[1] CUI L, CHEN L, XIA W, et al. Vertebral fracture in postmenopausal Chinese women: a population-based study. Osteoporos Int. 2017; 28(9):2583-2590.
[2] RAJASEKARAN S, KANNA RM, SCHNAKE KJ, et al. Osteoporotic Thoracolumbar Fractures-How Are They Different? Classification and Treatment Algorithm. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31 Suppl 4:S49-S56.
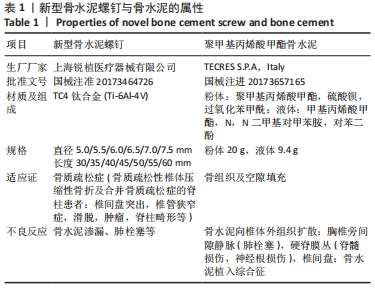
[3] 王复案,陈允震.骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折诊疗现状及其对策[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(5):590-594,599.
[4] 吴斗,刘强.骨质疏松性骨折手术治疗策略[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2019,25(5):581-584.
[5] OSTERHOUSE MD, KETTNER NW. Delayed posttraumatic vertebral collapse with intravertebral vacuum cleft. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2002;25(4):270-275.
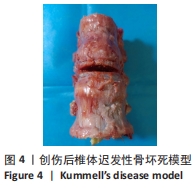
[6] YOUNG WF, BROWN D, KENDLER A, et al. Delayed post-traumatic osteonecrosis of a vertebral body (Kummell’s disease). Acta Orthop Belg. 2002; 68(1):13-19.
[7] CHEN L, DONG R, GU Y, et al. Comparison between Balloon Kyphoplasty and Short Segmental Fixation Combined with Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Kümmell’s Disease. Pain Physician. 2015;18(4):373-381.
[8] PEH WC, GELBART MS, GILULA LA, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: treatment of painful vertebral compression fractures with intraosseous vacuum phenomena. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003;180(5):1411-1417.
[9] MA R, CHOW R, SHEN FH. Kummell’s disease: delayed post-traumatic osteonecrosis of the vertebral body. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(7):1065-1070.
[10] LIU F, CHEN Z, LOU C, et al. Anterior reconstruction versus posterior osteotomy in treating Kümmell’s disease with neurological deficits: A systematic review. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2018;52(4):283-288.
[11] KRAUSS M, HIRSCHFELDER H, TOMANDL B, et al. Kyphosis reduction and the rate of cement leaks after vertebroplasty of intravertebral clefts. Eur Radiol. 2006;16(5):1015-1021.
[12] CHEN GD, LU Q, WANG GL, et al. Percutaneous Kyphoplasty for Kummell Disease with Severe Spinal Canal Stenosis. Pain Physician. 2015;18(6):E1021-1028.
[13] 陈峰,方文来.Kummell病的治疗进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2013,28(1):95-96.
[14] LEE SH, KIM ES, EOH W. Cement augmented anterior reconstruction with short posterior instrumentation: a less invasive surgical option for Kummell’s disease with cord compression. J Clin Neurosci. 2011; 18(4):509-514.
[15] HA KY, LEE JS, KIM KW, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for vertebral compression fractures with and without intravertebral clefts. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(5):629-633.
[16] NAKAMAE T, YAMADA K, TSUCHIDA Y, et al. Risk Factors for Cement Loosening after Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture with Intravertebral Cleft: A Retrospective Analysis. Asian Spine J. 2018; 12(5):935-942.
[17] LI HK, HAO DJ, YANG JS, et al. Percutaneous kyphoplasty versus posterior spinal fixation with vertebroplasty for treatment of Kümmell disease: A case-control study with minimal 2-year follow-up. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017; 96(51):e9287.
[18] ADAMSKA O, MODZELEWSKI K, STOLARCZYK A, et al. Is Kummell’s Disease a Misdiagnosed and/or an Underreported Complication of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures? A Pattern of the Condition and Available Treatment Modalities. J Clin Med. 2021;10(12): 2584.
[19] ZHU Y, CHENG J, YIN J, et al. Therapeutic effect of kyphoplasty and balloon vertebroplasty on osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(45):e17810.
[20] LOU S, SHI X, ZHANG X, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus non-operative treatment for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Osteoporos Int. 2019; 30(12):2369-2380.
[21] XU J, LIN J, LI J, et al. “Targeted Percutaneous Vertebroplasty” Versus Traditional Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture. Surg Innov. 2019;26(5):551-559.
[22] PIERCE TP, JAUREGUI JJ, ELMALLAH RK, et al. A current review of core decompression in the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2015;8(3):228-232.
[23] HANSEN EJ, SIMONY A, CARREON L, et al. Vertebroplasty vs. SHAM for Treating Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Double Blind RCT (VOPE) Integr. J Orthop Traumatol. 2019;2:1-6.
[24] WEI H, DONG C, ZHU Y, et al. Analysis of two minimally invasive procedures for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intravertebral cleft: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):401.
[25] PARK SJ, KIM HS, LEE SK, et al. Bone Cement-Augmented Percutaneous Short Segment Fixation: An Effective Treatment for Kummell’s Disease? J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015;58(1):54-59.
[26] CHO Y. Posterior Vertebrectomy and Circumferential Fusion for the Treatment of Advanced Thoracolumbar Kümmell Disease with Neurologic Deficit. Asian Spine J. 2017;11(4):634-640.
[27] HUANG YS, GE CY, FENG H, et al. Bone Cement-Augmented Short-Segment Pedicle Screw Fixation for Kümmell Disease with Spinal Canal Stenosis. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:928-935.
[28] TANG YC, GUO HZ, GUO DQ, et al. Effect and potential risks of using multilevel cement-augmented pedicle screw fixation in osteoporotic spine with lumbar degenerative disease. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):274.
[29] WANG B, WANG Y, ZHAO Q, et al. Pediculoplasty combined with vertebroplasty for the treatment of Kummell’s disease without neurological impairment: robot-assisted and fluoroscopy-guided. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(12):8019-8029.
[30] CHEN C, BIAN J, ZHANG W, et al. Unilateral versus bilateral vertebroplasty for severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014;27(8):E301-304.
|