中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (3): 380-384.doi: 10.12307/2023.003
• 组织工程骨材料 tissue-engineered bone • 上一篇 下一篇
3D打印聚醚醚酮材料修复颅骨缺损
翟红洁,韩冠达,李 磊,董小辉,姜之全,娄飞云
- 蚌埠医学院第一附属医院神经外科,安徽省蚌埠市 233000
3D printed polyetheretherketone material for skull defect repair
Zhai Hongjie, Han Guanda, Li Lei, Dong Xiaohui, Jiang Zhiquan, Lou Feiyun
- Department of Neurosurgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu 233000, Anhui Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
聚醚醚酮:是芳香族结晶型热塑性高分子材料,具有机械强度高、耐冲击、耐高温、耐酸碱、耐水解、耐辐照等特性,是与人体骨骼最接近的材料,因此可使用聚醚醚酮材料进行颅骨重建,为患者提供更好的颅骨修补材料。
嵌入式修补:是指聚醚醚酮材料形状和大小与缺损周围骨窗完全一致,可精准地嵌入到骨窗中,从而进行修补;包括聚醚醚酮材料四周的厚度与周围骨窗厚度一致,材料与骨窗内板与外板边缘精准对接,平滑衔接,使颅骨外表和内部更加光滑,既不会损伤内部脑组织也不会对头皮产生切割性伤害。
背景:在进行颅骨重建过程中,采用不同颅骨修补材料的术后效果有一定区别,术后并发症的发生也有较大差异。
目的:探讨采用3D打印聚醚醚酮材料行颅骨缺损成形的临床效果。
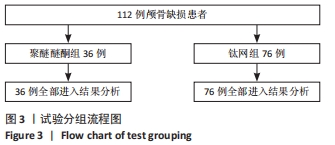
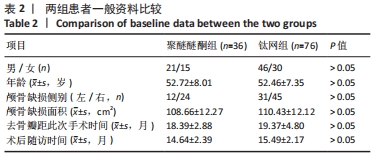
方法:选择蚌埠医学院第一附属医院2016年2月至2020年8月收治的112例颅骨缺损患者,其中男67例,女45例,均进行颅骨重建手术,其中36例使用3D打印聚醚醚酮材料,76例使用三维钛网材料。术后随访观察两组并发症发生情况,包括皮下积液、脑积水、硬膜外或硬膜下血肿、切口愈合不良或植入物外漏、感染等。
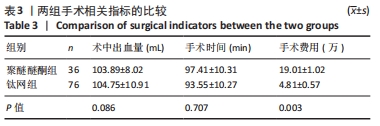
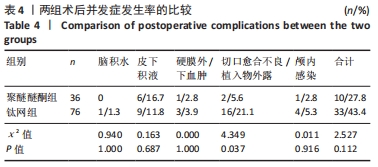
结果与结论:①聚醚醚酮组、钛网组患者分别获得术后(14.64±2.39),(15.49±2.17)个月随访,组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);两组均未出现因植入物材料原因导致植入失败的患者;②钛网组中33例患者出现并发症,其中1例为脑积水、9例为皮下积液、3例为硬膜外/下血肿、13例为切口愈合不良、3例为植入物外露、颅内感染4例,并发症发生率为43.4%;聚醚醚酮组中10例患者出现并发症,其中6例为皮下积液、1例为硬膜外/下血肿、2例为切口愈合不良、1例为颅内感染,并发症发生率为27.8%;两组术后总并发症发生率比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),但切口愈合不良/植入物外露发生率比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③结果表明,3D打印聚醚醚酮修补材料在颅骨缺损修补应用中具有良好的生物相容性,且安全性、精确性较好,相对于钛网材料在切口愈合方面具有更好的优势。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7687-5490 (翟红洁)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: