[1] FILIP S, GüNTER F. Vascularization strategies in bone tissue engineering. Cells. 2021;10(7):1749.
[2] 王子瑞,朱金亮,何志敏,等.人工合成骨修复材料的临床应用及展望[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2021,18(4):8-17.
[3] DE BAAIJ JH, HOENDEROP JG, BINDELS RJ. Magnesium in man:implications for health and disease. Physiol Rev. 2015;95(1):1-46.
[4] ZOFKOVA I, DAVIS M, BLAHOS J. Trace elements have beneficial, as well as detrimental effects on bone homeostasis. Physiol Res. 2017;66(3):391-402.
[5] 崔云霞,李保胜,韩春雨,等.生物可降解医用镁合金应用于骨缺损修复中的研究展望 [J]. 现代口腔医学杂志,2019,33(1):46-49.
[6] 刘印,马敏先.镁离子在骨再生应用的研究进展[J].生物医学工程与临床, 2021,25(4):522-526.
[7] 施泽文,刘辰,陈先军,等.表面改性可降解镁的生物性能及其在骨修复领域的应用[J].国际骨科学杂志,2021,42(4):226-230.
[8] WU L, LUTHRINGER BJ, FEYERABEND F, et al. Effects of extracellular magnesium on the differentiation and function of human osteoclasts. Acta Biomater. 2014; 10(6):2843-2854.
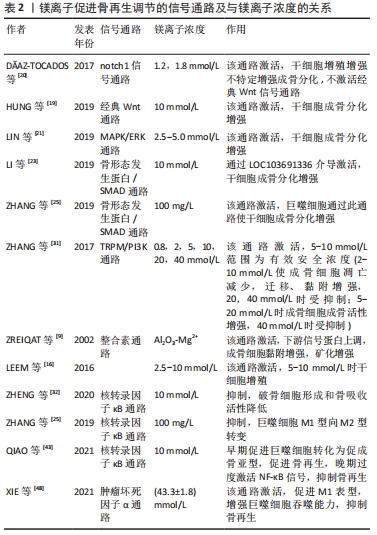
[9] ZREIQAT H, HOWLETT CR, ZANNETTINO A, et al. Mechanisms of magnesium-stimulated adhesion of osteoblastic cells to commonly used orthopaedic implants. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;62(2):175-184.
[10] AL ALAWI AM, MAJONI SW, FALHAMMAR H. Magnesium and human health: perspectives and research directions. Int J Endocrinol. 2018;2018:9041694.
[11] CASTIGLIONI S, ROMEO V, LOCATELLI L, et al. TRPM7 and MagT1 in the osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):16195.
[12] ZHENG J, MAO X, LING J, et al. Role of magnesium transporter subtype 1 (magt1) in the osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow stem cells. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016;171(1):131-137.
[13] ZHENG JM, KONG YY, LI YY, et al. MagT1 regulated the odontogenic differentiation of BMMSCs induced byTGC-CM via ERK signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):48.
[14] CHEN Y, LU X, ZHAO F, et al. A study on the biocompatibility of mgo coating prepared by anodic oxidation method on magnesium metal. J Bionic Eng. 2020; 17(1):76-91.
[15] YUAN Z, WEI P, HUANG Y, et al. Injectable PLGA microspheres with tunable magnesium ion release for promoting bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2019; 85:294-309.
[16] LEEM YH, LEE KS, KIM JH, et al. Magnesium ions facilitate integrin alpha 2- and alpha 3-mediated proliferation and enhance alkaline phosphatase expression and activity in hBMSCs. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;10(10):E527-E536.
[17] KUNYU Z, SIEN L, QIAN F, et al. Nanocomposite hydrogels stabilized by self-assembled multivalent bisphosphonate-magnesium nanoparticles mediate sustained release of magnesium ion and promote in-situ bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2017;64:389-400.
[18] WANG J, XU J, SONG B, et al. Magnesium (Mg) based interference screws developed for promoting tendon graft incorporation in bone tunnel in rabbits. Acta Biomater. 2017;63:393-410.
