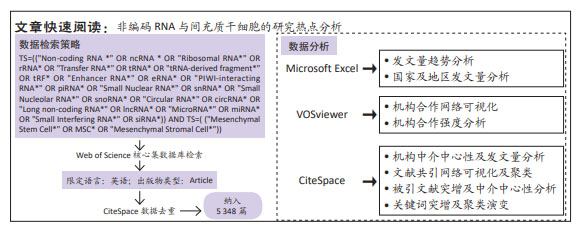
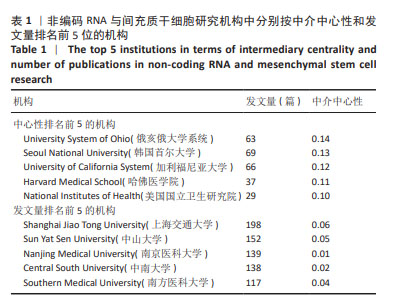
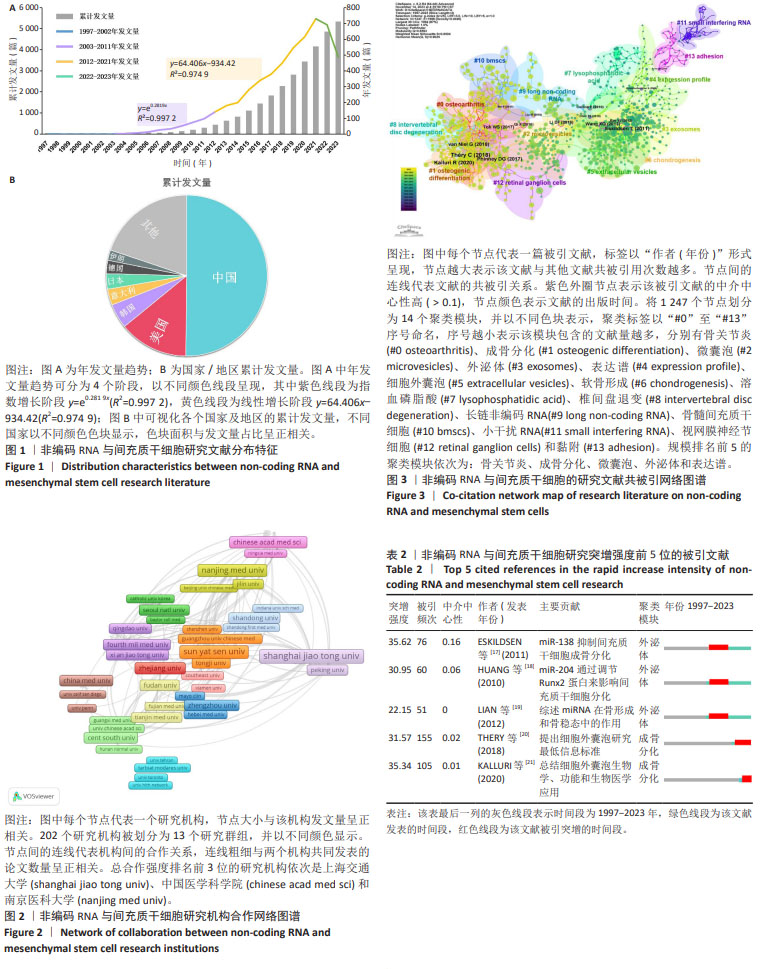
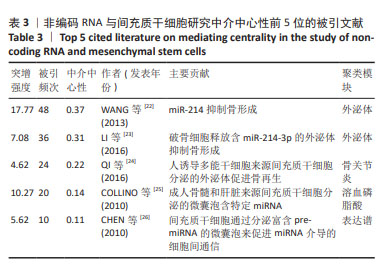
[1] EDDY SR. Non–coding RNA genes and the modern RNA world. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2(12):919-929.
[2] PENG Y, CROCE CM. The role of microRNAs in human cancer. Sig Transduct Target Ther. 2016;1:15004.
[3] SUN YM, CHEN YQ. Principles and innovative technologies for decrypting noncoding RNAs: from discovery and functional prediction to clinical application. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13(1):109.
[4] ZHAO C, XIE W, ZHU H, et al. LncRNAs and their RBPs: how to influence the fate of stem cells? Stem Cell Res Ther 2022;13(1):175.
[5] HUNKLER HJ, GROSS S, THUM T, et al. Non-coding RNAs: key regulators of reprogramming, pluripotency, and cardiac cell specification with therapeutic perspective for heart regeneration. Cardiovasc Res. 2022; 118(15):3071-3084.
[6] PITTENGER MF, DISCHER DE, PEAULT BM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell perspective: cell biology to clinical progress. NPJ Regen Med. 2019;4:22.
[7] GUO Y, YU Y, HU S, et al. The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells for cardiovascular diseases. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(5):349.
[8] WENG Z, ZHANG B, WU C, et al. Therapeutic roles of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14(1):136.
