[1] D’ORIA M, WANHAINEN A, DEMARTINO RR, et al. A scoping review of the rationale and evidence for cost-effectiveness analysis of fenestrated-branched endovascular repair for intact complex aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2020;72(5):1772-1782.
[2] KOSHY SKG, GEORGE LK, DAS P. Cost-effectiveness and outcomes with early or same-day discharge after elective percutaneous coronary intervention. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2020;22(6):42.
[3] ULLAH M, WAHAB A, KHAN SU, et al. Stent as a Novel technology for coronary artery disease and their clinical manifestation. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2023;48(1):101415.
[4] WU X, LI L, HE L. Drug-coated balloon versus drug-eluting stent in patients with small-vessel coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cardiol Res Pract. 2021;2021:1647635.
[5] 吴丹枫,沈蔺.快速康复外科卫生经济学效益分析[J].中国医院,2021,25(3):48-51.
[6] 高艳,周泓羽,赵庆华,等.医院感染的卫生经济学研究现状及启示[J].中国卫生资源,2021,24(5):520-524.
[7] 安思兰,王泠.国外护理服务的卫生经济学评价研究进展[J].护士进修杂志,2022, 37(14):1300-1304.
[8] 马冰,王晓春,黄求进,等.压力性损伤防治的卫生经济学评价研究进展[J].护理学杂志,2021,36(1):25-29.
[9] 孙利强,李晶,刘航,等.CT-血流储备分数指导稳定性冠心病患者的治疗观察[J].中华实验外科杂志,2023,40(1):153-156.
[10] 马云通,马慧慧,赵欣,等.定量血流分数在冠状动脉多支临界病变治疗中的价值[J].济宁医学院学报,2022,45(1):11-15.
[11] 孙明敏,王连生,赵俊.冠心病患者介入治疗应用进口和国产药物洗脱支架的成本-效果分析[J].江苏医药,2013,39(8):944-946.
[12] WILLICH SN, MÜLLER-RIEMENSCHNEIDER F, MCBRIDE D, et al. Health economic evaluation of the use of drug-eluting stents: first results from the drug-eluting stent registry (DES.de). Herz. 2012. doi: 10.1007/s00059-012-3581-5.
[13] 祁方家,冯莎,吴伟栋,等.药物洗脱支架火鹰(Firehawk)与XIENCE V治疗单支单处冠状动脉病变的卫生经济学评价[J].中国卫生资源,2015,18(4):283-286.
[14] ZBINDEN R, VON FELTEN S, WEIN B, et al. Impact of stent diameter and length on in-stent restenosis after DES vs BMS implantation in patients needing large coronary stents-A clinical and health-economic evaluation. Cardiovasc Ther. 2017;35(1):19-25.
[15] MATTKE S, HANSON M, DALLMANN AC, et al. Health economic evaluation of an ultrathin, bioresorbable-polymer sirolimus-eluting coronary stent compared to a thin, durable-polymer everolimus-eluting stent. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2019;20(9):752-757.
[16] ZHOU J, LIEW D, DUFFY SJ, et al. Intravascular ultrasound versus angiography-guided drug-eluting stent implantation: a health economic analysis. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2021;14(5):e006789.
[17] 刘畅,陶立波,王芳旭,等.血流导向密网支架(PED)对比支架辅助弹簧圈技术治疗颅内大型动脉瘤的卫生经济学评价[J].中国医疗保险,2022(3):61-67.
[18] 刘洪章,杜炎秋,刘瑾瑜,等.颈动脉内膜剥脱术与支架植入术治疗颈动脉狭窄的卫生经济学评价[J].中国卫生经济,2023,42(5):80-85.
[19] 潘希丁,周峰,荆莉,等.阿替普酶静脉溶栓桥接支架取栓对比直接支架取栓治疗急性缺血性卒中的卫生经济学评价[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2023,20(7):464-471.
