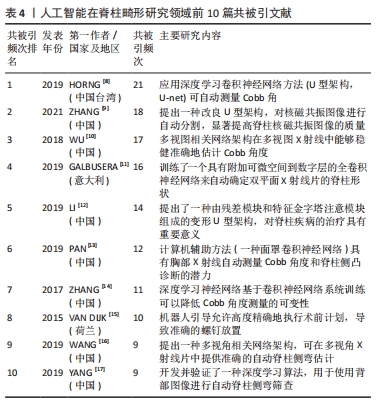
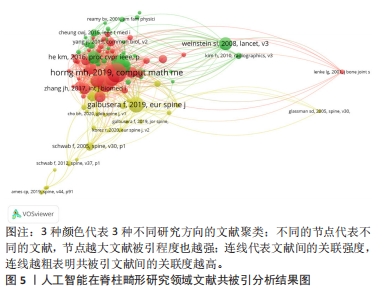
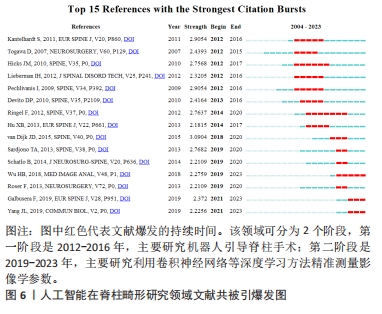
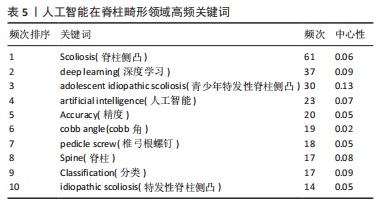
[1] DJURASOVIC M, GLASSMAN SD. Correlation of radiographic and clinical findings in spinal deformities. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2007;18(2):223-227.
[2] DIEBO BG, SHAH NV, BOACHIE-ADJEI O, et al. Adult spinal deformity. Lancet. 2019;394(10193):160-172.
[3] MACKEL CE, JADA A, SAMDANI AF, et al. A comprehensive review of the diagnosis and management of congenital scoliosis. Childs Nerv Syst. 2018; 34(11):2155-2171.
[4] DEVEZA LR, CHHABRA BN, HEYDEMANN J, et al. Comparison of baseline characteristics and postoperative complications in neuromuscular, syndromic and congenital scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2023;32(4):350-356.
[5] 陆洋阳,徐纯鑫,陈岑,等.基于三维运动捕捉系统建立青少年特发性脊柱侧弯胸廓容积与腹腔容积模型[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,36(26): 5807-5811.
[6] RAMESH AN, KAMBHAMPATI C, MONSON JR, et al. Artificial intelligence in medicine. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2004;86(5):334-338.
[7] BHATTAD PB, JAIN V. Artificial intelligence in modern medicine - the evolving necessity of the present and role in transforming the future of medical care. Cureus. 2020;12(5):e8041.
[8] HORNG MH, KUOK CP, FU MJ, et al. Cobb angle measurement of spine from x-ray images using convolutional neural network. Comput Math Methods Med. 2019;2019:6357171.
[9] ZHANG Q, DU Y, WEI Z, et al. Spine medical image segmentation based on deep learning. J Healthc Eng. 2021;2021:1917946.
[10] WU H, BAILEY C, RASOULINEJAD P, et al. automated comprehensive adolescent idiopathic scoliosis assessment using mvc-net. med image anal. 2018;48:1-11.
[11] GALBUSERA F, NIEMEYER F, WILKE HJ, et al. Fully automated radiological analysis of spinal disorders and deformities: a deep learning approach. Eur Spine J. 2019;28(5):951-960.
[12] LI H, LUO H, LIU Y. Paraspinal muscle segmentation based on deep neural network. Sensors (Basel). 2019;19(12):2650.
[13] PAN Y, CHEN Q, CHEN T, et al. Evaluation of a computer-aided method for measuring the Cobb angle on chest X-rays. Eur Spine J. 2019;28(12): 3035-3043.
