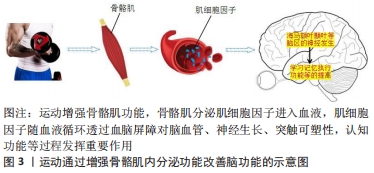
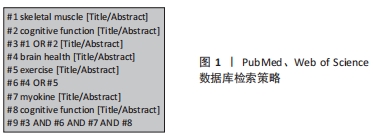
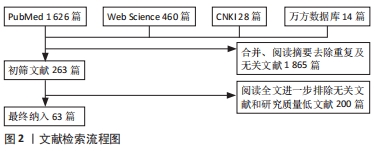
[1] CASTELLS-SáNCHEZ A, ROIG-COLL F, DACOSTA-AGUAYO R, et al. Exercise and fitness neuroprotective effects: molecular, brain volume and psychological correlates and their mediating role in healthy late-middle-aged women and men. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:615247.
[2] LIU-AMBROSE T, BARHA C, FALCK RS. Active body, healthy brain: Exercise for healthy cognitive aging. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019;147:95-120.
[3] BEKER N, GANZ A, HULSMAN M, et al. Association of cognitive function trajectories in centenarians with postmortem neuropathology, physical Health, and other risk factors for cognitive decline. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(1):e2031654.
[4] CHEN FT, HOPMAN RJ, HUANG CJ, et al. The effect of exercise training on brain structure and function in older Adults: a systematic review based on evidence from randomized control trials. 2020;9(4):914.
[5] 魏胜敏,高前进.运动对各年龄阶段人群脑健康的影响及机制研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2018,24(1):67-69.
[6] PEDERSEN BK. Physical activity and muscle-brain crosstalk. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019;15(7):383-392.
[7] SCISCIOLA L, FONTANELLA RA, SURINA, et al. Sarcopenia and cognitive function: role of myokines in muscle brain cross-talk. Life (Basel). 2021; 11(2):173.
[8] BENNIE JA, DE COCKER K, TITTLBACH S. The epidemiology of muscle strengthen-ing and aerobic physical activity guideline adherence among 24,016 German adults. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2021;31(5):1096-1104.
[9] BENNIE JA, DE COCKER K, SMITH JJ, et al. The epidemiology of muscle strengthen-ing exercise in Europe: A 28-country comparison including 280,605 adults. PLoS One. 2020;15(11):e0242220.
[10] PARRY HA, ROBERTS MD, KAVAZIS AN. Human skeletal muscle mitochondrial adaptations following resistance exercise training. Int J Sports Med. 2020;41(6):349-359.
[11] MCLEOD JC, STOKES T, PHILLIPS SM. Resistance exercise training as a primary countermeasure to age-related chronic disease. Front Physiol. 2019;10:645.
[12] WILKINSON DJ, PIASECKI M, ATHERTON PJ. The age-related loss of skeletal muscle mass and function: Measurement and physiology of muscle fibre atrophy and muscle fibre loss in humans. Ageing Res Rev. 2018;47:123-132.
[13] 首健, 陈佩杰, 肖卫华. 运动对老年骨骼肌的改善效应及其机制[J].中国康复医学杂志,2020,35(9):1140-1145.
[14] FRAGALA MS, CADORE EL, DORGO S, et al.Resistance training for older adults: position statement from the national strength and conditioning association. J Strength Cond Res. 2019;33(8):2019-2052.
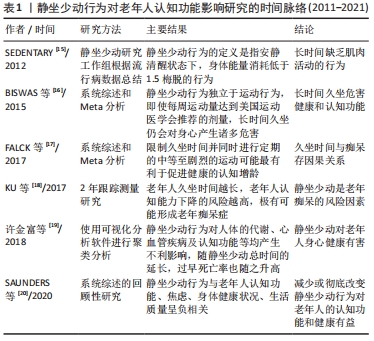
[15] SEDENTARY BRN. Letter to the editor: standardized use of the terms “sedentary” and “sendentary beviours” . Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2012;37(3):540-542.
[16] BISWAS A, OH PI, FAULKNER GE, et al. Sedentary time and it’s association with risk for disease incidence, mortality, and hospitalization in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intem Med. 2015; 162(2):123.
[17] FALCK RS, DAVIS JC, LIU-AMBROSE T. What is the association between sedentary behaviour and cognitive function? A systematic review. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(10):800-811.
[18] KU PW, LIU YT, LO MK, et al. Higher levels of objectively measured sedentary behavior is associated with worse cognitive ability: Two-year follow-up study in community-dwelling older adults. Exp Gerontol. 2017;99:110-114.
[19] 许金富,陈海春.国际静坐少动行为研究的知识图谱分析[J].山东体育学院学报,2018,34(6):109-116.
