29.
[21] 陈昆涛, 何健垣, 刘建民, 等. 兔超早期激素性股骨头坏死MR弥散成像与血管内皮生长因子表达的关系[J]. 广东医学,2013,34(23): 3561-3563.
[22] 陈冠儒, 王萧枫, 王利明, 等. 兔激素性股骨头坏死造模中的致死因素与干预分析[J]. 浙江中西医结合杂志,2012,22(5): 342-344.
[23] 陈光友, 邓友章, 江中潮, 等. 金骨片对激素性股骨头坏死BMP-2表达的影响[J]. 江西中医学院学报,2008,20(6):58-59.
[24] 陈兴灿, 俞锦清, 郑筱祥. 直接穿刺介入治疗激素性股骨头坏死的实验研究[J]. 介入放射学杂志,2003(6):442-444.
[25] 冯志尉, 邓云平, 赵慧, 等. shRNA干扰PPARγ基因表达预防兔激素性股骨头坏死的研究[J]. 成都医学院学报,2017,12(2):127-132.
[26] 马海龙, 赵振群, 刘万林, 等. 自噬基因微管相关蛋白1轻链3参与模型兔激素性股骨头缺血坏死的发生与发展[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(32):5167-5172.
[27] 齐振熙, 陈磊. 活血化瘀法对激素性股骨头缺血坏死血液流变学的影响[J]. 福建中医学院学报,2006,16(6):22-24.
[28] 齐振熙, 万甜, 洪昆达, 等. 羟基红花黄色素A对激素性股骨头缺血坏死兔股骨头组织JNK1表达的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2014,29(12):3962-3965.
[29] 王新民, 刘飞, 许杰, 等. 髓芯减压联合牙髓干细胞治疗兔早期激素性股骨头坏死[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(7): 1074-1079.
[30] 叶建红,李峻辉,宁亚功,等. 兔股骨头缺血性坏死模型的建立与评价[J]. 昆明医学院学报,2004,25(4):33-35.
[31] 马源,张善锋,刘鸣,等. 小干扰RNA预防兔激素性股骨头坏死的组织病理学观察[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2016,33(7): 1747-1749.
[32] 李峻辉,宁亚功,贺斌,等. 介入等综合治疗激素性股骨头坏死的实验研究[J]. 西南国防医药,2004,14(2):127-130.
[33] 李峻辉,宁亚功,彭仲杰,等. 络泰治疗激素性股骨头坏死的实验研究[J]. 中草药,2002(6):58-60.
[34] 王卫东,廖文胜,王义生. 辛伐他汀预防激素性股骨头坏死的实验研究[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版),2004,39(3):473-475.
[35] 张永乐, 王义生, 张世清, 等. 大剂量甲强龙对兔髋关节周围骨组织BMP-2表达的影响[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2012,47(3):358-361.
[36] 周强,李起,鸿杨柳,等. 大剂量糖皮质激素诱导兔股骨头坏死的研究[J]. 第三军医大学学报,2000,22(3):249-252.
[37] 朱磊, 周正新, 刘安平, 等. 辨证使用骨蚀宁胶囊Ⅰ号、Ⅱ号对激素性股骨头坏死家兔模型CD34、CYR61、CTGF表达影响的实验研究[J]. 中医药临床杂志, 2020,32(8):1482-1486.
[38] 朱磊, 周正新, 刘安平, 等. 辨证运用骨蚀宁Ⅰ号、Ⅱ号对激素性股骨头坏死兔股骨头血管内皮生长因子表达的影响[J]. 安徽中医药大学学报,2017,36(6):85-89.
[39] 纪志华, 贾丙申, 于鹏, 等. TIMP2在激素性股骨头坏死中作用的实验研究[J]. 海南医学,2016,27(18):2925-2927.
[40] XI H, TAO W, JIAN Z, et al. Levodopa attenuates cellular apoptosis in steroid-associated necrosis of the femoral head. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13(1):69-74.
[41] 段卫峰, 刘骏逸, 杜志军, 等. 补肾祛瘀法对激素诱导股骨头坏死兔血脂及凝血指标的影响[J]. 西部中医药,2019,32(11): 26-31.
[42] 张翔, 董晓俊, 吴泱, 等. 早期激素性股骨头缺血性坏死动物模型的建立研究[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2018,26(2):67-71.
[43] 李彪, 刘劲松, 李克涛, 等. 激素性股骨头缺血性坏死兔模型的构建[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(41): 7678-7682.
[44] 马焕芝, 曾炳芳, 李晓林, 等. 甲基强的松龙联合内毒素诱导兔股骨头缺血性坏死的实验研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2008,22(3):265-270.
[45] 田力, 梁晓鹏, 田晓晔, 等. 地塞米松联合脂多糖诱导股骨头坏死模型的构建[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(35):6571-6574.
[46] 张波, 韦冰丹, 甘坤宁, 等. 富血小板血浆联合骨髓间充质干细胞对兔股骨头坏死BMP-2/Smads通路的影响[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(2):131-134.
[47] 杜刚, 李林, 张波, 等. 富血小板血浆联合骨髓间充质干细胞对兔股骨头坏死的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2013, 19(16):213-216.
[48] 石包圣, 闫国珍, 李爱华, 等. 早期激素性股骨头坏死动物模型制备的实验研究[J]. 包头医学院学报,2021,37(5):109-112.
[49] 田润, 李越, 万世超, 等. 坏死状凋亡通路抑制剂在兔早期激素性股骨头坏死中的作用[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2017,11(2):150-156.
[50] 赵振群, 刘万林, 龚瑜林, 等. 骨髓造血细胞DNA氧化损伤与骨细胞凋亡在早期激素性股骨头坏死中的表现[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(11):1652-1657.
[51] 李瑞琦, 张国平, 李宜炯, 等. 提高激素性股骨头坏死模型成活率的方法[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(50):8729-8734.
[52] 李瑞琦, 张国平, 李宜炯, 等. 激素性股骨头坏死模型:不同构建技术分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(37):6676-6681.
[53] 赵小娟, 阿日嘎太, 臧苑彤, 等. 冲击波联合蒙医温针治疗家兔股骨头坏死的相关机理研究[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2019,19(93):302-314.
[54] 李春峰, 孙志涛, 周正新. 不同剂量骨蚀宁胶囊对兔激素性股骨头坏死微循环的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(20): 3723-3729.
[55] 李光庭, 赵铖, 刘秀华, 等. 激素性股骨头缺血性坏死应用云克综合疗法的实验研究[J]. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2015,9(11):2174-2178.
[56] 陈镇秋, 何伟, 魏秋实, 等. 祛痰逐瘀法对激素性股骨头坏死兔骨髓基质干细胞生物活性的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2016,31(7):2732-2735.
[57] 周金良, 阮志磊. 骨碎补总黄酮对激素性股骨头坏死病理学影响的实验研究[J]. 健康前沿,2016,5(23):147.
[58] 唐立明,樊粤光,张庆文,等. 药物介入治疗激素性股骨头坏死的实验研究[J]. 中医研究,2000(1):25-27.
[59] 宋红梅, 吴斌, 魏迎辰, 等. 温阳补肾方对激素性股骨头坏死模型兔股骨头形态学的影响[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2014,22(3):1-3.
[60] 孟东方, 李慧英, 王韬, 等. 补骨脂干预兔激素性股骨头坏死空骨陷窝的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2015,30(4):1313-1316.
[61] 宋红梅, 魏迎辰, 李楠, 等. 温阳补肾方对兔激素性股骨头坏死组织中骨保护素和核因子-κB受体活化因子及其配体mRNA表达的影响[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2019,25(2):178-183.
[62] 齐振熙, 余航, 万甜, 等. 髓芯减压联合羟基红花黄色素A对兔激素性股骨头坏死骨内压的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2015,30(6):2142-2145.
[63] 刘强, 刘昱. 钻孔减压自体骨复合CPC-丹参缓释体植入治疗激素性股骨头坏死的实验研究[J]. 中国医学创新,2011, 8(5):20-21.
[64] 佟鹏, 王洋, 梁瀛. 激素性股骨头缺血性坏死动物模型的建立及综合评估[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(32):5169-5174.
[65] 徐英杰, 姚辛敏, 尹羽薇, 等. 生骨胶囊对兔早期激素性股骨头坏死骨修复作用影响的研究[J]. 中医药信息,2014,31(3): 121-122.
[66] 李慧英, 孟东方, 阮志磊. 骨碎补总黄酮对激素性股骨头坏死血钙、血磷及空骨陷窝率的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2016,31(12):5352-5354.
[67] 孔令擘, 牛舜, 杨重飞, 等. 兔股骨头缺血坏死模型的建立研究及比较[J]. 第四军医大学学报,2009,30(2):138-141.
