中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (19): 2999-3004.doi: 10.12307/2023.660
• 牙髓及牙周膜干细胞 Dental pulp and periodontal ligament stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
慢病毒介导沉默Smad2基因对人牙髓干细胞成骨向分化的作用
汪 畅1,孙 帅2,陈晓涛3,张晓莉3
- 1新疆医科大学,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830001;2徐州市口腔医院彭城门诊部,江苏省徐州市 221000;3新疆维吾尔自治区人民医院口腔科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830001
Effects of lentivirus mediated silencing of Smad2 gene on osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells
Wang Chang1, Sun Shuai2, Chen Xiaotao3, Zhang Xiaoli3
- 1Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830001, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Pengcheng Outpatient Department of Xuzhou Stomatological Hospital, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Department of Stomatology, People’s Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830001, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
短发夹或小发夹RNA (a small hairpin RNA or a short hairpin RNA,shRNA):是设计为能够形成发夹结构的非编码小RNA分子,常用于RNA干扰来抑制靶基因的表达。利用载体将shRNA导入细胞,在特定条件下载体可以稳定地整合到基因组中,从而使基因沉默被遗传。慢病毒载体:是体内外实验研究中最常用的载体之一,可高效地将外源性基因或外源的shRNA整合到宿主染色体中,并介导目的序列稳定表达,对一些较难转染的细胞如牙髓干细胞,能够显著提高目的基因或目的shRNA的转染效率。
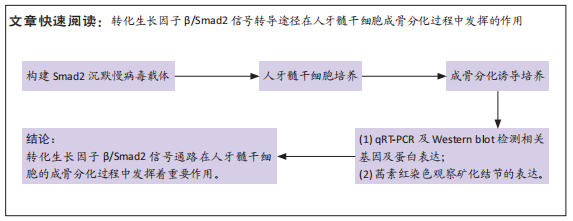
背景:人牙髓干细胞成骨分化的具体调控机制尚不明确,研究其具体机制对干细胞在组织工程中的应用有重要意义。
目的:探究慢病毒介导沉默Smad2基因对人牙髓干细胞成骨分化的影响。
方法:将培养的第3代人牙髓干细胞分为空白对照组、阴性对照组、Smad2-shRNA组和Smad2-shRNA+转化生长因子β3组。利用qRT-PCR技术检测成骨相关基因RUNX2、骨钙素、Smad2、Smad3及Smad4的 mRNA表达,利用Western blot技术检测RUNX2、骨钙素、Smad2/Smad3、p-Smad2/Smad3及Smad4的蛋白表达,各组细胞培养第7,14天进行茜素红染色。
结果与结论:①与阴性对照组及空白对照组比较,Smad2-shRNA组RUNX2、骨钙素、Smad2、Smad3和Smad4的mRNA表达量降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);与Smad2-shRNA组比较,Smad2-shRNA+转化生长因子β3组的骨钙素、Smad2、 Smad3及Smad4的mRNA表达量明显增高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);②与阴性对照组及空白对照组比较,Smad2-shRNA组RUNX2、骨钙素和Smad2/Smad3的蛋白表达量降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);与Smad2-shRNA组比较,Smad2-shRNA+转化生长因子β3组的RUNX2、骨钙素、Smad2/Smad3和Smad4的蛋白表达量明显增高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③使用常规培养基培养以及使用慢病毒载体转染不能诱导人牙髓干细胞的成骨分化,而转化生长因子β3能够正向调控人牙髓干细胞的成骨向分化;④结果表明,转化生长因子β/Smad2信号转导途径在人牙髓干细胞的成骨分化过程中发挥着重要作用。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8253-0173 (汪畅)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: