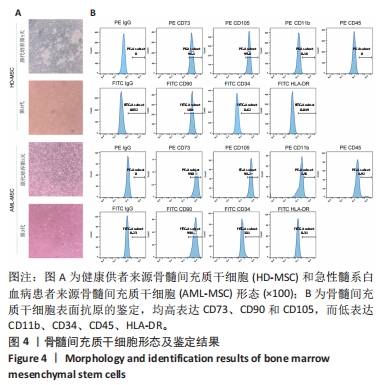
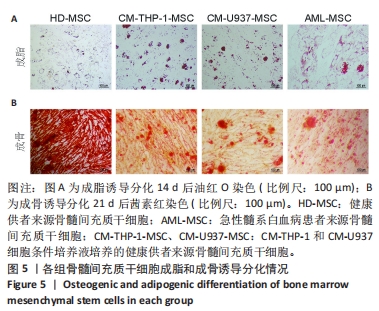
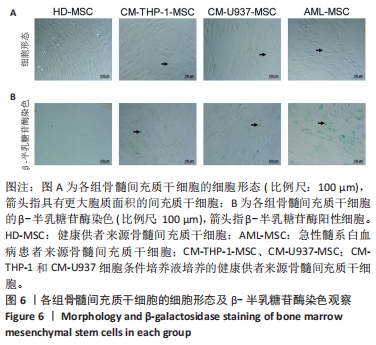
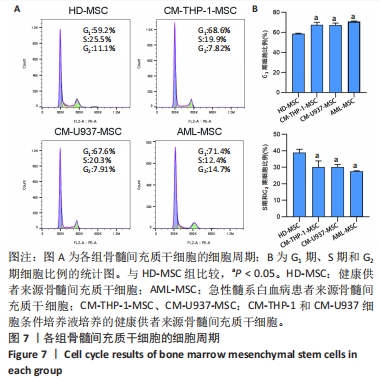
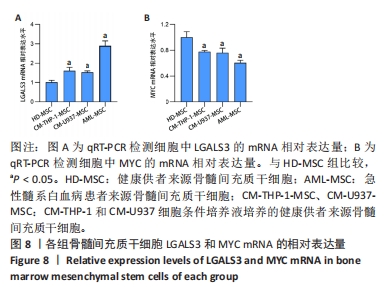
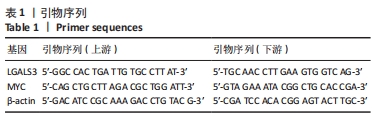
[1] DINARDO CD, ERBA HP, FREEMAN SD, et al. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet. 2023;401(10393):2073-2086.
[2] ZHAO X, LIU HQ, WANG LN, et al. Current and emerging molecular and epigenetic disease entities in acute myeloid leukemia and a critical assessment of their therapeutic modalities. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;83:121-135.
[3] SCHULPEN M, GOEMANS BF, KASPERS GJL, et al. Increased survival disparities among children and adolescents & young adults with acute myeloid leukemia: A Dutch population-based study. Int J Cancer. 2022;150(7):1101-1112.
[4] BEJANYAN N, WEISDORF DJ, LOGAN BR, et al. Survival of patients with acute myeloid leukemia relapsing after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a center for international blood and marrow transplant research study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21(3):454-459.
[5] CHEN Y, LI J, XU L, et al. The genesis and evolution of acute myeloid leukemia stem cells in the microenvironment: From biology to therapeutic targeting. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):397.
[6] CORRADI G, BASSANI B, SIMONETTI G, et al. Release of IFNγ by Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells Remodels Bone Marrow Immune Microenvironment by Inducing Regulatory T Cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28(14):3141-3155.
[7] BORELLA G, DA ROS A, BORILE G, et al. Targeting the plasticity of mesenchymal stromal cells to reroute the course of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2021; 138(7):557-570.
[8] BOLANDI SM, PAKJOO M, BEIGI P, et al. A Role for the Bone Marrow Microenvironment in Drug Resistance of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cells. 2021; 10(11):2833.
[9] GALÁN-DÍEZ M, BOROT F, ALI AM, et al. Subversion of Serotonin Receptor Signaling in Osteoblasts by Kynurenine Drives Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2022;12(4):1106-1127.
[10] HUANG D, SUN G, HAO X, et al. ANGPTL2-containing small extracellular vesicles from vascular endothelial cells accelerate leukemia progression. J Clin Invest. 2021;131(1):e138986.
[11] WOODS K, GUEZGUEZ B. Dynamic Changes of the Bone Marrow Niche: Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Their Progeny During Aging and Leukemia. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:714716.