[9] CAI Y, WU C, OU Q, et al. Enhanced osteoarthritis therapy by nanoengineered mesenchymal stem cells using biomimetic CuS nanoparticles loaded with plasmid DNA encoding TGF-beta1. Bioact Mater. 2023;19:444-457.
[10] LI Z, LIN Z, LIU S, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell-derived miniature joint system for disease modeling and drug testing. Adv Sci. 2022;9(21):e2105909.
[11] DONTHU N, KUMAR S, MUKHERJEE D, et al. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines. J Bus Res. 2021;133: 285-296.
[12] YING L, MINDEN V, DAMLE A. Simple, direct and efficient multi-way spectral clustering. Inf Inference. 2019;8(1):181-203.
[13] FREEMAN LC. A set of measures of centrality based on betweenness. Sociometry. 1977;40(1):35-41.
[14] SMALL H. Co‐citation in the scientific literature: a new measure of the relationship between two documents. J Assoc Inf Sci. 2007;24(4): 265-269.
[15] CHEN C, IBEKWE‐SANJUAN F, HOU J. The structure and dynamics of cocitation clusters: a multiple‐perspective cocitation analysis. J Assoc Inf Sci Technol. 2010;61(7):1386-1409.
[16] 陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等.CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J].科学学研究,2015,33(2):242-253.
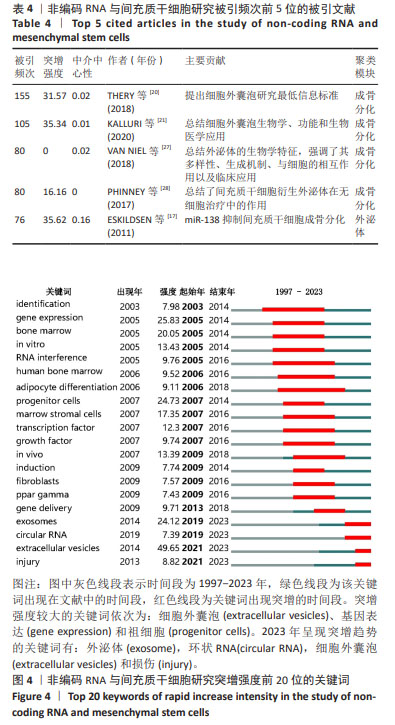
[17] ESKILDSEN T, TAIPALEENMAKI H, STENVANG J, et al. MicroRNA-138 regulates osteogenic differentiation of human stromal (mesenchymal) stem cells in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108(15):6139-6144.
[18] HUANG J, ZHAO L, XING L, et al. MicroRNA-204 regulates Runx2 protein expression and mesenchymal progenitor cell differentiation. Stem Cells. 2010;28(2):357-364.
[19] LIAN JB, STEIN GS, VAN WIJNEN AJ, et al. MicroRNA control of bone formation and homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012;8(4):212-227.
[20] THERY C, WITWER KW, AIKAWA E, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the international society for extracellular vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1535750.
[21] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977.
[22] WANG X, GUO B, LI Q, et al. miR-214 targets ATF4 to inhibit bone formation. Nat Med. 2013;19(1):93-100.
[23] LI D, LIU J, GUO B, et al. Osteoclast-derived exosomal miR-214-3p inhibits osteoblastic bone formation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10872.
[24] QI X, ZHANG J, YUAN H, et al. Exosomes secreted by human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells repair critical-sized bone defects through enhanced angiogenesis and osteogenesis in osteoporotic rats. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12(7):836-849.
[25] COLLINO F, DEREGIBUS MC, BRUNO S, et al. Microvesicles derived from adult human bone marrow and tissue specific mesenchymal stem cells shuttle selected pattern of miRNAs. PLoS One. 2010;5(7):e11803.
[26] CHEN TS, LAI RC, LEE MM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell secretes microparticles enriched in pre-microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010; 38(1):215-224.
[27] VAN NIEL G, D’ANGELO G, RAPOSO G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(4):213-228.
[28] PHINNEY DG, PITTENGER MF. Concise review: MSC-derived exosomes for cell-free therapy. Stem Cells. 2017;35(4):851-858.
[29] KOKOL P, BLAZUN VOSNER H, ZAVRSNIK J. Application of bibliometrics in medicine: a historical bibliometrics analysis. Health Info Libr J. 2021; 38(2):125-138.
[30] BORNMANN L, MUTZ R. Growth rates of modern science: a bibliometric analysis based on the number of publications and cited references. J Assoc Inf Sci Technol. 2015;66(11):2215-2222.
[31] MICHEEL J, SAFRASTYAN A, WOLLNY D. Advances in non-coding RNA sequencing. Noncoding RNA. 2021;7(4):70.
[32] 李晟,王国佐,朱正刚,等.基于国家自然科学基金资助项目分析miR-23研究现状[J].中国老年学杂志,2023,43(5):1243-1246.
