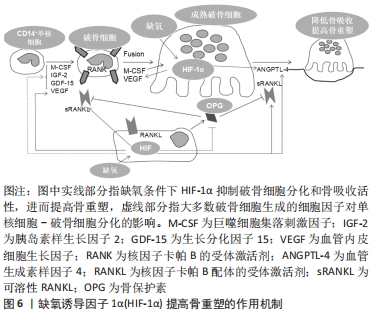
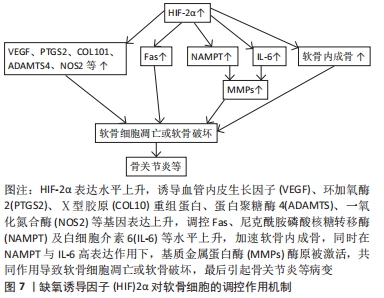
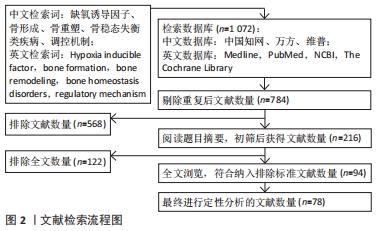
[1] SUN YL, PARK KH, YU HG, et al. Controlling hypoxia-inducible factor-2α is critical for maintaining bone homeostasis in mice. Bone Res. 2019;7(2):210-223.
[2] HELEN K. Hypoxic regulation of osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption activity. Hypoxia. 2015;3(3):73-82.
[3] DOMENE C, JORGENSEN C, Schofield CJ. Mechanism of molecular oxygen diffusion in a hypoxia-sensing prolyl hydroxylase using multiscale simulation. J Am Chem Soc. 2020;142(5)2253-2263.
[4] 张丹,任利玲.缺氧诱导因子1α在组织工程成骨和成血管中的作用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2016,30(4):504-508.
[5] SHOMENTO SH, CHAO W, CAO X, et al. Hypoxia‐inducible factors 1α and 2α exert both distinct and overlapping functions in long bone development. J Cell Biochem. 2010;109(1):196-204.
[6] HAHNE M, SCHUMANN P, MURSELL M, et al. Unraveling the role of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and HIF-2α in the adaption process of human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) to hypoxia: redundant HIF-dependent regulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Microvasc Res. 2018;116(16):34-44.
[7] DELGADO C JESUS. Osteocytes and their messengers as targets for the treatment of multiple myeloma. J Bone Miner Metab. 2017;15(1):49-56.
[8] GORDON J, MONTECINO MA, AQEILAN RI, et al. Epigenetic pathways regulating bone homeostasis: potential targeting for intervention of skeletal disorders. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2014;12(4):496-506.
[9] STEGEN S, CARMELIET G. Hypoxia, hypoxia-inducible transcription factors and oxygen-sensing prolyl hydroxylases in bone development and homeostasis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hy. 2019;28(4):328-335.
[10] ZOU D, ZHANG Z, HE J, et al. Blood vessel formation in the tissue-engineered bone with the constitutively active form of HIF-1α mediated BMSCs. Biomaterials. 2012;33(7):2097-2108.
[11] XU J, SUN Y, WU T, et al. Enhancement of bone regeneration with the accordion technique via HIF-1/VEGF activation in a rat distraction osteogenesis model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(2):1268-1276.
[12] 李昭,王学彬.缺氧诱导因子1α在风湿性疾病中的研究进展[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2018,22(1):54-57.
[13] HAI G, HONG Z, WU J, et al. The key role of microtubules in hypoxia preconditioning-induced nuclear translocation of HIF-1α in rat cardiomyocytes. Peer J. 2017;5(3):e3662.
[14] SARTORI-CINTRA AR, MARA CS, ARGOLO DL, et al. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) expression by interleukin-1β (IL-1 β), insulin-like growth factors I (IGF-I) and II (IGF-II) in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Clinics. 2012;67(1):35-40.
[15] FAYED HA, BARAKAT BM, ELSHAER SS, et al. Antiosteoporotic activities of isoquercitrin in ovariectomized rats: role of inhibiting hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;865(5):172785.