[12] LYU T, WANG Y, LI D, et al. Exosomes from BM-MSCs promote acute myeloid leukemia cell proliferation, invasion and chemoresistance via upregulation of S100A4. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2021;10(1):24.
[13] YOU R, WANG B, CHEN P, et al. Metformin sensitizes AML cells to chemotherapy through blocking mitochondrial transfer from stromal cells to AML cells. Cancer Lett. 2022;532:215582.
[14] LU J, DONG Q, ZHANG S, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)-derived mesenchymal stem cells induce chemoresistance and epithelial-mesenchymal transition-like program in AML through IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Cancer Sci. 2023;114(8):3287-3300.
[15] SHAFAT MS, OELLERICH T, MOHR S, et al. Leukemic blasts program bone marrow adipocytes to generate a protumoral microenvironment. Blood. 2017; 129(10):1320-1332.
[16] VON DER HEIDE EK, NEUMANN M, VOSBERG S, et al. Molecular alterations in bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells derived from acute myeloid leukemia patients. Leukemia. 2017;31(5):1069-1078.
[17] YU G, WANG LG, HAN Y, et al. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS. 2012;16(5):284-287.
[18] SZKLARCZYK D, GABLE AL, LYON D, et al. STRING v11: protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1): D607-D613.
[19] DOMINICI M, LE BLANC K, MUELLER I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.
[20] MENTER T, TZANKOV A. Tumor Microenvironment in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Adjusting Niches. Front Immunol. 2022;13:811144.
[21] AHMED HMM, NIMMAGADDA SC, AL-MATARY YS, et al. Dexamethasone-mediated inhibition of Notch signalling blocks the interaction of leukaemia and mesenchymal stromal cells. Br J Haematol. 2022;196(4):995-1006.
[22] MARLEIN CR, ZAITSEVA L, PIDDOCK RE, et al. NADPH oxidase-2 derived superoxide drives mitochondrial transfer from bone marrow stromal cells to leukemic blasts. Blood. 2017;130(14):1649-1660.
[23] ABDUL-AZIZ AM, SUN Y, HELLMICH C, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia induces protumoral p16INK4a-driven senescence in the bone marrow microenvironment. Blood. 2019;133(5):446-456.
[24] AL-AZAB M, SAFI M, IDIIATULLINA E, et al. Aging of mesenchymal stem cell: machinery, markers, and strategies of fighting. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022;27(1):69.
[25] KORNBLAU SM, RUVOLO PP, WANG RY, et al. Distinct protein signatures of acute myeloid leukemia bone marrow-derived stromal cells are prognostic for patient survival. Haematologica. 2018;103(5):810-821.
[26] CORRADI G, BALDAZZI C, OČADLÍKOVÁ D, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells from myelodysplastic and acute myeloid leukemia patients display in vitro reduced proliferative potential and similar capacity to support leukemia cell survival. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):271.
[27] ZHANG L, ZHAO Q, CANG H, et al. Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells Educate Mesenchymal Stromal Cells toward an Adipogenic Differentiation Propensity with Leukemia Promotion Capabilities. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(16):2105811.
[28] CHEN Y, HOFFMEISTER LM, ZAUN Y, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia-induced remodeling of the human bone marrow niche predicts clinical outcome. Blood Adv. 2020;4(20):5257-5268.
[29] TRATWAL J, ROJAS-SUTTERLIN S, BATACLAN C, et al. Bone marrow adiposity and the hematopoietic niche: A historical perspective of reciprocity, heterogeneity, and lineage commitment. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;35(4):101564.
[30] MAYNARD RS, HELLMICH C, BOWLES KM, et al. Acute Myeloid Leukaemia Drives Metabolic Changes in the Bone Marrow Niche. Front Oncol. 2022;12:924567.
[31] HARA A, NIWA M, NOGUCHI K, et al. Galectin-3 as a Next-Generation Biomarker for Detecting Early Stage of Various Diseases. Biomolecules. 2020;10(3):389.
[32] TARIGHAT SS, FEI F, JOO EJ, et al. Overcoming Microenvironment-Mediated Chemoprotection through Stromal Galectin-3 Inhibition in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(22):12167.
[33] SADOVSKAYA A, PETINATI N, DRIZE N, et al. Acute Myeloid Leukemia Causes Serious and Partially Irreversible Changes in Secretomes of Bone Marrow Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(10):8953.
[34] KARGAR-SICHANI Y, MOHAMMADI MH, AMIRI V, et al. Effect of Acute Myeloid Leukemia-derived Extracellular Vesicles on Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Expression of Poor Prognosis Genes. Arch Med Res. 2023;54(2):95-104.
