中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (19): 2986-2992.doi: 10.12307/2023.624
• 脐带脐血干细胞 umbilical cord blood stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
低氧预处理脐带间充质干细胞源外泌体抑制肺动脉平滑肌细胞的增殖
张雨薇1,2,刘川川2,3,毛稼琦2,张晴晴2,刘 红2,陈 英1,马 兰2
- 1青海大学医学部公共卫生系,青海省西宁市 810001;2青海大学高原医学研究中心,青海省西宁市 810001;3青海大学附属医院包虫病实验室,青海省西宁市 810001
Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes treated with hypoxic preconditioning inhibits proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells
Zhang Yuwei1, 2, Liu Chuanchuan2, 3, Mao Jiaqi2, Zhang Qingqing2, Liu Hong2, Chen Ying1, Ma Lan2
- 1Department of Public Health, Medical Department of Qinghai University, Xining 810001, Qinghai Province, China; 2High Altitude Medical Research Center of Qinghai University, Xining 810001, Qinghai Province, China; 3Hydatidosis Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Qinghai University, Xining 810001, Qinghai Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
低氧预处理:适当的低氧预处理可以改变细胞内氧自由基的产生,提高细胞的活性及代谢效能,以及增加移植后的细胞活力和存活率。外泌体:是由早期细胞膜内陷逐渐变为细胞膜释放的拥有多种生物功能的纳米级小囊泡,直径为30-150 nm。
背景:已有研究表明外泌体可以改善低氧性肺动脉高压,而且不同来源、不同环境的外泌体功能存在显著差别。低氧预处理脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体对大鼠肺动脉平滑肌细胞增殖的影响尚不清楚。
目的:探讨低氧预处理人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体对低氧诱导的大鼠肺动脉平滑肌细胞增殖的影响。
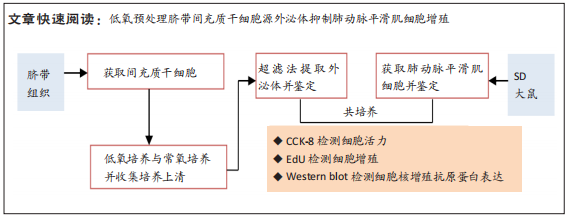
方法:采用组织贴壁法分离培养原代人脐带间充质干细胞,用超滤法提取人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体;采用组织消化法分离大鼠肺动脉平滑肌细胞,用CCK-8法测定不同质量浓度外泌体干预肺动脉平滑肌细胞不同时间后的细胞增殖抑制率,确定外泌体作用的适宜质量浓度和干预时间。将第3代肺动脉平滑肌细胞分为常氧对照组、低氧对照组、低氧+常氧外泌体处理组和低氧+低氧外泌体处理组,EdU法检测各组细胞增殖情况,Western blot检测各组细胞核增殖抗原蛋白表达水平。
结果与结论:①与常氧对照组相比,低氧对照组肺动脉平滑肌细胞增殖能力明显增加;与低氧对照组相比,低氧+常氧外泌体组细胞增殖能力下降,且低氧+低氧外泌体组增殖能力下降更明显;②与常氧对照组相比,低氧对照组细胞的细胞核增殖抗原蛋白表达升高;与低氧对照组相比,低氧+常氧外泌体组细胞核增殖抗原蛋白表达水平稍微降低,低氧+低氧外泌体组细胞核增殖抗原蛋白表达水平明显降低;③结果表明,低氧预处理人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体具有抑制肺动脉平滑肌细胞增殖的能力。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5313-5329 (张雨薇)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: