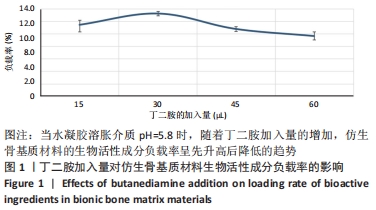
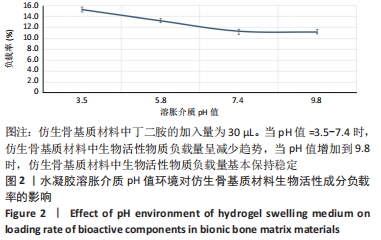
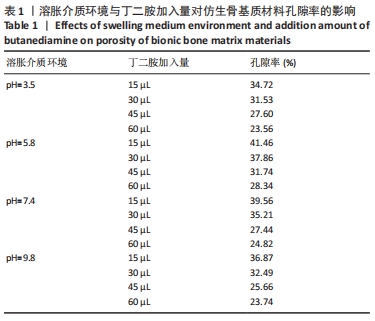
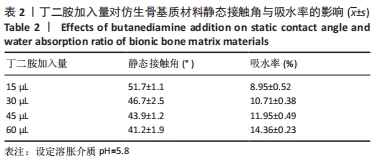
[1] CAMPANA V, MILANO G, PAGANO E, et al. Bone substitutes in orthopaedic surgery: from basic science to clinical practice. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25:2445-2461.
[2] QUARTO R, GIANNONI P. Bone tissue engineering: past-present-future Methods. Mol Biol. 2016;1416:21-33.
[3] SADEGHINIA A, SOLTANI S, AGHAZADEH M, et al. Design and fabrication of clinoptilolite-nanohydroxyapatite/chitosan-gelatin composite scaffold and evaluation of its effects on bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(2):221-233.
[4] CHEN P, LIU L, PAN J, et al. Biomimetic composite scaffold of hydroxyapatite/gelatin-chitosan core-shell nanofibers for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;97:325-335.
[5] MUSTAFA R, RAINER L, PHILIPP R, et al. Bone response to biomimetic implants delivering BMP-2 and VEGF:An immunohistochemical study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2013;41:826-835.
[6] STOCKMANN P, PARK J, VON WILMOWSKY C, et al. Guided bone regeneration in pig calvarial bone defects using autologous mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells-a comparison of different tissue sources. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2012;40:310-320.
[7] 赵鸣岐,黄威嫔,胡米,等.生物医用材料表面高分子基涂层的功能化构筑[J].材料导报,2019,33(1):27-33.
[8] YU W, LI R, LONG J, et al. Use of a three-dimensional printed polylactide-coglycolide/tricalcium phosphate composite scaffold incorporating magnesium powder to enhance bone defect repair in rabbits. J Orthop Transl. 2019;16:62-70.
[9] GUGLIELMOTTI MB, OLMEDO DG, CABRINI RL. Research on implants and osseointegration. Periodontology 2000. 2019;79(1):178-189.
[10] JANUARIYASA IK, ANA ID, YUSUF Y. Nanofibrous poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan contained carbonated hydroxyapatite nanoparticles scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020; 107:110347.
[11] HU Y, CHEN J, FAN T, et al. Biomimetic mineralized hierarchical hybrid scaffolds based on in situ synthesis of nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan/chondroitin sulfate/hyaluronic acid for bone tissue engineering. Colloids Surf B. 2017;157:93-100.
[12] COJOCARU FD, BALAN V, POPA MI, et al. Biopolymer calcium phosphates composites with inclusions of magnetic nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;125:612-620.
[13] KUTTAPPAN S, MATHEW D, NAIR MB. Biomimetic composite scaffolds containing bioceramics and collagen/gelatin for bone tissue engineering - A mini review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;93:1390-1401.
[14] PATEL PP, BUCKLEY C, TAYLOR BL, et al. Mechanical and biological evaluation of a hydroxyapatite-reinforced scaffold for bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(4):732-741.
[15] HU J, HOU Y, PARK H, et al. Visible light crosslinkable chitosan hydrogels for tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2012;8:1730-1738.
[16] NAZEER MA, YILGOR E, YILGOR I. Intercalated chitosan/hydroxyapatite nanocomposites: promising materials for bone tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;175:38-46.
[17] ZHU W, WANG M, FU YB, et al. Engineering a biomimetic three-dimensional nanostructured bone model for breast cancer bone metastasis study. Acta Biomater. 2015;14:164-174.