[20] SRIVASTAVA R, SRIVASTAVA S. Bibliometric analysis of indian journal of palliative care from 1995 to 2022 using the VOSviewer and bibliometrix software. Indian J Palliat Care. 2022;28(4):338-353.
[21] ARRUDA H, SILVA ER, LESSA M, et al. VOSviewer and bibliometrix. J Med Libr Assoc. 2022;110(3):392-395.
[22] COHEN DJ, BAKHAI A, SHI C, et al. Cost-effectiveness of sirolimus-eluting stents for treatment of complex coronary stenoses: results from the sirolimus-eluting balloon expandable stent in the treatment of patients with de novo native coronary artery lesions (SIRIUS) trial. Circulation. 2004;110(5):508-514.
[23] PARISE H, MAEHARA A, STONE GW, et al. Meta-analysis of randomized studies comparing intravascular ultrasound versus angiographic guidance of percutaneous coronary intervention in pre-drug-eluting stent era. Am J Cardiol. 2011;107(3):374-382.
[24] SHIREMAN TI, WANG K, SAVER JL, et al. Cost-effectiveness of solitaire stent retriever thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: results from the SWIFT-PRIME Trial (Solitaire With the Intention for Thrombectomy as Primary Endovascular Treatment for Acute Ischemic Stroke). Stroke. 2017;48(2):379-387.
[25] Weaver WD, Reisman MA, Griffin JJ, et al. Optimum percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty compared with routine stent strategy trial (OPUS-1): a randomised trial. Lancet. 2000;355(9222):2199-2203.
[26] COHEN DJ, TAIRA DA, BEREZIN R, et al. Cost-effectiveness of coronary stenting in acute myocardial infarction: results from the stent primary angioplasty in myocardial infarction (stent-PAMI) trial. Circulation. 2001;104(25):3039-3045.
[27] COLBY GP, LIN LM, PAUL AR, et al. Cost comparison of endovascular treatment of anterior circulation aneurysms with the pipeline embolization device and stent-assisted coiling. Neurosurgery. 2012;71(5):944-948; discussion 948-950.
[28] ANG HY, BULLUCK H, WONG P, et al. Bioresorbable stents: current and upcoming bioresorbable technologies. Int J Cardiol. 2017;228:931-939.
[29] 姜英,王乃东.颅内外血管狭窄术后支架内再狭窄的研究进展[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2022,19(2):130-135.
[30] 何钰,王建波,王武.颅内动脉粥样硬化性狭窄支架植入术后再狭窄机制及治疗新进展[J].介入放射学杂志,2021,30(11):1184-1189.
[31] 赵霞,左洪炜,藤碧云,等.支架置入在人工血管内瘘回流静脉狭窄中应用的长期效果分析[J].中国血液净化,2023,22(7):546-550.
[32] 马金阳,汪雷,董元训,等.Willis覆膜支架治疗复杂颈内动脉病变的临床应用[J].介入放射学杂志,2022,31(12):1185-1189.
[33] 赵铮,丁文飞,邵淑馨,等.西罗莫司-聚三亚甲基碳酸酯改性镁合金的降解和药物释放行为[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(30):4836-4843.
[34] 王江平,焦勇,许志斌,等.腹腔镜3D打印血管外支架植入术治疗胡桃夹综合征的安全性和有效性[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2018,39(3):200-204.
[35] 方振威,石秀锦,赵紫楠,等.CYP2C19基因指导急性冠状动脉综合征或经皮冠状动脉介入治疗患者P2Y12受体拮抗剂个体化治疗的长期疗效与安全性Meta分析[J].临床药物治疗杂志,2022,20(1):43-52.
[36] 崔耀刚,吕小宁,庞然.冠心病PCI术后SICAM-1、RDW及vWF水平与支架内再狭窄的关系[J].分子诊断与治疗杂志,2022,14(3):426-429.
