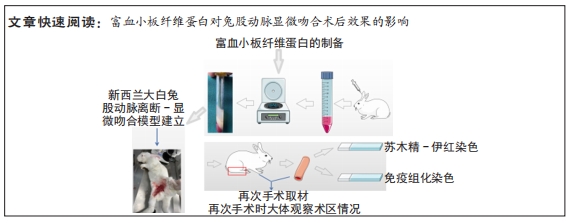
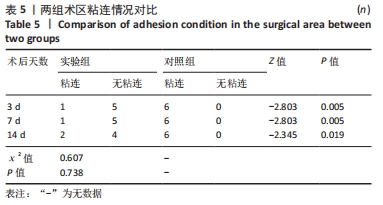
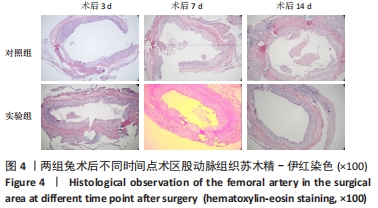
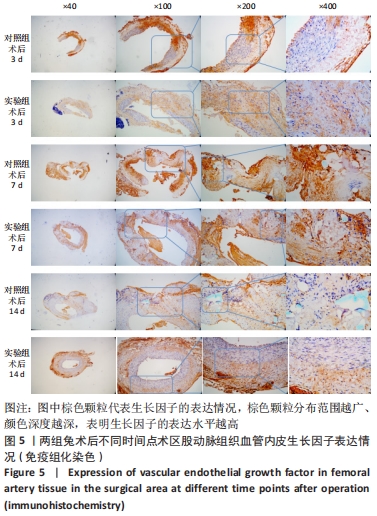
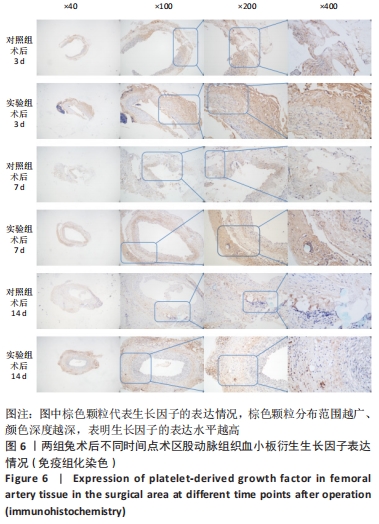
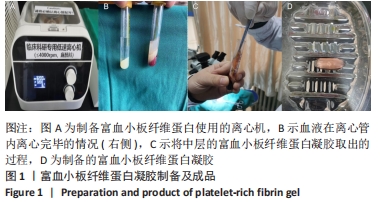
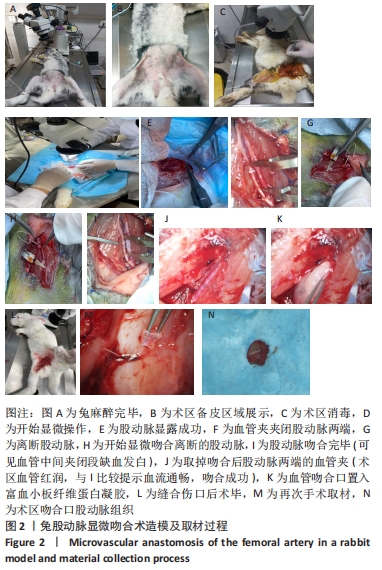
[1] PAKALA R, WILLERSON JT, BENEDICT CR. Effect of serotonin, thromboxane A2, and specific receptor antagonists on vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Circulation. 1997;96(7):2280-2286.
[2] 张铁慧, 梁武, 任远飞, 等. 含血管内皮生长因子缓释微粒显微缝线促进大鼠小血管吻合后的内皮再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(6):877-882.
[3] ZHANG L, SI T, FISCHER AJ, et al. Coaxial Electrospray of Ranibizumab-Loaded Microparticles for Sustained Release of Anti-VEGF Therapies. PLoS One. 2015; 10(8):e0135608.
[4] 贾亚超, 康庆林, 柴益民. 显微血管吻合术后血栓形成的防治进展[J]. 中华显微外科杂志,2015,38(2):205-208.
[5] HANASONO MM, BUTLER CE. Prevention and treatment of thrombosis in microvascular surgery. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2008;24(5):305-314.
[6] 肖得力, 孙崟喆, 崔城, 等. 浓缩生长因子纤维蛋白膜的制备及降解性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(34):5413-5419.
