中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (15): 2446-2453.doi: 10.12307/2022.605
• 骨与关节综述 bone and joint review • 上一篇 下一篇
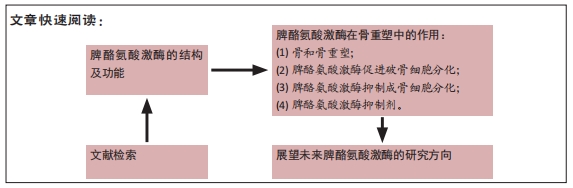
脾酪氨酸激酶在骨重塑中的作用
陈艺元,杨 倩,吴赛璇,张 咪,董 明,刘婷姣,牛卫东
- 大连医科大学口腔医学院,辽宁省大连市 116041
-
收稿日期:2021-04-17修回日期:2021-04-20接受日期:2021-05-27出版日期:2022-05-28发布日期:2022-01-07 -
通讯作者:牛卫东,博士,教授,大连医科大学口腔医学院,辽宁省大连市 116041 -
作者简介:陈艺元,女,1996年生,辽宁省营口市人,汉族,大连医科大学在读硕士。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(82073001),项目负责人:刘婷姣;辽宁省教育厅自然科学基础研究项目(LZ2019038),项目负责人:牛卫东
The role of spleen tyrosine kinase in bone remodeling
Chen Yiyuan, Yang Qian, Wu Saixuan, Zhang Mi, Dong Ming, Liu Tingjiao, Niu Weidong
- School of Stomatology, Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116041, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2021-04-17Revised:2021-04-20Accepted:2021-05-27Online:2022-05-28Published:2022-01-07 -
Contact:Niu Weidong, MD, Professor, School of Stomatology, Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116041, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Chen Yiyuan, Master candidate, School of Stomatology, Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116041, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82073001 (to LTJ); the Natural Science Basic Research Project of Education Department of Liaoning Province, No. LZ2019038 (to NWD)
摘要:
文题释义:
脾酪氨酸激酶:即Syk,是一种非受体型酪氨酸激酶,主要位于细胞质中,也存在于细胞核中,由3个串联的Src同源性2(SH2)结构域和一个C-末端酪氨酸激酶结构域组成,在细胞的形态发生、生长、迁移和存活中起着关键作用。
骨重塑:是通过更新骨来维持机械强度和矿物质平衡的过程,包括不断去除离散的旧骨,新合成的蛋白质基质取代这些旧骨并矿化形成新骨。重塑过程吸收旧骨并形成新骨,防止微损伤的积累。
背景:最初研究认为脾酪氨酸激酶仅是一种造血细胞特异性激酶,参与多种造血细胞反应和免疫受体的信号传递。近年来研究表明,脾酪氨酸激酶及其信号通路与骨重塑密切相关,并且脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂对骨的作用也受到了广泛的关注。
目的:综述脾酪氨酸激酶及其信号通路在骨重塑中的作用,为骨修复及临床治疗提供思路。
方法:检索中国知网和PubMed数据库收录的相关文献。中文检索词为“脾酪氨酸激酶、骨、破骨细胞、成骨细胞、抑制剂”,英文检索词为“Syk,bone,osteoclast,osteoblast,inhibitor”,最终纳入68篇文献进行归纳总结。
结果与结论:①脾酪氨酸激酶在破骨细胞和成骨细胞等非造血细胞中广泛表达,在细胞的形态发生、生长、迁移和存活中起着关键作用。②骨通过成骨细胞协同的骨基质形成和矿化以及破骨细胞的矿化骨基质降解不断地进行重塑,这对维持正常的骨结构和功能至关重要。③脾酪氨酸激酶及其信号通路在骨重塑过程中促进破骨细胞分化,抑制成骨细胞分化,进而促进骨重塑的发生发展。④脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂可改善骨性和炎性疾病的症状,特别是在疾病的侵袭性和破坏性阶段。⑤目前脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂的研究方向主要为自身免疫与炎症,在骨及骨性疾病方面的研究仍需深入探索,同时提高脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂的选择性也是今后研究的重点。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3663-1579 (陈艺元) ;https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8880-1301 (牛卫东)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈艺元, 杨 倩, 吴赛璇, 张 咪, 董 明, 刘婷姣, 牛卫东. 脾酪氨酸激酶在骨重塑中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(15): 2446-2453.