[68] 黄进, 张翼飞, 颜慧玫, 等. 三七总皂苷对股骨头坏死血清VEGF及BMP-2的mRNA表达水平的影响[J]. 吉林医学, 2017,38(7):1208-1210.
[69] 胡志明, 王海彬, 周明乾, 等. 激素性股骨头坏死股骨头微血管的变化[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2006(6):785-787.
[70] 洪嵩, 张天宏. 非创伤性股骨头坏死模型的血液流变学及脂质代谢[J]. 遵义医学院学报,2009,32(2):136-138.
[71] 段卫峰, 高书图, 刘又文. 股骨头坏死愈胶囊对兔激素性股骨头坏死血管内皮生长因子表达影响的实验研究[J]. 世界中西医结合杂志,2012,7(11):944-947.
[72] 吉浩宇, 王小龙. 早期激素性股骨头坏死过程中细胞色素c的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016,20(42):6252-6258.
[73] 李福军, 王小龙, 赵建民, 等. 经口腔深部灌注给药与传统给药方法的对比实验研究[J]. 医学研究生学报,2015,28(7): 745-749.
[74] 杜晨阳, 李慧英, 汪利合, 等. “三补一活”方干预兔激素性股骨头坏死作用机制研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2021,32(10): 2369-2373.
[75] GANG SNR, LIU FA. Experimental study on the expression of VEGF and BMP-2 insteroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Life Sci J. 2013;1(10):2853-2857.
[76] 熊明月, 王坤正, 党晓谦. 早期激素性股骨头坏死骨细胞凋亡的实验研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2007(3):262-265.
[77] 田雷, 王坤正, 党晓谦, 等. 阿魏酸钠对兔激素性股骨头坏死早期的干预作用及对骨细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版),2011,32(2):220-225.
[78] 刘昱, 姚志刚. 钻孔减压自体微小颗粒骨复合CPC-丹参缓释体植入治疗激素性股骨头坏死的实验研究[J]. 黑龙江中医药,2011,40(2):45-46.
[79] 刘金辉,聂喜增,周吉怀,等. 一氧化氮对激素性股骨头缺血坏死治疗的生化研究[J]. 骨与关节损伤杂志,2003(5): 313-315.
[80] 颜冰, 王和鸣. 活血补肾汤对兔激素性股骨头坏死VEGF的影响[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2010,18(5):1-4.
[81] 余永强,朱赤,陈小妹,等. 激素性股骨头缺血坏死介入溶通治疗实验研究[J]. 中国医学影像技术,1999,15(6):11-12.
[82] 方龙云,李林,李明学. 激素性股骨头坏死家兔血浆及软骨中一氧化氮含量的变化[J]. 延边大学医学学报,2005,28(1): 8-12.
[83] 李传将, 王万明, 庄颜峰, 等. 改良激素性股骨头坏死动物模型的建立与评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(24):4393-4397.
[84] 曹凯, 安洪, 黄伟, 等. 激素诱导血清病动物骨坏死模型中的脂类代谢异常[J]. 中国实验动物学报,2005,13(4):222-226.
[85] 白玉, 卢中道, 王迪. 激素性股骨头坏死中药治疗实验研究[J]. 医药论坛杂志, 2007,28(10):40-41.
[86] NA Y, ZHAOGANG G, WENCHEN J, et al. Exosomes Secreted from Hypoxia-Preconditioned Mesenchymal Stem Cells Prevent Steroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head by Promoting Angiogenesis in Rats. BioMed Res Int. 2021;2021:6655225.
[87] LIN Y, SONG L, XUEMEI B, et al. Oxytocin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in microglial cells and attenuates microglial activation in lipopolysaccharide-treated mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2016;13(1):77.
[88] 李子荣, 张念非, 岳德波, 等. 激素性股骨头坏死动物模型的诱导和观察[J]. 中华外科杂志,1995(8):485-487.
[89] KERACHIAN MA, HARVEY EJ, COURNOYER D, et al. A rat model of early stage osteonecrosis induced by glucocorticoids. J Orthop Surg Res. 2011;6:62.
[90] 肖春生, 林娜, 林诗富, 等. 不同糖皮质激素诱导鸡股骨头坏死的实验研究[J]. 中国骨伤,2010,23(3):184-187.
[91] 苏强, 孙天胜, 王秋良, 等. 不同剂量内毒素联合激素建立兔股骨头缺血性坏死模型的影像学评估[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(11):2108-2111.
|