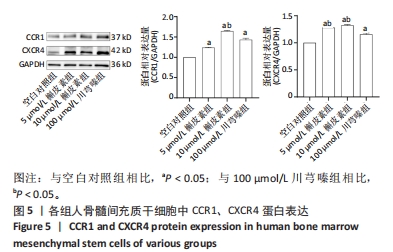
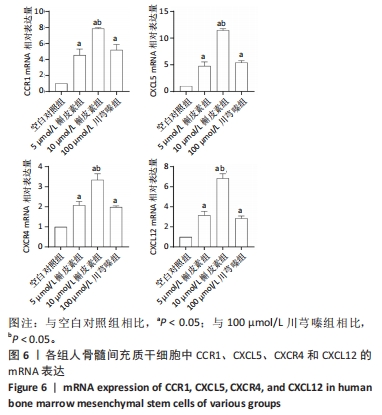
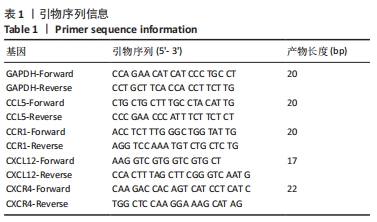
[1] TSIAPALIS D, O’DRISCOLL L. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine Applications. Cells. 2020;9(4):991.
[2] JANICKI P, SCHMIDMAIER G. What should be the characteristics of the ideal bone graft substitute? Combining scaffolds with growth factors and/or stem cells. Injury. 2011;42 Suppl 2:S77-81.
[3] BIANCO P, RIMINUCCI M, GRONTHOS S, et al. Bone marrow stromal stem cells: nature, biology, and potential applications. Stem Cells. 2001; 19(3):180-192.
[4] LEIBACHER J, HENSCHLER R. Biodistribution, migration and homing of systemically applied mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:7.
[5] ZHOU Y, WU Y, JIANG X,et al. The Effect of Quercetin on the Osteogenesic Differentiation and Angiogenic Factor Expression of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. PLoS One. 2015;10(6): e0129605.
[6] 胡啸天,邓志钦,段莉,等.间充质干细胞归巢效应的研究进展 [J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2020,17(5):53-57.
[7] BIAN W, XIAO S, YANG L, et al. Quercetin promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation through the H19/miR-625-5p axis to activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021;21(1):243.
[8] FENG L, YANG Z, HOU N, et al. Long Non-Coding RNA Malat1 Increases the Rescuing Effect of Quercetin on TNFα-Impaired Bone Marrow Stem Cell Osteogenesis and Ovariectomy-Induced Osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5965.
[9] PANG XG, CONG Y, BAO NR, et al. Quercetin Stimulates Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation through an Estrogen Receptor-Mediated Pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:4178021.
[10] 王彦超,邓蓉蓉,叶亚东,等.补肾活血舒筋方含药血清对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、迁移的影响及其机制[J].山东医药,2017, 57(16):38-40.
[11] 李薇懿,李国春,魏乐心,等.凉血通瘀方干预高血压大鼠急性脑出血模型对脑组织中差异miRNA表达的影响[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2022,24(5):1933-1943.
[12] NING Y, WU Y, ZHOU Q, et al. The effect of quercetin in the yishen tongluo jiedu recipe on the development of prostate cancer through the akt1-related CXCL12/CXCR4 pathway. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023. doi: 10.2174/1386207326666230530095355.
[13] LI L, CHU L, FANG Y, et al. Preconditioning of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells by tetramethylpyrazine enhances cell migration and improves functional recovery after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):112.
[14] LIVAK KJ, SCHMITTGEN TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402-408.
[15] HSIN KY, GHOSH S, KITANO H. Combining machine learning systems and multiple docking simulation packages to improve docking prediction reliability for network pharmacology. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e83922.
[16] GU JJ, LI HX, WEI W, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation alleviates radiation-induced myocardial fibrosis through inhibition of the TGF-β1/Smad2/3 signaling pathway in rabbit model. Regen Ther. 2023;24:1-10.
[17] HE Y, CHEN D, YANG L, et al. The therapeutic potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in premature ovarian failure. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):263.
[18] LV J, HAO YN, WANG XP, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-30e-5p ameliorates high-glucose induced renal proximal tubular cell pyroptosis by inhibiting ELAVL1. Ren Fail. 2023;45(1):2177082.
[19] JACKSON JS, GOLDING JP, CHAPON C, et al. Homing of stem cells to sites of inflammatory brain injury after intracerebral and intravenous administration: a longitudinal imaging study. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2010; 1(2):17.