Chen Yiyuan, Yang Qian, Wu Saixuan, Zhang Mi, Dong Ming, Liu Tingjiao, Niu Weidong. The role of spleen tyrosine kinase in bone remodeling[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(15): 2446-2453.
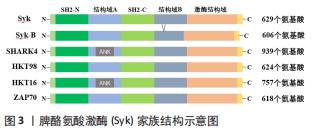
脾酪氨酸激酶家族激酶有一个古老的进化起源,在物种间的结构高度保守。小鼠的脾酪氨酸激酶与人类相似,由2个SH2结构域和1个C-末端的激酶结构域组成,仅比人类短6个氨基酸,与人脾酪氨酸激酶的氨基酸序列同源性为92%。果蝇中表达单个脾酪氨酸激酶相关分子SHARK4,它在2个SH2结构域之间含有锚蛋白样(ANK)重复,长蛇类和海绵类生物中表达2种脾酪氨酸激酶相关激酶,一种(HTK98)类似于人类的脾酪氨酸激酶表达形式,另一种(HTK16)与果蝇SHARK4更密切相关,但在秀丽隐杆线虫的基因组中不包含脾酪氨酸激酶相关激酶[7]。哺乳动物细胞表达另一种脾酪氨酸激酶家族激酶(ZAP70),ZAP70与脾酪氨酸激酶结构几乎相同,由2个SH2结构域和1个激酶结构域组成,但氨基酸序列与脾酪氨酸激酶同源性较低(小于50%),其表达主要局限于T细胞和NK细胞谱系[8]。脾酪氨酸激酶家族结构示意图见图3。
脾酪氨酸激酶最初被认为仅是一种造血细胞特异性激酶,参与多种造血细胞反应和免疫受体的信号传递,在血液恶性肿瘤和自身免疫性疾病中起着至关重要的作用。进一步研究表明脾酪氨酸激酶在其他组织中也有所表达,脾酪氨酸激酶在非造血细胞如成纤维细胞、上皮细胞、乳腺组织、肝细胞、神经细胞、血管内皮细胞、破骨细胞和成骨细胞中表现出更广泛的表达模式,在细胞形态发生、生长、迁移和存活中起着关键作用[9]。
2.2 骨和骨重塑 骨是一种特殊的结缔组织,具有高度矿化的结构和构造,由成骨细胞、破骨细胞及其各自的前体细胞以及骨髓间充质、髓样和淋巴样细胞等复杂混合物组成。骨为身体的其余部分提供结构支撑,为肌肉提供杠杆来完成运动,保护重要的内部器官和结构,维持矿物质稳态和酸碱平衡,充当生长因子和细胞因子的储库,并为骨髓空间内的造血提供环境[10-12]。在整个生命过程中,骨通过成骨细胞协同的骨基质形成和矿化以及破骨细胞的矿化骨基质降解不断地进行重塑,这对维持正常的骨结构和功能至关重要[2]。破骨细胞负责旧骨吸收,成骨细胞负责新骨形成,吸收和形成在生理条件下保持平衡稳定。但当平衡状态被打破时,骨的结构和功能就会出现异常,发生骨性疾病,如骨质疏松症或骨质硬化等[3]。
骨组织不断自我更新的过程称作骨代谢,人终生都进行着骨代谢,影响着骨吸收和骨形成平衡,进而调控骨重建。骨生长发育过程中的生长发生主要在儿童期和青春期。骨重建是指通过更新骨组织来维持机械强度和矿物质平衡的过程,包括不断去除离散的旧骨,用新合成的蛋白质基质取代这些旧骨,然后基质矿化形成新骨。骨重建由破骨细胞和成骨细胞参与,这些细胞依次进行旧骨的吸收和新骨的形成[13]。
2.3 脾酪氨酸激酶对破骨细胞的作用