[19] HUNG CC, CHAYA A, LIU K, et al. The role of magnesium ions in bone regeneration involves the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Acta Biomater. 2019;98:246-255.
[20] DÃAZ-TOCADOS JM, HERENCIA C, MARTÃNEZ-MORENO JM, et al. Magnesium chloride promotes osteogenesis through notch signaling activation and expansion of mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):7839.
[21] LIN S, YANG G, JIANG F, et al. A magnesium-enriched 3D culture system that mimics the bone development microenvironment for vascularized bone regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019;6(12):1900209.
[22] WANG L, WANG Y, LI Z, et al. Differential expression of long noncoding ribonucleic acids during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Int Orthop. 2015;39(5):1013-1019.
[23] LI D, YU K, XIAO T, et al. LOC103691336/miR-138-5p/BMPR2 axis modulates Mg-mediated osteogenic differentiation in rat femoral fracture model and rat primary bone marrow stromal cells. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(11):21316-21330.
[24] ZHANG Y, XU J, RUAN YC, et al. Implant-derived magnesium induces local neuronal production of CGRP to improve bone-fracture healing in rats. Nat Med. 2016;22(10):1160-1169.
[25] ZHANG X, CHEN Q, MAO X, et al. Magnesium Enhances Osteogenesis of BMSCs by Tuning Osteoimmunomodulation. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:7908205.
[26] QIAN W, LEI X, REGINE W, et al. Macrophage-derived oncostatin M/bone morphogenetic protein 6 in response to Mg-based materials influences pro-osteogenic activity of human umbilical cord perivascular cells. Acta Biomater. 2020;133:268-279.
[27] MARADZE D, MUSSON D, ZHENG Y, et al. High magnesium corrosion rate has an effect on osteoclast and mesenchymal stem cell role during bone remodelling. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):10003.
[28] SUN Y, LIU H, SUN X, et al. In vitro and in vivo study on the osseointegration of magnesium and strontium ion with two different proportions of mineralized collagen and its mechanism. J Biomater App. 2021;36(3):528-540.
[29] BURMESTER A, WILLUMEIT-ROMER R, FEYERABEND F. Behavior of bone cells in contact with magnesium implant material. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105(1):165-179.
[30] GAO P, FAN B, YU X, et al. Biofunctional magnesium coated Ti6Al4V scaffold enhances osteogenesis and angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo for orthopedic application. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(3):680-693.
[31] ZHANG X, ZU H, ZHAO D, et al. Ion channel functional protein kinase TRPM7 regulates Mg ions to promote the osteoinduction of human osteoblast via PI3K pathway:In vitro simulation of the bone-repairing effect of Mg-based alloy implant. Acta Biomater. 2017;63:369-382.
[32] ZHENG LZ, WANG JL, XU JK, et al. Magnesium and vitamin C supplementation attenuates steroid-associated osteonecrosis in a rat model. Biomaterials. 2020; 238:119828.
[33] ANDREIA C, FRANCISCO R-G, IñAKI G-A, et al. Characterization of magnesium doped sol-gel biomaterial for bone tissue regeneration:The effect of Mg ion in protein adsorption. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;125:112114.
[34] CHOI S, KIM KJ, CHEON S, et al. Biochemical activity of magnesium ions on human osteoblast migration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;531(4):588-594.
[35] LIU C, YANG G, ZHOU M, et al. Magnesium ammonium phosphate composite cell-laden hydrogel promotes osteogenesis and angiogenesis in vitro. ACS Omega. 2021;6(14):9449-9459.
[36] YANG Y, WANG H, YANG H, et al. Magnesium-based whitlockite bone mineral promotes neural and osteogenic activities. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(10): 5785-5796.
[37] ZHANG X, HUANG P, JIANG G, et al. A novel magnesium ion-incorporating dual-crosslinked hydrogel to improve bone scaffold-mediated osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;121:111868.
[38] TIAN L, SHENG Y, HUANG L, et al. An innovative Mg/Ti hybrid fixation system developed for fracture fixation and healing enhancement at load-bearing skeletal site. Biomaterials. 2018;180:173-183.