[20] ZHANG D, YU K, YANG J, et al. Senolytic controls bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells fate improving bone formation. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(6):3078-3088.
[21] JIANG D, WU X, SUN X, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-7-5p inhibits progression of acute myeloid leukemia by targeting OSBPL11. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):29.
[22] DING N, LI E, OUYANG X, et al. The Therapeutic Potential of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Articular Cartilage Regeneration in Osteoarthritis. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;16(7):840-847.
[23] ZHANG J, RONG Y, LUO C,et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes prevent osteoarthritis by regulating synovial macrophage polarization. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(24): 25138-25152.
[24] XU H, XU B. BMSC-Derived Exosomes Ameliorate Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Pyroptosis of Cartilage via Delivering miR-326 Targeting HDAC3 and STAT1//NF-κB p65 to Chondrocytes. Mediators Inflamm. 2021;2021:9972805.
[25] WANG B, IRIGUCHI S, WASEDA M, et al. Generation of hypoimmunogenic T cells from genetically engineered allogeneic human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biomed Eng. 2021;5(5):429-440.
[26] 何波,何志军,李金鹏,等.提高间充质干细胞治疗皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的策略[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(25):4065-4017.
[27] 樊飞燕,张运克.益气活血中药联合骨髓间充质干细胞促进缺血性脑卒中血管新生的作用与机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(13):2060-2069.
[28] MA Y, LI Y, ZHANG S, et al. Study on the function of Huazhuo Jiedu Decoction in promoting the homing of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and contributing to the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Heliyon. 2023;9(8):e18802.
[29] WANG N, WANG L, YANG J, et al. Quercetin promotes osteogenic differentiation and antioxidant responses of mouse bone mesenchymal stem cells through activation of the AMPK/SIRT1 signaling pathway. Phytother Res. 2021. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7010.
[30] YUAN Z, MIN J, ZHAO Y, et al. Quercetin rescued TNF-alpha-induced impairments in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis and improved osteoporosis in rats. Am J Transl Res. 2018; 10(12):4313-4321.
[31] SADEGHI A, KHAZAEEL K, TABANDEH MR, et al. Prenatal exposure to crude oil vapor reduces differentiation potential of rat fetal mesenchymal stem cells by regulating ERK1/2 and PI3K signaling pathways: Protective effect of quercetin. Reprod Toxicol. 2023;120: 108440.
[32] ZHAO WJ, LIU X, HU M, et al. Quercetin ameliorates oxidative stress-induced senescence in rat nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells via the miR-34a-5p/SIRT1 axis. World J Stem Cells. 2023; 15(8):842-865.
[33] 任明亮.新型含槲皮素复合骨替代材料的制备、生物学性能及骨修复功能研究[D].广州:南方医科大学, 2019.
[34] 余富勇,余翔,乡晓岚,等.补肾法促干细胞归巢在骨质疏松中的应用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(11):1711-1716.
[35] XU J, YANG F, LUO S, et al. The Role of SDF-1α-CXCR4/CXCR7 in Migration of Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells. Int J Stem Cells. 2023;16(2):180-190.
[36] HUANG J, ZHANG Z, GUO J, et al. Genetic modification of mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing CCR1 increases cell viability, migration, engraftment, and capillary density in the injured myocardium. Circ Res. 2010;106(11):1753-1762.
[37] AZIZ NS, AZLINA A, YUSOP N. Angiogenic and Migratory Gene Expression Analysis of Stem Cells From Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth for Wound Repair Application. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;17(5):466-479.
[38] ZHAO Z, MA X, MA J, et al. Naringin enhances endothelial progenitor cell (EPC) proliferation and tube formation capacity through the CXCL12/CXCR4/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 2018; 286:45-51.
[39] ZHAO A, CHUNG M, YANG Y, et al. The SDF-1/CXCR4 Signaling Pathway Directs the Migration of Systemically Transplanted Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Towards the Lesion Site in a Rat Model of Spinal Cord Injury. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;18(2):216-230.
[40] 朱磊,连紫宇,胡静怡,等.健脾补肾、清肠化湿复方及其拆方对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖趋化的影响及机制研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(8):4568-4572.
[41] GUO F, YANG Y, DUAN Y, et al. Quality Marker Discovery and Quality Evaluation of Eucommia ulmoides Pollen Using UPLC-QTOF-MS Combined with a DPPH-HPLC Antioxidant Activity Screening Method. Molecules. 2023;28(13):5288.
|