2.3.1 破骨细胞 是由单核/巨噬细胞系细胞形成的多核细胞,由髓系祖细胞通过特定的成熟程序发育而成,随后进行同型融合。破骨细胞分化和功能受多种细胞因子、激素和生长因子的调节,巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和核因子κB受体激活剂配体(receptor activator of NF-κB ligand,RANKL)在破骨前体细胞增殖、黏附、迁移和细胞-细胞融合形成多核细胞以及成熟破骨细胞的迁移、存活和骨吸收功能的调节中起着不可缺少的作用。巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和RANKL通过有丝分裂原激活蛋白激酶(receptor activator of NF-κB ligand,MAPKs)、细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)、c-Jun氨基末端激酶(JNK)和p38信号转导途径发挥作用。巨噬细胞集落刺激因子激活的MAPK信号主要参与破骨前体细胞增殖的调节,而RANKL诱导的MAPK激活主要参与破骨细胞分化[14]。破骨细胞是哺乳动物中唯一能够主动吸收骨组织的细胞类型,因此在骨稳态中发挥关键作用。破骨细胞发育或功能缺陷会导致骨量增加,引发骨硬化等骨性疾病,而过度或病理性骨吸收会导致骨质疏松症、炎性关节疾病,如风湿性关节炎等[15-18]。破骨细胞通过在骨吸收区分泌H+、Cl-、组织蛋白酶K和基质金属蛋白酶降解骨组织[19-20]。
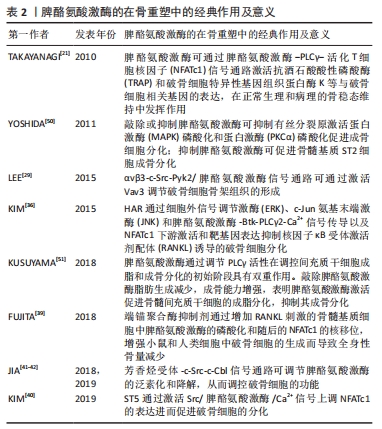
2.3.2 脾酪氨酸激酶促进破骨细胞分化 有许多研究表明,Src家族和脾酪氨酸激酶在人类和小鼠破骨细胞的分化和功能中起着关键作用。集落刺激因子1及其受体激活MAPK级联通路,维持破骨前体细胞的生长和增殖。RANKL及其受体RANK通过肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6(Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor,TRAF6)转导信号,激活核转录因子κB和MAPK通路,促进破骨细胞分化[21]。破骨形成的主要调节因子活化T细胞核因子(Nuclear factor of activated T cells c1,NFATc1)的表达是由核转录因子κB驱动的。同时NFATc1的激活也受到经典共刺激信号通路的调控,其中Fc受体γ链(FcRγ)、12 kD的DNAX激活蛋白(DNAX-activation protein 12,DAP12)、破骨细胞相关受体、髓样细胞表达触发受体2(triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cell 2,TREM2)可招募脾酪氨酸激酶,当脾酪氨酸激酶与受体结合时,能引起下游底物的活化来完成酪氨酸磷酸化,将信号向下传导。磷脂酶C(PLCγ)被激活后可以将质膜水通道蛋白2水解,产生第二信使三磷酸肌醇(IP3)和二酰基甘油(DAG),激活钙调蛋白信号,进一步激活钙调磷酸酶[22]。在细胞核中,NFATc1与其他转录因子如转录因子激活蛋白1、PU.1、小眼症相关转录因子和环磷腺苷效应元件结合蛋白共同作用,调节多种破骨细胞特异性基因,包括抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶(TRAP)、组织蛋白酶K和降钙素受体 [21,23]。表明脾酪氨酸激酶可通过脾酪氨酸激酶-PLCγ-NFATC1信号通路激活TRAP和组织蛋白酶K等与破骨细胞相关基因的表达,进而在破骨细胞的分化和功能中发挥作用。破骨细胞中脾酪氨酸激酶经典信号通路示意图,见图4。

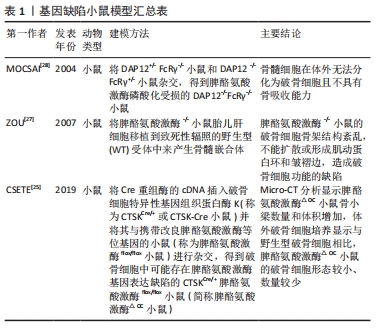