[20] SAUNDERS TJ, MCISAAC T, Douillette K, et al. Sedentary behaviour and health in adults: an overview of systematic reviews. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2020;45(10 (Suppl. 2)):S197-S217.
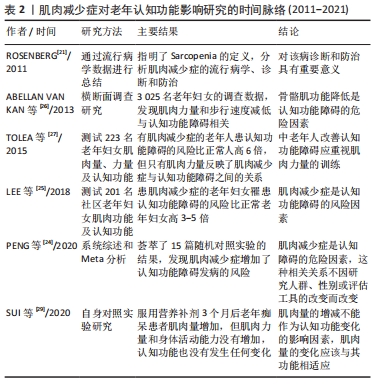
[21] ROSENBERG IH. Sarcopenia: origins and clinical relevance. Clin Geriatr Med. 2011;27(3):337-339.
[22] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019; 48(1):16-31.
[23] BIčIKOVá M, MáčOVá L, JANDVOá D, et al. Movement as a positive modulator of aging. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(12):6278.
[24] PENG TC, CHEN WL, WU LW, et al. Sarcopenia and cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Nutr. 2020; 39(9):2695-2701.
[25] LEE I, CHO J, HONG H, et al. Sarcopenia is associated with cognitive impairment and depression in elderly korean women. Iran J Public Health. 2018;47(3):327-334.
[26] ABELLAN VAN KAN G, CESARI M, GILLETTE-GUYONNET S, et al. Sarcopenia and cognitive impairment in elderly women: results from the EPIDOS cohort. Age Ageing. 2013;42(2):196-202.
[27] TOLEA MI, GALVIN JE. Sarcopenia and impairment in cognitive and physical performance. Clin Interv Aging. 2015;10:663-671.
[28] SUI SX, HOLLOWAY-KEW KL, HYDE NK, et al. Muscle strength and gait speed rather than lean mass are better indicators for poor cognitive function in older men. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):10367.
[29] SUI SX, WILLIAMS LJ, HOLLOWAY-KEW KL, et al. Skeletal Muscle Health and Cognitive Function: A Narrative Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;22(1):255.
[30] EMERENZIANI GP, VACCARO MG, IZZO G, et al. Prediction equation for estimating cognitive function using physical fitness parameters in older adults. PLoS One. 2020;15(5):e0232894.
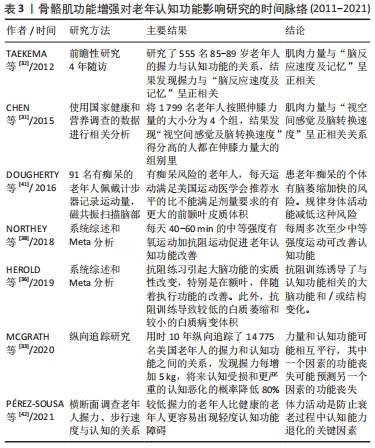
[31] CHEN WL, PENG TC, SUN YS, et al. Examining the association between quadriceps strength and cognitive performance in the elderly. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(32):e1335.
[32] TAEKEMA DG, LING CHY, KURRLE SE, et al. Temporal relationship between handgrip strength and cognitive performance in oldest old people. Age Ageing. 2012;41:506-512.
[33] MCGRATH R, VINCENT BM, HACKNEY KJ, et al. The longitudinal associations of handgrip strength and cognitive function in aging Americans. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020;21(5):634-639.
[34] HORTOBáGYI T, GRANACHER U, FERNANDEZ-DEL-OLMO M, et al. Functional relevance of resistance training-induced neuroplasticity in health and disease. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021;122:79-91.
[35] DE LA ROSA A, OLASO-GONZALEZ G, ARC-CHAGNAUD C, et al.Physical exercise in the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J Sport Health Sci. 2020;9(5):394-404.
[36] HEROLD F, TöRPEL A, SCHEGA L, et al. Functional and/or structural brain changes in response to resistance exercises and resistance training lead to cognitive improvements - a systematic review. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2019;16:10.
[37] BROADHOUSE KM, SINGH MF, SUO C, et al. Hippocampal plasticity underpins long-term cognitive gains from resistance exercise in MCI. Neuroimage Clin. 2020;25:102182.
[38] NORTHEY JM, CHERBUIN N, PUMPA KL, et al. Exercise interventions for cognitive function in adults older than 50: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2018;52(3):154-160.
[39] GUADAGNI V, DROGOS LL, TYNDALL AV, et al. Aerobic exercise improves cognition and cerebrovascular regulation in older adults. Neurology. 2020;94(21):e2245-e2257.
[40] PESCATELLO LS, ARENAR, RIEBE D, et al. ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription. America: WoltersKluwer. 2013:27.