[18] IM O, LI J, WANG M, et al. Biomimetic three-dimensional nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite and magnetically synthesized single-walled carbon nanotube chitosan nanocomposite for bone regeneration. Int J Nanomed. 2012;7:2087-2099.
[19] SUBHADRA G, ARVIND SM. Biomimetic nanocomposites of carboxymethylcellulose-hydroxyapatite: Novel three dimensional load bearingbone grafts. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014;115:182-190.
[20] WANG JC, LIU CZ. Biomimetic Collagen/Hydroxyapatite Composite Scaffolds: Fabrication and Characterizations. J Bionic Eng. 2014;11:600-609.
[21] RONG CB, NAOKI K, CHEN GP. Influence of surfaces modified with biomimetic extracellular matriceson adhesion and proliferation of mesenchymal stem cells andosteosarcoma cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;126:381-386.
[22] SARKAR SK, LEE BT. Hard tissue regeneration using bone substitutes: an update on innovations in materials. Korean J Intern Med. 2015;30:279-293.
[23] DE WITTE TM, FRATILA-APACHITEI LE, ZADPOOR AA, et al. Bone tissue engineering via growth factor delivery: from scaffolds to complex matrices. Regen Biomater. 2018;5:197-211.
[24] ARABNEJAD S, BURNETT JOHNSTON R, PURA JA, et al. High-strength porous biomaterials for bone replacement: a strategy to assess the interplay between cell morphology, mechanical properties, bone ingrowth and manufacturing constraints. Acta Biomater. 2016;30:345-356.
[25] LIU F, MAO Z, ZHANG P, et al. Functionally graded porous scaffolds in multiple patterns: new design method, physical and mechanical properties. Mater Des. 2018;160: 849-860.
[26] WU S, LIU XM, KELVIN WK, et al. Biomimetic porous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng R Rep. 2014;80:1-36.
[27] WANG T, ZHAI Y, NUZZO M, et al. Layer-by-layer nanofiber-enabled engineering of biomimetic periosteum for bone repair and reconstruction. Biomaterials. 2018;182:279-288.
[28] JIANG H, ZUO Y, ZOU Q, et al. Biomimetic spiral-cylindrical scaffold based on hybrid chitosan/cellulose/nano-hydroxyapatite membrane for bone regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(22):12036-12044.
[29] AMIRTHALINGAM S, RAMESH A, LEE SS, et al. Injectable in Situ Shape-Forming Osteogenic Nanocomposite Hydrogel for Regenerating Irregular Bone Defects. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2018;1 (4):1037-1046.
[30] ROSETI L, PARISI V, PETRETTA M, et al. Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering: State of the art and new perspectives. Mater Sci Eng. 2017;78:1246-1262.
[31] LEE SS, KIM JH, JEONG J, et al. Sequential growth factor releasing double cryogel system for enhanced bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2020;257:120223.
[32] YAO Q, COSME JG, XU T, et al. Three dimensional electrospun PCL/PLA blend nanofibrous scaffolds with significantly improved stem cells osteogenic differentiation and cranial bone formation. Biomaterials. 2017;115:115-127.
[33] HUANG YZ, JI YR, KANG ZW, et al. Integrating eggshell-derived CaCO3/MgO nanocomposites and chitosan into a biomimetic scaffold for bone regeneration. Chem Eng J. 2020;395:125098.
[34] CHEN X, ZHU L, WEN W, et al. Biomimetic mineralisation of eggshell membrane featuring natural nanofiber network structure for improving its osteogenic activity. Colloid Surf B-Biointerfaces. 2019;179:299-308.
[35] ZHAO PP, GE YW, LIU XL, et al. Ordered arrangement of hydrated GdPO4 nanorods in magnetic chitosan matrix promotes tumor photothermal therapy and bone regeneration against breast cancer bone metastases. Chem Eng J. 2020;381:122694.
[36] OU Q, HUANG K, FU C, et al. Nanosilverincorporated halloysite nanotubes/gelatin methacrylate hybrid hydrogel with osteoimmunomodulatory and antibacterial activity for bone regeneration. Chem Eng J. 2019;382:123019.
[37] 彭坤,孙姣霞,李玉筱,等. MGF-Ct24E功能化聚乳酸仿生骨基质材料的制备与表征[J].功能材料,2014,14(45):14156-14160.
[38] 张通,蔡金池,袁志发,等.基于透明质酸的复合水凝胶修复骨关节炎软骨损伤: 应用与机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(4):617-625.
[39] PING H, WAGERMAIER WG, HORBELT N, et al. Mineralization generates megapascal contractile stresses in collagen fibrils. Science. 2022;376:188-192.
|