脾酪氨酸激酶在破骨细胞介导的体内骨吸收中发挥着不可或缺的作用,脾酪氨酸激酶?/?突变会导致小鼠围产期死亡,因此无法分析成年脾酪氨酸激酶?/?小鼠的骨骼形态[24]。Csete等[25]学者通过将Cre重组酶的cDNA插入破骨细胞特异性基因组织蛋白酶K(称为CTSKCre/+或CTSK-Cre小鼠)并将其与携带改良脾酪氨酸激酶等位基因的小鼠(称为脾酪氨酸激酶flox/flox小鼠)进行杂交,得到了破骨细胞中可能存在脾酪氨酸激酶基因表达缺陷的CTSKCre/+脾酪氨酸激酶flox/flox小鼠(简称脾酪氨酸激酶△OC小鼠)[26]。Micro-CT分析显示脾酪氨酸激酶△OC小鼠骨小梁数量和体积增加,体外破骨细胞培养显示与野生型破骨细胞相比,脾酪氨酸激酶△OC小鼠的破骨细胞形态较小、数量较少。ZOU等[27]通过将脾酪氨酸激酶?/?小鼠胎儿肝细胞移植到致死性辐照的野生型受体中来产生骨髓嵌合体,克服了脾酪氨酸激酶?/?小鼠的围产期致死性。研究结果表明,脾酪氨酸激酶?/?小鼠的破骨细胞骨架结构紊乱,不能扩散或形成肌动蛋白环和皱褶边,这并不是破骨细胞募集的失败,而是破骨细胞功能的缺陷,导致体外和体内骨吸收低于正常水平。有研究发现DAP12?/?FcR?/?小鼠的骨髓细胞脾酪氨酸激酶磷酸化受损,在体外无法分化为破骨细胞且不具有骨吸收能力[28]。以上结果表明,脾酪氨酸激酶位于调节破骨细胞生成的免疫调节蛋白如Dap12和FcRγ以及调节细胞骨架的整合素的下游,脾酪氨酸激酶?/?小鼠的破骨细胞骨架结构紊乱,破骨细胞功能缺陷,脾酪氨酸激酶是破骨细胞正常行使功能所必需的。基因缺陷小鼠模型汇总见表1。
LEE等[29]发现根皮素是肌动蛋白足体和封闭区的抑制剂,可通过破坏αvβ3-c-Src-富含脯氨酸的酪氨酸激酶2(Pyk2)/脾酪氨酸激酶信号通路调节肌动蛋白细胞骨架组织的形成。破骨细胞富含整合素αvβ3,具有调节细胞极化、扩散和降解骨的能力,占据αvβ3配体会使c-Src的激活,以ITAM依赖的方式使脾酪氨酸激酶磷酸化[30]。脾酪氨酸激酶是FcRγ和DAP12启动ITAM信号传导的关键介质,活化的脾酪氨酸激酶的SH2结构域与Dap12的Py残基相互作用,并招募含SH2结构域的白细胞蛋白(SLP-76),该蛋白是鸟嘌呤核苷酸交换因子(Vav3)的接头。脾酪氨酸激酶磷酸化并激活Vav3,Vav3将RAC(Rho GTP酶家族成员)从不活跃的GDP结合构象转变为活跃的GTP结合构象。Vav3介导的RAC活化是肌动蛋白细胞骨架通过Arp2/3复合体重组形成肌动蛋白环的核心,Arp2/3复合体在足体形成、破骨细胞运动和破骨细胞吸收中发挥重要作用[31]。以上研究表明,αvβ3-c-Src-Pyk2/脾酪氨酸激酶信号通路可通过激活Vav3调节破骨细胞骨架组织的形成。
RANKL可产生细胞内活性氧进而增加破骨细胞前体骨髓巨噬细胞中RANKL介导的信号传导。DJ-1也称为PARK7,是一种能够破坏活性氧的抗氧化蛋白和活性氧清除剂,抑制RANK-TRAF6和RANK-FcRγ/脾酪氨酸激酶信号通路的激活 [28,32]。KIM等[33]发现在RANKL刺激破骨形成过程中,DJ-1通过降低细胞内活性氧浓度来增加Src同源区2结构域磷酸酶1的活性,激活的结构域磷酸酶1抑制RANK介导的信号,最终抑制破骨细胞形成。在体外,与野生型骨髓巨噬细胞相比,DJ-1缺陷型骨髓巨噬细胞中RANK依赖性信号的激活增强。小鼠DJ-1消融导致骨体积减少和破骨细胞数量增加。在关节炎和RANKL诱发的骨病的小鼠模型中,DJ-1的消融导致骨组织细胞数量增加和骨损伤的恶化。以上研究表明,可通过RANK-FcRγ/脾酪氨酸激酶信号通路调节破骨细胞生成,在正常生理和病理的骨稳态维持中发挥作用。