[16] 邵进,张岩,王治,等.低氧诱导因子1α参与骨发育及骨代谢调控的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(3):349-355.
[17] 解友邦,侯艳,杨红艳,等.HIF-1α对K562细胞血管生成相关因子的影响[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2019,27(5):1476-1481.
[18] 谢虎,李永忠,郭风劲,等.骨肉瘤中低氧诱导因子2α(HIF-2α),骨桥蛋白(OPN),血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)的表达及其临床意义[J].中国实验诊断学,2011,15(1):117-119.
[19] RYU JH, SHIN Y, HUH YH, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α regulates Fas-mediated chondrocyte apoptosis during osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19(3):440-450.
[20] SAITO T, FUKAI A, IKEDA T, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF-2α) controls sequential steps of endochondral ossification during skeletal growth and osteoarthritis progression. Bone. 2009,44(1):41-42.
[21] 赵光宗,方军,丁刚,等.拉喹莫德抑制成骨细胞中缺氧诱导因子2α的表达及其功能[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(7):917-924.
[22] 周文婷.HIF-1活性调控机制的研究进展[J].生理科学进展,2020, 51(6):443-448.
[23] YOON D, PASTORE YD, DIVOKY V, et al. Hypoxia-inducible Factor-1 Deficiency Results in Dysregulated Erythropoiesis Signaling and Iron Homeostasis in Mouse Development. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(35): 25703-25711.
[24] 张申尧,董克芳,王凡.红景天苷抵抗骨细胞凋亡的作用和对绝经后骨质疏松患者的影响[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2020,36(22): 3624-3629.
[25] 宋亚琼,周播江.低氧诱导因子1在调控骨骼肌缺氧时能量代谢发生适应性变化的机制研究进展[J].解剖学报,2017,48(2):236-240.
[26] 张俊宇,何鹏杰,程傲,等.缺氧复氧环境对成骨细胞自噬水平的影响[J].中华医学杂志,2019,99(11):844-849.
[27] YU TM, WEN MC, LI CY, et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) in infiltrating inflammatory cells is associated with chronic allograft dysfunction and predicts long-term graft survival. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013;28(3):659-670.
[28] 谢杨丽,翁士军,易玲娴,等.成年期软骨中敲除Vh1加速小鼠老年及不稳定所致骨性关节炎的进程[C].中华医学会第七次全国骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病学术会议论汇编,2013:258.
[29] 李晓娟,吴华,李浩,等.缺氧环境通过HIF-1α/YAP信号促进大鼠生长板软骨细胞表型维持[J].骨科,2019,10(2):134-139.
[30] WANG Y, WAN C, DENG L, et al. The hypoxia-inducible factor α pathway couples angiogenesis to osteogenesis during skeletal development. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(6):1616-1626.
[31] 刘晓东,邓廉夫,王君,等.低氧诱导因子1α在骨形成过程中对成骨细胞功能的调控作用[J].中华医学杂志,2007,87(47):3357-3361.
[32] SCHROEPPEL JP, CRIST JD, ANDERSON HC, et al. Molecular regulation of articular chondrocyte function and its significance in osteoarthritis. Histol Histopathol. 2011;26(3):377-394.
[33] 侯婧瑛,于萌蕾,郭天柱,等.缺氧预处理激活HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞生存和血管再生[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(7):985-990.
[34] BROWN ST, KELLY KF, DANIEL JM, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-2 alpha is required for the development of the catecholaminergic phenotype of sympathoadrenal cells. J Neurochem. 2009;110(2):622-630.
[35] DUCO K, LEJLA M, MARISKA V, et al. Nur77 variants solely comprising the amino-terminal domain activate hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and affect bone marrow homeostasis in mouse and man. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(39):15070-15083.
[36] MERCERON C, LEVI B, GIACCIA A J, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 2α is a negative regulator of osteoblastogenesis and bone mass accrual. Bone Res. 2019;7(1):91-104.
[37] ZHANG X, PRASADAM I, FANG W, et al. Chondromodulin-1 ameliorates osteoarthritis progression by inhibiting HIF-2α activity. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(11):1970-1980.