[35] LIU ZZ, HONG CG, HU WB, et al. Autophagy receptor OPTN (optineurin) regulates mesenchymal stem cell fate and bone-fat balance during aging by clearing FABP3. Autophagy. 2021;17(10):2766-2782.
[36] YAMADA T, FUKASAWA K, HORIE T, et al. The role of CDK8 in mesenchymal stem cells in controlling osteoclastogenesis and bone homeostasis. Stem Cell Reports. 2022;17(7):1576-1588.
[37] GUO H, ZHAO M, QIU X, et al. Niemann-Pick type C2 deficiency impairs autophagy-lysosomal activity, mitochondrial function, and TLR signaling in adipocytes. J Lipid Res. 2016;57(9):1644-1658.
[38] XIONG Y, SI Y, FENG Y, et al. Prognostic value of lipid metabolism-related genes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2021;9(1):196-209.
[39] DING M, MA YJ, DU RQ, et al. CHCHD10 Modulates Thermogenesis of Adipocytes by Regulating Lipolysis. Diabetes. 2022;71(9):1862-1879.
[40] GLADYCK S, ARAS S, HÜTTEMANN M, et al. Regulation of COX Assembly and Function by Twin CX9C Proteins-Implications for Human Disease. Cells. 2021; 10(2):197.
[41] 王诗,谢凯,任志健,等. SNARE蛋白在肿瘤发生中作用的研究进展[J].医学研究生学报,2022,35(8):872-876.
[42] APPUNNI S, RUBENS M, RAMAMOORTHY V, et al. Lumican, pro-tumorigenic or anti-tumorigenic: A conundrum. Clin Chim Acta. 2021;514:1-7.
[43] LAMA-SHERPA TD, JEONG MH, JEWELL JL. Regulation of mTORC1 by the Rag GTPases. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023;51(2):655-664.
[44] WALKER GE, MERLIN S, ZANOLINI D, et al. Factor VIII as a potential player in cancer pathophysiology. J Thromb Haemost. 2022;20(3):648-660.
[45] MELNIK S, WERTH N, BOEUF S, et al. Impact of c-MYC expression on proliferation, differentiation, and risk of neoplastic transformation of human mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):73.
[46] ZHOU C, GE Z, SONG L, et al. Strontium-modified titanium substrate promotes osteogenic differentiation of MSCs and implant osseointegration via upregulating CDH2. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2023;34(4):297-311.
[47] PARKER J, HOCKNEY S, BLASCHUK OW, et al. Targeting N-cadherin (CDH2) and the malignant bone marrow microenvironment in acute leukaemia. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2023;25:e16.
[48] KHAN AA, HUAT TJ, AL MUTERY A, et al. Significant transcriptomic changes are associated with differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells into neural progenitor-like cells in the presence of bFGF and EGF. Cell Biosci. 2020;10:126.
[49] KNIGHT C, JAMES S, KUNTIN D, et al. Epidermal growth factor can signal via β-catenin to control proliferation of mesenchymal stem cells independently of canonical Wnt signalling. Cell Signal. 2019;53:256-268.
[50] LIU P, LI Y, WANG W, et al. Role and mechanisms of the NF-ĸB signaling pathway in various developmental processes. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113513.
[51] MALKOVA AM, GUBAL AR, PETROVA AL, et al. Pathogenetic role and clinical significance of interleukin-1β in cancer. Immunology. 2023;168(2):203-216.
[52] CAMBIER S, GOUWY M, PROOST P. The chemokines CXCL8 and CXCL12: molecular and functional properties, role in disease and efforts towards pharmacological intervention. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023;20(3):217-251.
[53] SADOVSKAYA AV, PETINATI NA, KAPRANOV NM, et al. Dynamics of Changes in the Properties of Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Patients with Acute Leukemia. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2023;174(4):556-563.
[54] HU S, ZHAO X, LI R, et al. Activating transcription factor 3, glucolipid metabolism, and metabolic diseases. J Mol Cell Biol. 2023;14(10):mjac067.
[55] ZANDI Z, KASHANI B, ALISHAHI Z, et al. Dual-specificity phosphatases: therapeutic targets in cancer therapy resistance. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022;148(1):57-70.
[56] MAKITA S, TAKATORI H, NAKAJIMA H. Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Immune Responses and Inflammatory Diseases by RNA-Binding ZFP36 Family Proteins. Front Immunol. 2021;12:711633.
[57] RIVAS S, MARÍN A, SAMTANI S, et al. MET Signaling Pathways, Resistance Mechanisms, and Opportunities for Target Therapies. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(22): 13898.
|