CAI等[34]发现DOK3通过在体外限制ERK、脾酪氨酸激酶、核转录因子κB和NFATc1的激活以及在体内限制DAP12依赖的破骨细胞生成,以DAP12依赖的方式抑制巨噬细胞集落刺激因子诱导的巨噬细胞增殖和RANKL诱导的破骨细胞生成。DOK3正调控成骨细胞RANKL的表达并抑制骨保护素,从而提供额外的成骨细胞对破骨形成的调节。PERUZZI等[35]发现DOK3可以通过竞争DAP12 ITAM结合来限制脾酪氨酸激酶的激活,或者使脾酪氨酸激酶靶向蛋白酶体。在没有DOK3的情况下,巨噬细胞集落刺激因子或RANKL过度激活脾酪氨酸激酶有望导致破骨前体细胞内钙信号增加,从而增加DOK3-/-破骨细胞的大小和复杂性。以上研究表明,DOK3是破骨细胞生成的关键性负调节因子,也是成骨细胞生成的正调节因子,通过调节ERK、脾酪氨酸激酶、核转录因子κB和NFATc1的表达,调控破骨细胞和成骨细胞的功能,为治疗骨质疏松症等骨性疾病提供新的治疗靶点。KIM等[36]发现HAR(一种从魔鬼爪中分离出的环烯醚萜苷,可用于治疗疼痛、发热、溃疡、脓肿等症状)通过ERK,JNK和脾酪氨酸激酶-Btk-PLCγ2-Ca2+信号传导以及NFATc1下游激活和靶基因表达抑制RANKL诱导的破骨细胞分化,为临床治疗炎症相关的骨疾病,如炎性骨质疏松症和类风湿性关节炎等提供了一个新思路。
HARA等[37]发现来自面包酵母的葡聚糖与破骨细胞前体表达的β-葡聚糖凝集素受体(dectin-1)结合,通过自噬-溶酶体和泛素-蛋白酶体途径对脾酪氨酸激酶蛋白进行降解,下调脾酪氨酸激酶介导的信号传导,并通过下调NFATc1的活性减弱RANKL诱导的破骨细胞分化[38]。这些结果表明,来自面包酵母的葡聚糖可抑制RANKL诱导的破骨细胞生成,可作为骨相关疾病的新治疗策略。FUJITA等[39]发现tankyrase[也称为PARP5,是一种多聚(ADP-核糖)聚合酶,可与目标蛋白相互作用并催化聚合,导致泛素化和目标蛋白的降解]抑制剂通过增加RANKL刺激的骨髓基质细胞中脾酪氨酸激酶的磷酸化和随后的NFATc1的核移位,增强小鼠和人类细胞中破骨细胞的生成而导致全身性骨量减少。KIM等[40]发现ST5通过激活Src/脾酪氨酸激酶/Ca2+信号上调NFATc1的表达进而促进破骨细胞的分化,ST5调节NFATC1表达而不影响C-FOS的表达和核转录因子κB的激活。表明抑制Src/脾酪氨酸激酶/Ca2+信号通路的信号传导可能是临床中治疗骨质疏松性疾病的有效策略。
芳香烃受体是一种调节异生素代谢的配体激活转录因子,以配体和浓度特异性等方式调节破骨细胞生成。粉防己碱是一种天然生物碱,常用于治疗风湿痛和关节痛。粉防己碱可以通过增强脾酪氨酸激酶的泛素化和降解来抑制RANKL诱导的破骨细胞生成和破骨相关基因的表达,并减轻胶原诱导的关节炎大鼠的骨破坏。此外有研究表明,粉防己碱是芳香烃受体的潜在配体。JIA等[41-42]发现在破骨前体细胞中,粉防己碱通过芳香烃受体/c-Src/c-Cbl信号通路增强脾酪氨酸激酶的泛素化和降解,下调磷酸化脾酪氨酸激酶和磷酸化PLCγ2的表达,并抑制NFATc1的核移位。粉防己碱可促进芳香烃受体与c-Src的解离,增加芳香烃受体与c-Cbl和脾酪氨酸激酶的结合,脾酪氨酸激酶的泛素化和降解降低了脾酪氨酸激酶的功能,并向脾酪氨酸激酶的下游信号通路扩散[33,43]。在胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠中,口服粉防己碱可减少磷酸化脾酪氨酸激酶阳性细胞和破骨细胞的数量,并减少胫骨近端骨骺(不包括皮质骨)区域的骨侵蚀。以上研究证明,粉防己碱可通过芳香烃受体-c-Src-c-Cbl途径增强脾酪氨酸激酶的泛素化和降解,从而抑制破骨细胞生成和骨破坏。表明芳香烃受体-c-Src-c-Cbl信号通路可调节脾酪氨酸激酶的活性,从而调控破骨细胞的功能。