[38] LEE J Y, LEE K, LEE K, et al. Pharmacokinetic Characterization of LW6, a Novel Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α (HIF-1α) Inhibitor in Mice. Molecules. 2021;26(8):2226.
[39] HIRAGA T, KIZAKA-KONDOH S, HIROTA K, et al. Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 expression enhance osteolytic bone metastases of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67(9):4157-4163.
[40] 谢瑞燕,方雪玲, HAMZE I RAGE,等.红景天苷上调HIF-1α减轻高糖诱导的大鼠肾小球内皮细胞损伤[J].中国病理生理杂志,2019, 35(2):237-242.
[41] 杨梦思,周娜,王志钢,等.转录因子HIF-1α及其信号通路在疾病发生中的作用研究进展[J].生物技术通报,2016,32(8):8-13.
[42] JOHNSON RW, SCHIPANI E, GIACCIA AJ. HIF targets in bone remodeling and metastatic disease. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;150(150):169-177.
[43] 金培程,程正江.闭合复位髓内钉固定治疗股骨干骨折对VEGF, HIF-1α表达的影响[J].现代医学,2020,320(2):53-58.
[44] 闫奇奇,郝丽,张森.慢性肾脏病患者血清FGF23水平与钙磷代谢及临床相关性[J].安徽医科大学学报,2020,48(2):201-206.
[45] SCHIPANI E, WU C, RANKIN EB, et al. Regulation of bone marrow angiogenesis by osteoblasts during bone development and homeostasis. Front Endocrinol. 2013;4(85):1-6.
[46] RYU JH, YANG S, SHIN Y, et al. Interleukin-6 plays an essential role in hypoxia-inducible factor 2α-induced experimental osteoarthritic cartilage destruction in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2014;63(9):2732-2743.
[47] 范凯健,吴菁,李钦,等.基质金属蛋白酶13在软骨重塑和关节炎中的研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2018,34(5):607-611.
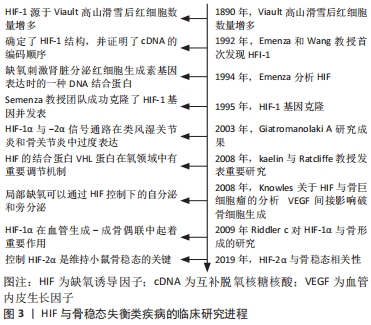
[48] GIATROMANOLAKI A, SIVRIDIS E, MALTEZOS E, et al. Upregulated hypoxia inducible factor-1α and -2α pathway in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rrd. Ther. 2003;5(4):193-201.
[49] 李启芳,王祥瑞.HIF-1α和HIF-2α对基因表达的调控[J].国际病理科学与临床杂志,2005,25(5):447-449.
[50] YIN ZN, FAN J, XIA WB. Tumor-induced osteomalacia. Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2018;4(4):119-127.
[51] 苏永蔚,周山健,肖大伟,等.负载miRNA-27b的BMSCs来源的外泌体治疗实验性骨关节炎[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(8):59-67.
[52] 张涛,徐枫,高明丽,等.右美托咪定对肺癌小鼠低氧时HIF-1α信号通路的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2019,39(9):1132-1134.
[53] COIMBRA IB, JIMENEZ SA, HAWKINS DF, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha expression in human normal and osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2004;12(4):336-345.
[54] 王莹,吴成爱,阎国强,等.胶原蛋白酶诱发兔膝关节骨性关节炎软骨组织中HIF2α表达上调[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(11): 1318-1322.
[55] 韩巧巧,王艳玲,朱月春木.NADPH氧化酶与HIF-α在肿瘤中的相互调控[J].命的化学,2016,36(5):691-697.
[56] ZHANG, FANG N, LUO W, et al. Role of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2015;82(3):144-147.
[57] MIYAMOTO T. Mechanism underlying post-menopausal osteoporosis: HIF1α is required for osteoclast activation by estrogen deficiency. Keio J Med. 2015;64(3):44-47.
[58] RIDDLE RC, KHATRI R, SCHIPANI E, et al. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in angiogenic–osteogenic coupling. J Mol Med. 2009;87(6): 583-590.