[37] TEPE G, BRODMANN M, MICARI A, et al. 5-year outcomes of drug-coated balloons for peripheral artery in-stent restenosis, long lesions, and CTOs. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2023;16(9):1065-1078.
[38] YI Y, WANG B, LI C. Sensors-based monitoring and treatment approaches for in-stent restenosis. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2023;111(2):490-498.
[39] 胡仁杰,张磊,张文,等.术中置入肺动脉分支血管支架的镶嵌技术治疗肺动脉分支狭窄[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2017,33(1):25-27.
[40] BERTOGLIO L, MELLONI A, BUGNA C, et al. In-hospital cost-effectiveness analysis of open versus staged fenestrated/branched endovascular elective repair of thoracoabdominal aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2023;78(2):300-312.e3.
[41] D’ORIA M, WANHAINEN A, DEMARTINO RR, et al. A scoping review of the rationale and evidence for cost-effectiveness analysis of fenestrated-branched endovascular repair for intact complex aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2020;72(5):1772-1782.
[42] 李洪坤,王新生,李江峰,等.冠心病经皮冠状动脉介入治疗患者住院费用影响因素分析[J].精准医学杂志,2022,37(4):332-336,341.
[43] 周力,李宇能,朱仕文,等.一期减张内固定与延迟手术治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折合并筋膜间隔综合征的比较研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(5):394-399.
[44] 丁轶.脑血管金属支架植入脑动脉血管血栓形成的风险评估[J].血栓与止血学, 2020,26(5):789-791.
|

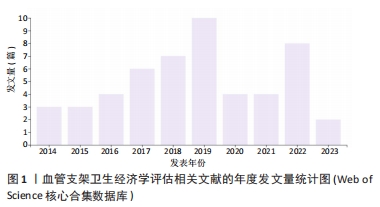

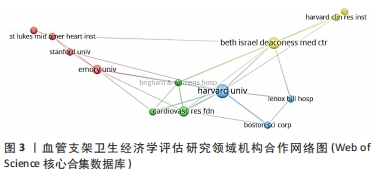
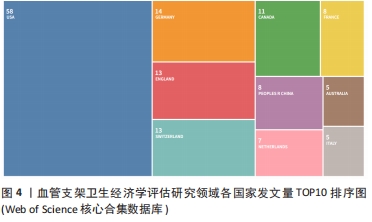
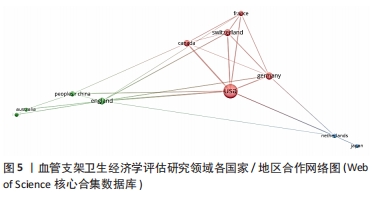
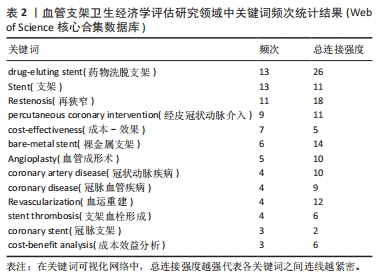
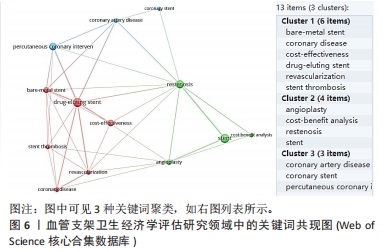


 鉴于此,文章采用文献计量学的分析方法,对血管支架的相关卫生经济学评估研究的文献数据进行可视化分析,分析其研究热点和发展趋势,并从医疗质量管理角度进行讨论,希望能更好地指导医疗决策,确保患者获得高质量及经济合理的治疗。
鉴于此,文章采用文献计量学的分析方法,对血管支架的相关卫生经济学评估研究的文献数据进行可视化分析,分析其研究热点和发展趋势,并从医疗质量管理角度进行讨论,希望能更好地指导医疗决策,确保患者获得高质量及经济合理的治疗。