破骨前体细胞中受体相互作用蛋白140(RIP140)的表达及其蛋白调节对破骨细胞的分化、活性和偶联骨形成至关重要,RIP140的降解是破骨细胞生成和骨稳态的关键。LEE等[44]发现脾酪氨酸激酶在破骨细胞分化过程中刺激RIP140降解,导致破骨细胞分化增强,抑制脾酪氨酸激酶降低了RANKL诱导的RIP140蛋白降解和破骨细胞基因表达。从特异性敲除RIP140的小鼠中分离的破骨前体细胞分化潜能显著增加,原代破骨细胞培养物的条件培养基可显著抑制成骨细胞分化,特异性脾酪氨酸激酶刺激的RIP140蛋白降解可以迅速有效地终止这种抑制活性。该研究进一步表明脾酪氨酸激酶在破骨细胞分化过程中发挥着不可或缺的作用。
以上研究表明,脾酪氨酸激酶及其信号通路在破骨细胞的分化和功能中起到不可或缺的作用,脾酪氨酸激酶促进破骨细胞分化,临床中可以通过抑制或降解脾酪氨酸激酶及其信号通路,抑制破骨细胞的功能和活性,抑制骨破坏,为临床治疗骨性疾病提供了一个新思路。
2.4 脾酪氨酸激酶对成骨细胞的作用
2.4.1 成骨细胞 起源于间充质干细胞,呈立方状位于骨表面,通过沉积有机基质并参与随后的骨矿化而具有显著的成骨能力[10]。间充质干细胞具有多种功能,可以分化为骨骼、脂肪、肌肉、软骨等多种谱系,这种分化取决于细胞外信号传导和影响常见细胞内信号传导网络的转录因子的激活或抑制[45]。Runt相关转录因子2(Runx2)、骨形态发生蛋白等基因以及Wnt、Notch等信号通路在间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化过程中扮演重要角色[8]。
2.4.2 脾酪氨酸激酶抑制成骨细胞分化 脾酪氨酸激酶是磷脂酰肌醇3激酶(phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase,PI3K)/蛋白激酶B (protein kinase B,Akt)途径的主要上游效应因子,参与PI3K活化,在调节细胞运动中具有重要作用[46]。骨桥蛋白是一种细胞外基质蛋白,在骨细胞外基质中高度表达,在骨重塑过程中调节细胞增殖、存活和凋亡且与炎症发展密切相关,骨桥蛋白缺失可改善关节炎小鼠的炎症反应并减少骨破坏[47]。白细胞介素17在类风湿性关节炎发病中有促炎作用,并通过增强间充质干细胞和成骨细胞的增殖和分化以及促进破骨细胞存活和分化所需的促破骨生成因子来加速骨代谢[48]。Tsai等[49]发现骨桥蛋白通过脾酪氨酸激酶/PI3K/Akt信号通路对miR-129-3p的负调节促进成骨细胞中骨桥蛋白17的表达,进而减少单核细胞浸润。YOSHIDA等[50]发现敲除或抑制脾酪氨酸激酶可抑制MAPK磷酸化和蛋白激酶(PKCα)磷酸化促进成骨细胞分化。脾酪氨酸激酶在MC3T3-E1细胞的成骨分化中通过上调Runx2的表达来抑制成骨细胞的分化。此外,抑制脾酪氨酸激酶可促进骨髓基质ST2细胞成骨分化。KUSUYAMA等[51]发现脾酪氨酸激酶通过调节PLCγ活性在调控间充质干细胞成脂和成骨分化的初始阶段具有双重作用。敲除脾酪氨酸激酶脂肪生成减少,以脂滴出现减少和脂肪酸结合蛋白4(Fabp4)表达减少为主要特征,同时上调成骨能力,表现为基质矿化和骨钙素表达增加,表明脾酪氨酸激酶激活促进成脂分化,但抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。巨核细胞是造血祖细胞在骨髓增殖成骨细胞生态位中形成的,是血小板的细胞前体。MAZHARIAN等[52]发现整合素αIIbβ3通过调节SFKs-脾酪氨酸激酶-PLCγ2信号促进原代骨髓来源的巨核细胞的运动,为整合素介导的信号在巨核细胞迁移和血小板形成中的作用提供了新的线索。以上研究表明,可通过抑制脾酪氨酸激酶/PI3K/Akt信号通路促进成骨细胞的分化,也可通过敲除或抑制脾酪氨酸激酶,抑制MAPK和PKCα磷酸化进而促进成骨细胞分化。