[41] DOUGHERTY RJ, ELLINGSON LD, SCHULTZ SA, et al. Meeting physical activity recommendations may be protective against temporal lobe atrophy in older adults at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2016;4:14-17.
[42] PÉREZ-SOUSA MÁ, DEL POZO-CRUZ J, OLIVARES PR, et al. Role for physical fitness in the association between age and cognitive function in older adults: a mediation analysis of the SABE colombia study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(2):751.
[43] GOMARASCA M, BANFI G, LOMBARDI G. Myokines: The endocrine coupling of skeletal muscle and bone. Adv Clin Chem. 2020;94:155-218.
[44] BOSTRöM P, WU J, JEDRYVHOWSKI MP, et al. A PGC1α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012;81(7382):463-468.
[45] DE FREITAS GB, LOURENCO MV, DE FELICE FG. Protective actions of exercise-related FNDC5/-Irisin in memory and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem. 2020;155(6):602-611.
[46] BABAEI A, NOURSHAHI M, FANI M, et al. The effectiveness of continuous and interval exercise preconditioning against chronic unpredictable stress: Involvement of hippocampal PGC-1alpha/FNDC5/BDNF pathway. J Psychiatr Res. 2021;136:173-183.
[47] CHOI SH, BYLYKBASHI E, CHATILA ZK, et al. Combined adult neurogenesis and BDNF mimic exercise effects on cognition in an Alzheimer’s mouse model. Science. 2018;361(6404):eaan8821.
[48] LOPRINZI PD, FRITH E. A brief primer on the mediational role of BDNF in the exercise-memory link. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2019;39:9-14.
[49] KUSTER OC, LAPTINSKAYA D, FISSLER P, et al. Novel blood-based biomarkers of cognition, stress, and physical or cognitive training in older adults at risk of dementia: preliminary evidence for a role of BDNF, Irisin, and the kynurenine pathway. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;59(3):1097-111.
[50] PIGNATARO P, DICARLO M, ZERLOTIN R, et al. FNDC5/Irisin system in neuroinfla-mmation and neurodegenerative diseases: update and novel perspective. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1605.
[51] MOON HY, BECK A, BERRON D, et al. Running-induced systemic cathepsinB secretion is associated with memory function. Cell Metab. 2016;24(2):332-340.
[52] DE LA ROSA A, SOLANA E, CORPAS R, et al. Long-term exercise training improves memory in middle-aged men and modulates peripheral levels of BDNF and Cathep- sin B. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):3337.
[53] KOBILO T, YUAN C, VAN PRAAG H. Endurance factors improve hippocampal neurogenesis and spatial memory in mice. Learn Me. 2011;18(2):103-107.
[54] VALENZUELA PL, CASTILLO-GARCIA A, Morales JS, et al. Exercise benefits on Alzheimer’s disease: State-of-the-science. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;62:101108.
[55] KIM S, CHOI JY, MOON S, et al. Roles of myokines in exercise-induced improvement of neuropsychiatric function. Pflugers Arch. 2019;471(3): 491-505.
[56] VOSS MW, SOTO C, YOO S, et al. Exercise and Hippocampal Memory Systems. Trends Cogn Sci. 2019;23(4):318-333.
[57] GHOLAMNEZHAD Z, BOSKABADY MH, JAHANGIRI Z. Exercise and Dementia. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1228:303-315.
[58] RENDEIRO C, RHODES JS. A new perspective of the hippocampus in the origin of exercise-brain interactions. Brain Struct Funct. 2018; 223(6):2527-2545.
[59] BROADHOUSE KM, SINGH MF, SUO C, et al. Hippocampal plasticity underpins long-term cognitive gains from resistance exercise in MCI. Neuroimage Clin. 2020;25:102182.
[60] AARSLAND D. Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Dementia-Related Psychosis. J Clin Psychiatry. 2020; 81(5):AD19038BR1C.
[61] GARCIA-HERMOSO A, CAVERO-REDONDO I, RAMIREZ-VéLEZ R, et al. Muscular Strength as a Predictor of All-Cause Mortality in an Apparently Healthy Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Data From Approximately 2 Million Men and Women. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2018;99(10):2100-2113.
[62] CELIS-MORALES CA, WELSH P, LYALL DM, et al. Associations of grip strength with cardiovascular, respiratory, and cancer outcomes and all cause mortality: prospective cohort study of half a million UK Biobank participants. BMJ. 2018;361:k1651.
[63] SOYSAL P, HURST C, DEMURTAS J, et al.Handgrip strength and health outcomes: Umbrella review of systematic reviews with meta-analyses of observational studies. J Sport Health Sci. 2021;10(3):290-295.
|