[1] WANG S, DUAN Y. LncRNA OIP5-AS1 inhibits the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response and promotes osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells by sponging miR-92a-3p. Bioengineered. 2022;13(5):12055-12066.
[2] ZHAO Y, QUAN Y, LEI T, et al. The role of inflammasome NLPR3 in the development and therapy of periodontitis. Int J Med Sci. 2022;19(10): 1603-1614.
[3] USKOKOVIC V, PEJCIC A, KOLIQI R, et al. Polymeric nanotechnologies for the treatment of periodontitis: A chronological review. Int J Pharm. 2022;625(1):122065-122086.
[4] LI C, QI Y, ZHOU Q, et al. Betulinic acid promotes the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells by upregulating EGR1. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021;53(10): 1266-1276.
[5] HUA L, ZHANG X. MALAT1 regulates osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells through mediating miR-155-5p/ETS1 axis. Tissue Cell. 2021;73(1):101619-101648.
[6] ADACHI O, SUGII H, ITOYAMA T, et al. Decorin promotes osteoblastic differentiation of Human periodontal ligament stem cells. Molecules. 2022;27(23):8224-8239.
[7] HOU J, XU J, LIU Y, et al. Sodium butyrate inhibits osteogenesis in human periodontal ligament stem cells by suppressing smad1 expression. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):301-310.
[8] LI SX, YAN W, LIU JP, et al. Long noncoding RNA SNHG4 remits lipopolysaccharide-engendered inflammatory lung damage by inhibiting METTL3 - Mediated m6A level of STAT2 mRNA. Mol Immunol. 2021;139(1):10-22.
[9] WU D, MA L. Downregulating microRNA-152-3p promotes the viability and osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells via targeting integrin alpha 5. Arch Oral Biol. 2020;120(1):104930-104939.
[10] SHI F, HE R, ZHU J, et al. miR-589-3p promoted osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells through targeting ATF1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):221-232.
[11] LI J, WANG Z, HUANG X, et al. Dynamic proteomic profiling of human periodontal ligament stem cells during osteogenic differentiation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):98-113.
[12] QUEIROZ A, ALBUQUERQUE-SOUZA E, GASPARONI LM, et al. Therapeutic potential of periodontal ligament stem cells. World J Stem Cells. 2021;13(6):605-618.
[13] 董霞,王训霞,杨芳.miR-34a对人牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的促进作用及其机制[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2021,47(6):1362-1370.
[14] 刘娟,陈斌,闫福华.富血小板血浆和浓缩生长因子对人牙周膜细胞增殖和成骨分化影响的研究[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2021,48(5): 520-527.
[15] 邹小炎,陈霞,冀道之,等.在牙周膜成纤维细胞中过表达 Lnc RNA-KAT7可抑制脂多糖诱导的炎症因子 IL-17 的表达[J/OL].实用口腔医学杂志.https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/61.1062.R. 20221115.0850.002.html
[16] LI J, JIN F, CAI M, et al. LncRNA nron inhibits bone resorption in periodontitis. J Dent Res. 2022;101(2):187-195.
[17] QIN Q, YANG H, ZHANG C, et al. lncRNA HHIP-AS1 promotes the osteogenic differentiation potential and inhibits the migration ability of periodontal ligament stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:5595580.
[18] 庄晓鹏,刘友东,郑宾宾,等.LncRNA SNHG4在结直肠癌中的表达及对细胞奥沙利铂耐药性的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2022, 22(2):207-212.
[19] 韩涵,喻鑫,周波,等.长非编码RNA-SNHG4促进胃癌细胞增殖生长并介导对化疗药物顺铂耐药性的研究[J].安徽医科大学学报, 2021,56(7):1047-1051.
[20] KAWANE T, QIN X, JIANG Q, et al. Runx2 is required for the proliferation of osteoblast progenitors and induces proliferation by regulating Fgfr2and Fgfr3. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):13551-13567.
[21] ZENG L, HE H, SUN M, et al. Runx2 and Nell-1 in dental follicle progenitor cells regulate bone remodeling and tooth eruption. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):486-498.
[22] KUSUYAMA J, AMIR MS, ALBERTSON BG, et al. JNK inactivation suppresses osteogenic differentiation,but robustly induces osteopontin expression in osteoblasts through the induction of inhibitor of DNAbinding 4 (Id4). FASEB J. 2019;33(6):7331-7347.
[23] 罗小玲,张丽,杨茂桦,等.柚皮素干预人牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化能力[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(7):1051-1056.
[24] WAN HY, SHIN RLY, CHEN JCH, et al. Dextran sulfate-amplified extracellular matrix deposition promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2022;140(1):163-177.
[25] YU Z, GAUTHIER P, TRAN QT, et al. Differential properties of human ALP+periodontal ligament stem cells vs their ALP-counterparts. J Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;5(7):292-302.
[26] ZHANG X, ZHANG Y, YANG L, et al. IRF4 suppresses osteogenic differentiation of BM-MSCs by transcriptionally activating miR-636/DOCK9 axis. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2022;77(1):100019-100024.
[27] WANG Q, LIN H, RAN J, et al. miR-200a-3p represses osteogenesis of human periodontal ligament stem cells by targeting ZEB2 and activating the NF-κB pathway. Acta Odontol Scand. 2022;80(2):140-149.
[28] ZHOU H, CHEN D, XIE G, et al. LncRNA-mediated ceRNA network was identified as a crucial determinant of differential effects in periodontitis and periimplantitis by high-throughput sequencing. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2020;22(3):424-450.
[29] SAYAD A, MIRZAJANI S, GHOLAMI L, et al. Emerging role of long non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of periodontitis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129(1):110362-110367.
[30] 李双庆,崔书伟,武瑞臣.miR-152-3p通过调控DUSP1对激素性股骨头坏死BMSCs成骨分化的作用研究[J].重庆医学,2022,51(14): 2341-2345.
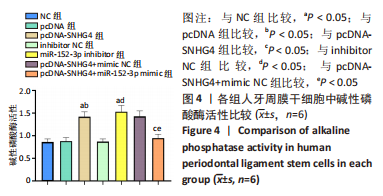
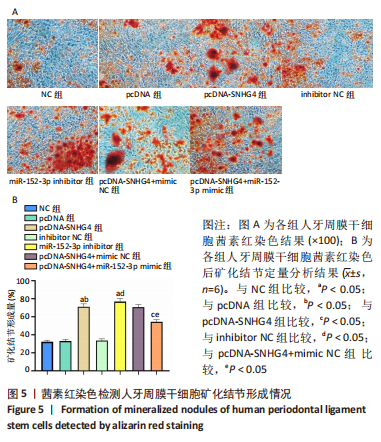
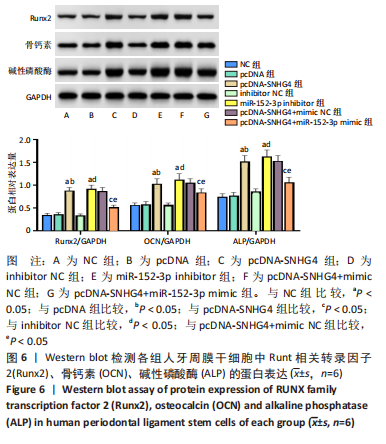
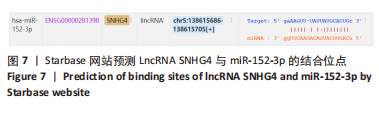
|