[7] KUBESCH A, BARBECK M, AL-MAAWI S, et al. A low-speed centrifugation concept leads to cell accumulation and vascularization of solid platelet-rich fibrin: an experimental study in vivo. Platelets. 2019;30(3):329-340.
[8] DOHAN EHRENFEST DM, PINTO NR, PEREDA A, et al. The impact of the centrifuge characteristics and centrifugation protocols on the cells, growth factors, and fibrin architecture of a leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF) clot and membrane. Platelets. 2018;29(2):171-184.
[9] CHIARAVALLOTI AJ, ZUBKOV B, ZUBKOV A. Treatment of a Chronic Cutaneous Surgical Wound With Platelet-Rich Fibrin. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44(3):449-452.
[10] BIELECKI T, DOHAN EHRENFEST DM. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF): surgical adjuvants, preparations for in situ regenerative medicine and tools for tissue engineering. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012;13(7):1121-1130.
[11] PHILLIPS R, DUDLEY H. The effect of tetracyline lavage and trauma on visceral and parietal peritoneal ultrastructure and adhesion formation. Br J Surg. 1984; 71(7):537-539.
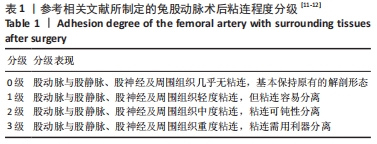
[12] 刘洋波. 几丁聚糖对显微血管吻合后血管壁愈合过程的影响研究[D]. 衡阳:南华大学,2007.
[13] MARUCCIA M, FATIGATO G, ELIA R, et al. Microvascular coupler device versus hand‐sewn venous anastomosis: A systematic review of the literature and data meta‐analysis. Microsurgery. 2020;40(5):608-617.
[14] 侯彪. 一种新型光敏粘合剂联合温敏材料泊洛沙姆行血管吻合的实验研究[D]. 衡阳:南华大学,2016.
[15] 查选平. 微型钛血管吻合夹吻合血管的实验研究[D]. 上海:第二军医大学,2002.
[16] 侯毅, 顾立强. 显微血管吻合技术的现状与展望[J]. 中华显微外科杂志,2014, 37(2):201-204.
[17] ZHANG SM, ZHU LH, CHEN HZ, et al. Interferon regulatory factor 9 is critical for neointima formation following vascular injury. Nat Commun. 2014;5(1):1-17.
[18] WEINTRAUB WS. The pathophysiology and burden of restenosis. Am J Cardiol. 2007;100(5A):3K-9K.
[19] SONG SH, KIM K, JO EK, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 12 is a novel regulator of vascular smooth muscle cell plasticity and fate. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016;36(9):1928-1936.
[20] SHI N, CHEN SY. Mechanisms simultaneously regulate smooth muscle proliferation and differentiation. J Biomed Res. 2014;28(1):40-46.
[21] 何凌锋, 李学渊, 王欣, 等. 断指再植术后不同用药方案的临床病例对照研究[J]. 中华手外科杂志,2014,30(3):230-231.
[22] 贾亚超. 内皮祖细胞在血管吻合术后血栓预防及血管修复中的作用[D]. 上海:上海交通大学,2016.
[23] KNAFL D, THALHAMMER F, VOSSEN MG. In-vitro release pharmacokinetics of amikacin, teicoplanin and polyhexanide in a platelet rich fibrin-layer (PRF)-a laboratory evaluation of a modern, autologous wound treatment. PLoS One. 2017;12(7):e0181090.
[24] CHOUKROUN J, ADDA F, SCHOEFFER C, et al. PRF: an opportunity in perio-implantology. Implantodontie, 2000;42:55-62.
[25] KARIMI K, BSC HR. The Benefits of Platelet-Rich Fibrin - ScienceDirect. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2019;27(3):331-340.
[26] UTOMO DN, MAHYUDIN F, HERNUGRAHANTO KD, et al. Implantation of platelet rich fibrin and allogenic mesenchymal stem cells facilitate the healing of muscle injury: An experimental study on animal. Int J Surg. 2018;11:4-9.
[27] MIRON RJ, FUJIOKA-KOBAYASHI M, BISHARA M, et al. Platelet-Rich Fibrin and Soft Tissue Wound Healing: A Systematic Review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2017;23(1):83-99.
[28] ANITUA E, NURDEN P, PRADO R, et al. Autologous fibrin scaffolds: When platelet- and plasma-derived biomolecules meet fibrin. Biomaterials. 2019;192:440-460.
[29] TALBOT S, FOSTER SL, WOOLF CJ. Neuroimmunity: Physiology and Pathology. Annu Rev Immunol. 2016;34(1):421-447.