[39] BELéN RRG, MANUEL DLJ, MICHELE I, et al. Biomimetic mineralization of recombinant collagen type I derived protein to obtain hybrid matrices for bone regeneration. J Struct Biol. 2016;196(2):138-146.
[40] HE LY, ZHANG XM, LIU B, et al. Effect of magnesium ion on human osteoblast activity. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2016;49(7):e5257.
[41] JäHN K, SAITO H, TAIPALEENMäKI H, et al. Intramedullary Mg2Ag nails augment callus formation during fracture healing in mice. Acta Biomater. 2016;36:350-360.
[42] TAKUYA N, MIYUKI K, AKIKO H, et al. Role of lysosomal channel protein TPC2 in osteoclast differentiation and bone remodeling under normal and low-magnesium conditions. J Biol chem. 2017;292(51):20998-1010.
[43] QIAO W, WONG KHM, SHEN J, et al. TRPM7 kinase-mediated immunomodulation in macrophage plays a central role in magnesium ion-induced bone regeneration. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):2885.
[44] WANG M, YU Y, DAI K, et al. Improved osteogenesis and angiogenesis of magnesium-doped calcium phosphate cement via macrophage immunomodulation. Biomater Sci. 2016;4(11):1574-1583.
[45] COSTANTINO MD, SCHUSTER A, HELMHOLZ H, et al. Inflammatory response to magnesium-based biodegradable implant materials. Acta Biomater. 2020;101: 598-608.
[46] BESSA-GONçALVES M, SILVA AM, BRáS JP, et al. Fibrinogen and magnesium combination biomaterials modulate macrophage phenotype, NF-kB signaling and crosstalk with mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Acta Biomater. 2020;114:471-484.
[47] ZHENG Z, CHEN Y, HONG H, et al. The “Yin and Yang” of immunomodulatory magnesium-enriched graphene oxide nanoscrolls decorated biomimetic scaffolds in promoting bone regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(2):e2000631.
[48] XIE K, WANG N, GUO Y, et al. Additively manufactured biodegradable porous magnesium implants for elimination of implant-related infections: an in vitro and in vivo study. Bioact Mater. 2021;8:140-152.
[49] 李旭, 陈依民, 王鼎予, 等.骨血管形成机制及功能的研究进展[J].解剖学报, 2019,50(5):703-706.
[50] GU Y, ZHANG J, ZHANG X, et al. Three-dimensional printed mg-doped β-TCP bone tissue engineering scaffolds:effects of magnesium ion concentration on osteogenesis and angiogenesis in vitro. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;16(4):415-429.
[51] XU L, WILLUMEIT-ROMER R, LUTHRINGER-FEYERABEND B. Hypoxia influences the effects of magnesium degradation products on the interactions between endothelial and mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2020;101:624-636.
[52] LIU W, GUO S, TANG Z, et al. Magnesium promotes bone formation and angiogenesis by enhancing MC3T3-E1 secretion of PDGF-BB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;528(4):664-670.
[53] XU L, WILLUMEIT-ROMER R, LUTHRINGER-FEYERABEND BJC. Effect of magnesium-degradation products and hypoxia on the angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Acta Biomater. 2019;98:269-283.
[54] ZHU D, YOU J, ZHAO N, et al. Magnesium regulates endothelial barrier functions through TRPM7, MagT1, and S1P1. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019;6(18):1901166.
[55] GU Y, ZHANG J, ZHANG X, et al. Three-dimensional printed Mg-doped beta-TCP bone tissue engineering scaffolds: effects of magnesium ion concentration on osteogenesis and angiogenesis in vitro. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;16(4):415-429.
[56] MA L, CHENG S, JI X, et al. Immobilizing magnesium ions on 3D printed porous tantalum scaffolds with polydopamine for improved vascularization and osteogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;117:111303.
[57] HAMUSHAN M, CAI W, ZHANG Y, et al. High-purity magnesium pin enhances bone consolidation in distraction osteogenesis model through activation of the VHL/HIF-1alpha/VEGF signaling. J Biomater Appl. 2020;35(2):224-236.
[58] YE L, XU J, MI J, et al. Biodegradable magnesium combined with distraction osteogenesis synergistically stimulates bone tissue regeneration via CGRP-FAK-VEGF signaling axis. Biomaterials. 2021;275:120984.
[59] KUSUMBE AP, RAMASAMY SK, ADAMS RH. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014;507(7492): 323-328.
[60] RAMASAMY SK, KUSUMBE AP, WANG L, et al. Endothelial Notch activity promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis in bone. Nature. 2014;507(7492):376-380.
[61] KENSWIL KJG, JARAMILLO AC, PING Z, et al. Characterization of endothelial cells associated with hematopoietic niche formation in humans identifies IL-33 as an anabolic factor. Cell Rep. 2018;22(3):666-678.
[62] HAN HS, JUN I, SEOK HK, et al. Biodegradable magnesium alloys promote angio-osteogenesis to enhance bone repair. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(15):2000800.
[63] STAIGER MP, PIETAK AM, HUADMAI J, et al. Magnesium and its alloys as orthopedic biomaterials:a review. Biomaterials. 2006;27(9):1728-1734.
[64] ZHANG C, LIN J, NGUYEN NT, et al. Antimicrobial bioresorbable Mg-Zn-Ca alloy for bone repair in a comparison study with Mg-Zn-Sr alloy and pure Mg. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(1):517-538.
[65] OSHIBE N, MARUKAWA E, YODA T, et al. Degradation and interaction with bone of magnesium alloy WE43 implants: a long-term follow-up in vivo rat tibia study. J Biomater Appl. 2019;33(9):1157-1167.
[66] HAN J, WAN P, GE Y, et al. Tailoring the degradation and biological response of a magnesium-strontium alloy for potential bone substitute application. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;58:799-811.
[67] LIU C, FU X, PAN H, et al. Biodegradable Mg-Cu alloys with enhanced osteogenesis, angiogenesis, and long-lasting antibacterial effects. Sci Rep. 2016;6:27374.
[68] CHEN Y, DOU J, YU H, et al. Degradable magnesium-based alloys for biomedical applications: the role of critical alloying elements. J Biomater Appl. 2019;33(10): 1348-1372.
[69] YU K, DAI Y, LUO Z, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of novel biodegradable Mg-Ag-Y alloys for use as resorbable bone fixation implant. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(7):2059-2069.
[70] YANG J, KOONS GL, CHENG G, et al. A review on the exploitation of biodegradable magnesium-based composites for medical applications. Biomed Mater. 2018; 13(2):022001.
[71] ROJAEE R, FATHI M, RAEISSI K. Comparing nanostructured hydroxyapatite coating on AZ91 alloy samples via sol-gel and electrophoretic deposition for biomedical applications. IEEE Trans Nanobiosci. 2014;13(4):409-414.
[72] HIROMOTO S, NOZOE E, HANADA K, et al. In vivo degradation and bone formation behaviors of hydroxyapatite-coated Mg alloys in rat femur. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;122:111942.
[73] CHAI H, GUO L, WANG X, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluations on osteogenesis and biodegradability of a β-tricalcium phosphate coated magnesium alloy. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100(2):293-304.
[74] CHEN Z, MAO X, TAN L, et al. Osteoimmunomodulatory properties of magnesium scaffolds coated with β-tricalcium phosphate. Biomaterials. 2014;35(30):8553-8565.
[75] LI L Y, CUI LY, ZENG RC, et al. Advances in functionalized polymer coatings on biodegradable magnesium alloys - A review. Acta Biomater. 2018;79:23-36.
[76] KIM YK, LEE KB, KIM SY, et al. Improvement of osteogenesis by a uniform PCL coating on a magnesium screw for biodegradable applications. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):13264.
[77] PERUMAL G, RAMASAMY B, NANDKUMAR AM, et al. Bilayer nanostructure coated AZ31 magnesium alloy implants: in vivo reconstruction of critical-sized rabbit femoral segmental bone defect. Nanomedicine. 2020;29:102232.