[33] 刘田园,戴璇,石涵芬,等.2012-2022年国家自然科学基金骨质疏松相关项目研究分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(8):1121-1128.
[34] YU B, KIM HW, GONG M, et al. Exosomes secreted from GATA-4 overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells serve as a reservoir of anti-apoptotic microRNAs for cardioprotection. Int J Cardiol. 2015;182: 349-360.
[35] GONG M, YU B, WANG J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells release exosomes that transfer miRNAs to endothelial cells and promote angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(28):45200-45212.
[36] LEE JK, PARK SR, JUNG BK, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells suppress angiogenesis by down-regulating VEGF expression in breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e84256.
[37] KIM H, LEE MJ, BAE EH, et al. Comprehensive molecular profiles of functionally effective MSC-derived extracellular vesicles in immunomodulation. Mol Ther. 2020;28(7):1628-1644.
[38] ZHOU W, ZHOU Y, CHEN X, et al. Pancreatic cancer-targeting exosomes for enhancing immunotherapy and reprogramming tumor microenvironment. Biomaterials. 2021;268:120546.
[39] ZHU YG, FENG XM, ABBOTT J, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell microvesicles for treatment of Escherichia coli endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. Stem Cells. 2014;32(1):116-125.
[40] MA Y, WANG J, WANG Y, et al. The biphasic function of microglia in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 2017;157:247-272.
[41] LIU L, LIU Y, FENG C, et al. Lithium-containing biomaterials stimulate bone marrow stromal cell-derived exosomal miR-130a secretion to promote angiogenesis. Biomaterials. 2019;192:523-536.
[42] LIU W, YU M, CHEN F, et al. A novel delivery nanobiotechnology: engineered miR-181b exosomes improved osteointegration by regulating macrophage polarization. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19(1):269.
[43] LIU YJ, WANG C. A review of the regulatory mechanisms of extracellular vesicles-mediated intercellular communication. Cell Commun Signal. 2023;21(1):77.
[44] MEMCZAK S, JENS M, ELEFSINIOTI A, et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature. 2013;495(7441): 333-338.
[45] HANSEN TB, JENSEN TI, CLAUSEN BH, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013;495(7441):384-388.
[46] HE AT, LIU J, LI F, et al. Targeting circular RNAs as a therapeutic approach: current strategies and challenges. Sig Transduct Target Ther 2021;6(1):185.
[47] SUN M, YANG Y. Biological functions and applications of circRNA-next generation of RNA-based therapy. J Mol Cell Biol. 2023;15(5):mjad031.
[48] DOS SANTOS CC, AMATULLAH H, VASWANI CM, et al. Mesenchymal stromal (stem) cell therapy modulates miR-193b-5p expression to attenuate sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Eur Respir J. 2022;59(1): 2004216.
[49] SUN Z, WU J, BI Q, et al. Exosomal lncRNA TUG1 derived from human urine-derived stem cells attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by interacting with SRSF1 to regulate ASCL4-mediated ferroptosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):297.
[50] YU Z, WEN Y, JIANG N, et al. TNF-alpha stimulation enhances the neuroprotective effects of gingival MSCs derived exosomes in retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury via the MEG3/miR-21a-5p axis. Biomaterials. 2022;284:121484.
[51] WECHSLER ME, SHEVCHUK M, PEPPAS NA. Developing a multidisciplinary approach for engineering stem cell organoids. Ann Biomed Eng. 2020;48(7):1895-1904.
[52] WANG Y, ZONEFF ER, THOMAS JW, et al. Hydrogel oxygen reservoirs increase functional integration of neural stem cell grafts by meeting metabolic demands. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):457.
[53] YIN Z, QIN C, PAN S, et al. Injectable hyperbranched PEG crosslinked hyaluronan hydrogel microparticles containing mir-99a-3p modified subcutaneous ADSCs-derived exosomes was beneficial for long-term treatment of osteoarthritis. Mater Today Bio. 2023;23:100813.
[54] SUNG YK, KIM SW. Recent advances in the development of gene delivery systems. Biomater Res. 2019;23(1):8.
[55] TASSET A, BELLAMKONDA A, WANG W, et al. Overcoming barriers in non-viral gene delivery for neurological applications. Nanoscale. 2022;14(10):3698-3719.
[56] KIM SJ, KO WK, HAN GH, et al. Axon guidance gene-targeted siRNA delivery system improves neural stem cell transplantation therapy after spinal cord injury. Biomater Res. 2023;27(1):101.
[57] LIU S, LIU B, LI Q, et al. Transplantation of fibrin-thrombin encapsulated human induced neural stem cells promotes functional recovery of spinal cord injury rats through modulation of the microenvironment. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(2):440-446.
[58] WEI X, CAO S, MA W, et al. Intra-amniotic delivery of CRMP4 siRNA improves mesenchymal stem cell therapy in a rat spina bifida model. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;20:502-517. |