[30] MEDZHITOV R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature. 2008; 454(7203):428-435.
[31] NASIRZADE J, KARGARPOUR Z, HASANNIA S, et al. Platelet Rich Fibrin Elicits an Anti inflammatory Response in Macrophages In Vitro. J Periodontol. 2020; 91(2):244-252.
[32] CIESLIK-BIELECKA A, DOHAN EHRENFEST DM, LUBKOWSKA A, et al. Microbicidal properties of Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Plasma/Fibrin (L-PRP/L-PRF): new perspectives. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2012;26(2 Suppl 1):43S-52S.
[33] 王煜慧, 吕慧欣, 张明锐, 等. 富血小板纤维蛋白促进牙龈组织修复和再生的研究[J]. 口腔医学研究,2022,38(2):144-149.
[34] 徐海燕, 刘斌, 戴太强, 等. PRF 促进小鼠全层皮肤损伤修复的实验研究[J]. 口腔医学研究,2017,33(8):816-819.
[35] NURDEN AT. The biology of the platelet with special reference to inflammation, wound healing and immunity. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2018;23(4):726-751.
[36] BAI MY, WANG CW, WANG JY, et al. Three-dimensional structure and cytokine distribution of platelet-rich fibrin. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2017; 72(2):116-124.
[37] MARTÍNEZ CE, SMITH PC, PALMA ALVARADO VA. The influence of platelet-derived products on angiogenesis and tissue repair: a concise update. Front Physiol. 2015;6:290.
[38] MELINCOVICI CS, BOSCA AB, SUSMAN S, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) - key factor in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2018;59(2):455-467.
[39] 冒慧敏, 史大卓, 刘秀华. 血小板源性生长因子对血管平滑肌细胞效应的机制研究进展[J]. 生理科学进展,2015,46(5):359-364.
[40] PARK ES, PA LEE K, JUNG SH, et al. Compound K, an intestinal metabolite of ginsenosides, inhibits PDGF-BB-induced VSMC proliferation and migration through G1 arrest and attenuates neointimal hyperplasia after arterial injury. Atherosclerosis. 2013;228(1):53-60.
[41] KIM JY, KIM KH, LEE WR, et al. Apamin inhibits PDGF-BB-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration through suppressions of activated Akt and Erk signaling pathway. Vasc Pharmacol. 2015;70:8-14.
[42] CHEN Z, CAI Y, ZHANG W, et al. Astragaloside IV inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-BB-stimulated proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via the inhibition of p38 MAPK signaling. Exp Ther Med. 2014;8(4):1253-1258.
[43] 朱晋坤, 毛华, 尹扬光, 等. 血小板源性生长因子和血小板源性内皮细胞生长因子在内皮细胞和血管平滑肌细胞中的作用研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2015, 18(9):1023-1028.
[44] DAVIS VL, ABUKABDA AB, RADIO NM, et al. Platelet-rich preparations to improve healing. Part I: workable options for every size practice. J Oral Implantol. 2014; 40(4):500-510.
[45] BARRIENTOS S, STOJADINOVIC O, GOLINKO MS, et al. Growth factors and cytokines in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2008;16(5):585-601.
[46] WU LM, WANG JK, LIU J, et al. Gait analysis combined with the expression of TGF-β1, TGF-β3 and CREB during Achilles tendon healing in rat. Chin J Traumatol. 2021;24(6):360-367.
[47] LIU X, JOSHI SK, RAVISHANKAR B, et al. Upregulation of transforming growth factor-β signaling in a rat model of rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(11):1709-1716.
[48] 周蓉芳. 自体纤维蛋白凝胶在甲状腺手术中的应用探索[D]. 衡阳:南华大学, 2019.
[49] 宋建星, 郭恩覃. 微型血管吻合夹与针线吻合方法的比较研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2001,15(5):312-314.
[50] 苏铁柱,宗双乐,齐巍,等.动脉硬化患者动静脉内瘘术不同血管吻合方法的临床效果比较[J]. 中国医药,2018,13(10):1544-1546.
[51] 郑守华,张水军,宋燕,等.人造血管动静脉端侧吻合移植手术71例体会[J].中华显微外科杂志,2017,40(2):185-187.
[52] 杨鹏鹏,李柯柯. 动静脉内瘘术中不同血管吻合方法在尿毒症并动脉硬化患者中的应用效果比较[J].河南医学研究,2021,30(5):867-869.
[53] 王思夏,战杰,石强,等. 应用微血管吻合器吻合动脉与静脉的临床体会[J]. 中华显微外科杂志,2015,38(1):84-85.
|