[78] LAI Y, LI Y, CAO H, et al. Osteogenic magnesium incorporated into PLGA/TCP porous scaffold by 3D printing for repairing challenging bone defect. Biomaterials. 2019;197:207-219.
[79] GO EJ, KANG EY, LEE SK, et al. An osteoconductive PLGA scaffold with bioactive β-TCP and anti-inflammatory Mg(OH)(2) to improve in vivo bone regeneration. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(3):937-948.
[80] ZHAO S, XIE K, GUO Y, et al. Fabrication and biological activity of 3D-printed polycaprolactone/magnesium porous scaffolds for critical size bone defect repair. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(9):5120-5131.
[81] PENG Z, WANG C, LIU C, et al. 3D printed polycaprolactone/beta-tricalcium phosphate/magnesium peroxide oxygen releasing scaffold enhances osteogenesis and implanted BMSCs survival in repairing the large bone defect. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(28):5698-5710.
|
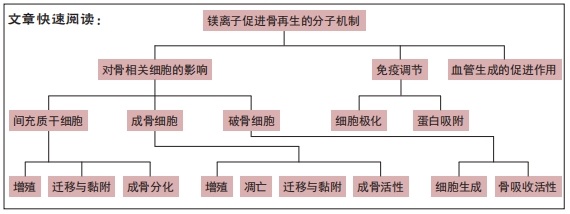
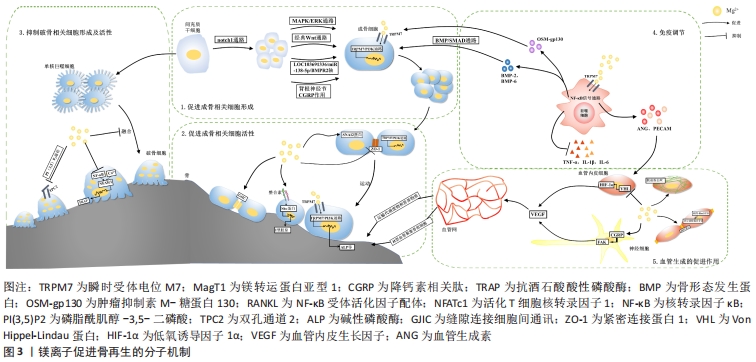

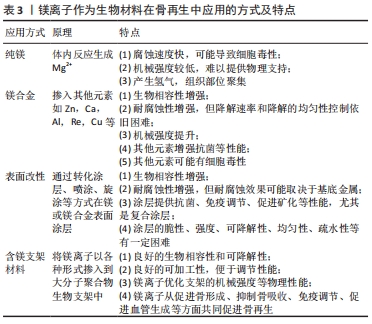

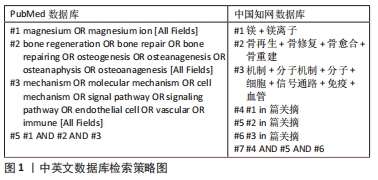
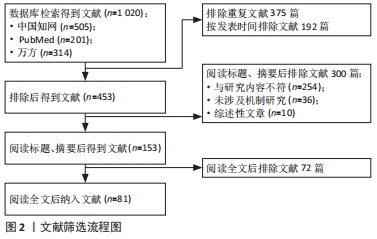
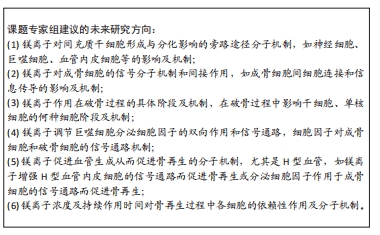 尽管目前镁离子促进骨再生的分子机制研究需进一步深入研究,但其作用已得到明确证实,机制研究明晰后会进一步拓展镁离子在骨再生方面的应用范围并提高其应用效率,值得广大研究者深入拓展研究。
尽管目前镁离子促进骨再生的分子机制研究需进一步深入研究,但其作用已得到明确证实,机制研究明晰后会进一步拓展镁离子在骨再生方面的应用范围并提高其应用效率,值得广大研究者深入拓展研究。