[14] ZHANG J, LI H, LV L, et al. Computer-aided cobb measurement based on automatic detection of vertebral slopes using deep neural network. Int J Biomed Imaging. 2017;2017:9083916.
[15] VAN DIJK JD, VAN DEN ENDE RP, STRAMIGIOLI S, et al. Clinical pedicle screw accuracy and deviation from planning in robot-guided spine surgery: robot-guided pedicle screw accuracy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015; 40(17):E986-E991.
[16] WANG L, XU Q, LEUNG S, et al. Accurate automated Cobb angles estimation using multi-view extrapolation net. Med Image Anal. 2019;58:101542.
[17] YANG J, ZHANG K, FAN H, et al. Development and validation of deep learning algorithms for scoliosis screening using back images. Commun Biol. 2019;2:390.
[18] KANTELHARDT SR, MARTINEZ R, BAERWINKEL S, et al. Perioperative course and accuracy of screw positioning in conventional, open robotic-guided and percutaneous robotic-guided, pedicle screw placement. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(6):860-868.
[19] 魏锦强,黄登承,曹学伟,等.中医药治疗软骨疾病近20年文献知识图谱分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(20):3202-3209.
[20] 叶慧,许悦,章雨桐,等.运动疗法在绝经后骨质疏松症中应用的可视化文献计量分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(2):255-261, 268.
[21] ANWAR SM, MAJID M, QAYYUM A, et al. Medical image analysis using convolutional neural networks: a review. J Med Syst. 2018;42(11):226.
[22] FALK T, MAI D, BENSCH R, et al. U-Net: deep learning for cell counting, detection, and morphometry. Nat Methods. 2019;16(1):67-70.
[23] ALOM MZ, YAKOPCIC C, HASAN M, et al. Recurrent residual U-Net for medical image segmentation. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2019;6(1): 014006.
[24] ZHU G, LUO X, YANG T, et al. Deep learning-based recognition and segmentation of intracranial aneurysms under small sample size. Front Physiol. 2022;13:1084202.
[25] HAN B, WEI Y, WANG Q, et al. Dual adaptive learning multi-task multi-view for graph network representation learning. Neural Netw. 2023;162:297-308.
[26] WANG S, CHEN Z, DU S, et al. Learning deep sparse regularizers with applications to multi-view clustering and semi-supervised classification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2022;44(9):5042-5055.
[27] ZIRAKI N, DORNAIKA F, BOSAGHZADEH A. Multiple-view flexible semi-supervised classification through consistent graph construction and label propagation. Neural Netw. 2022;146:174-180.
[28] PERFETTI DC, KISINDE S, ROGERS-LAVANNE MP, et al. Robotic spine surgery: past, present, and future. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2022;47(13):909-921.
[29] ZHANG Q, HAN XG, XU YF, et al. Robotic navigation during spine surgery. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2020;17(1):27-32.
[30] 周立金,程云忠,海涌,等.全基因组关联分析在青少年特发性脊柱侧凸病因学研究中的进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2022,32(3):269-273.
[31] MAKKI N, ZHAO J, LIU Z, et al. Genomic characterization of the adolescent idiopathic scoliosis-associated transcriptome and regulome. Hum Mol Genet. 2021;29(22):3606
[32] BARLOW DP, BARTOLOMEI MS. Genomic imprinting in mammals. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014;6(2):a018382.
[33] KHANSHOUR AM, KOU I, FAN Y, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis and replication studies in multiple ethnicities identify novel adolescent idiopathic scoliosis susceptibility loci. Hum Mol Genet. 2018;27(22):3986-3998.
[34] KIMES PK, LIU Y, NEIL HAYES D, et al. Statistical significance for hierarchical clustering. Biometrics. 2017;73(3):811-821.
[35] PANG X, CAO J, CHEN S, et al. Unsupervised clustering reveals distinct subtypes of biliary atresia based on immune cell types and gene expression. Front Immunol. 2021;12:720841.
[36] KARIM MR, BEYAN O, ZAPPA A, et al. Deep learning-based clustering approaches for bioinformatics. Brief Bioinform. 2021;22(1):393-415.
|