[59] LI L, QU Y, JIN X, et al. Protective effect of salidroside against bone loss via hypoxia-inducible factor-1α pathway-induced angiogenesis. Sci Rep. 2016;25(6):32131.
[60] 倪晓琳,夏维波.肿瘤性骨软化症的致病机制及治疗方法[J].中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志,2020,13(6):547-555.
[61] WAGEGG M, GABER T, LOHANATHA FL, et al. Hypoxia promotes osteogenesis but suppresses adipogenesis of human mesenchymal stromal cells in a hypoxia-inducible factor-1 dependent manner. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):46483.
[62] SHAO J, ZHANG Y, YANG T, et al. HIF-1α disturbs osteoblasts and osteoclasts coupling in bone remodeling by up-regulating OPG expression. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2015;51(51):808-814.
[63] ONUORA S. Osteoarthritis: Cartilage matrix stiffness regulates chondrocyte metabolism and OA pathogenesis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(9):504.
[64] MING L, DAN W, NING L. MicroRNA-20b downregulates HIF-1α and inhibits the proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Res. 2016;23(5):257-266.
[65] KOUVARAS E, CHRISTONI Z, SIASIOS I, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor in cartilage tumors. Biotech Histochem. 2019;94(4):283-289.
[66] WANG Y, YAO J, MENG H, et al. A novel long non-coding RNA, hypoxia-inducible factor-2α promoter upstream transcript, functions as an inhibitor of osteosarcoma stem cells in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2015; 11(4):2534-2540.
[67] 滑雅娜,鲁芙爱,王永福. HIF-1相关信号通路及其在自身免疫性疾病中作用[J].中国免疫学杂志,2019,35(8):1013-1017.
[68] YANG G, SUN Q, TENG Y, et al. PTEN deficiency causes dyschondroplasia in mice by enhanced hypoxia-inducible factor 1α signaling and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Development. 2008;135(21):3587-3597.
[69] 陈焕,张燕,刘梦思,等.肢端肥大症患者骨转换标记物和骨平衡变化及其影响因素分析[J].中华医学杂志,2021,101(33):2600-2605.
[70] 杨庆诚,曾炳芳,施忠民,等.组蛋白去乙酰化酶抑制剂对骨肉瘤侵袭性及HIF-1α表达的影响[J].肿瘤,2008,28(6):472-475.
[71] ZHOU XF, GUO XJ, CHEN M, et al. HIF-3α promotes metastatic phenotypes in pancreatic cancer by transcriptional regulation of the RhoC-ROCK1 signaling pathway. Mol Cancer Res. 2018;16(1):124-134.
[72] ZULKIFLI AF, TOSHIHARU Y, OSAMU O. Deterioration of alveolar development in mice with both HIF-3α knockout and HIF-2α knockdown. BMC Res Notes. 2018;11(1):449-452.
[73] ANDO H, NATSUME A, IWAMI K, et al. A hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-3α splicing variant, HIF-3α4 impairs angiogenesis in hypervascular malignant meningiomas with epigenetically silenced HIF-3α4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;433(1):139-144.
[74] LI QF, WANG XR, YANG YW, et al. Hypoxia upregulates hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-3alpha expression in lung epithelial cells: characterization and comparison with HIF-1alpha. Cell Res. 2006;16(6):548-558.
[75] CHEN WC, CHI CH, CHUANG CC, et al. Three novel EXT1 and EXT2 gene mutations in taiwan patients with multiple exostoses. J Formos Med Assoc. 2006;105(5):434-437.
[76] RUAN W, CAO L, CHEN Z, et al. Novel exostosin-2 mutation identified in a Chinese family with hereditary multiple osteochondroma. Oncol Lett. 2018;15(4):4383-4389.
[77] LEMOS MC, PETER K, CHRISTIE PT, et al. A novel EXT1 splice site mutation in a kindred with hereditary multiple exostosis and osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metat. 2005,90(9):5386-5392.
[78] BAASANJAV S, JAMSHEER A, KOLANCZYK M, et al. Osteopoikilosis and multiple exostoses caused by novel mutations in LEMD3 and EXT1 genes respectively - coincidence within one family. BmC Med Genet. 2010;11(1):110.
|