低强度脉冲超声是一种机械性微波刺激,临床上常用于促进近期骨折的愈合,低强度脉冲超声诱导的胚胎干细胞转录因子(Nanog)参与了成骨潜能的恢复[53]。KUSUYAMA等[54]发现脾酪氨酸激酶参与了Nanog mRNA的表达和蛋白稳定性的提高,脾酪氨酸激酶的激活由Rho相关激酶1(ROCK1)和细胞外ATP以旁分泌的方式调节,ROCK1是细胞骨架锚定分子,通过肌动蛋白细胞骨架的动态重塑激活[55]。低强度脉冲超声处理诱导MC3T3-E1细胞释放的ATP对破骨细胞中脾酪氨酸激酶的激活有促进作用[56]。值得注意的是,低强度脉冲超声诱导的Nanog mRNA表达的增加受ATP-嘌呤受体P2X4-脾酪氨酸激酶 Y323激活的调控,而提高Nanog蛋白稳定性受ROCK1-脾酪氨酸激酶 Y525/526通路的控制。这些结果表明,低强度脉冲超声刺激可以通过脾酪氨酸激酶-Nanog轴恢复和维持连续传代的成骨细胞的成骨能力,提高传代的充质干细胞的多能性及其临床应用能力,为骨修复提供一种有效且低成本的治疗方法。
脾酪氨酸激酶抑制成骨细胞的分化和功能,敲除或抑制脾酪氨酸激酶及其信号通路可促进成骨细胞分化,促进骨修复,为临床中需要骨修复的骨性疾病的治疗提供一个新的选择。脾酪氨酸激酶的在骨重塑中的经典作用及意义见表2。
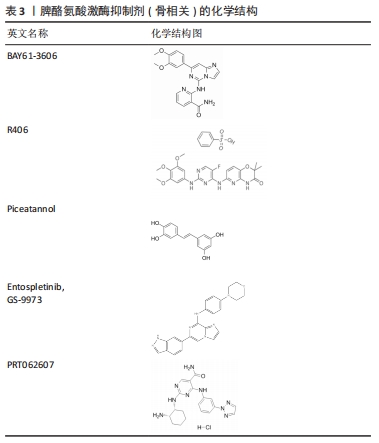
2.5 脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂对破骨细胞和成骨细胞的作用 BAY61-3606(2-[7-(3,4-二甲氧基苯基)-咪唑并[1,2-c]嘧啶-5-基氨基]-烟酰胺二盐酸盐)和R406(N4-(2,2-二甲基-3-oxo-4H-吡啶[1,4]oxazin-6-yl)-5-氟-N2-(3,4,5-三甲氧基苯基)-2,4-嘧啶二胺)是两种具有ATP竞争性的选择性脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂。Mukai等[57]发现BAY61-3606和R406以剂量依赖的方式抑制肿瘤坏死因子α处理的骨髓巨噬细胞中TRAP的形成。此外,BAY61-3606处理可抑制骨髓巨噬细胞中NFATc1的核转位。脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂BAY61-3606可通过抑制Mincle(C型凝集素)/脾酪氨酸激酶/核转录因子κB反馈通路,减少活性氧的产生和NLRP3炎性小体的激活,从而下调M1巨噬细胞的活性,抑制巨噬细胞的炎症反应[58-60]。BAY61-3606抑制巨噬细胞炎症的简化途径模型为炎症发展的临床干预提供了新的研究方向。弓形虫可通过脾酪氨酸激酶-CARD9-核转录因子κB信号轴在人外周血单核细胞中诱导骨桥蛋白1β的释放,PANDORI等[61]发现脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂R406以剂量依赖的方式显著减少在4 h时间点用弓形虫感染或用脂多糖刺激的单核细胞中骨桥蛋白1β的释放。表明脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂在骨修复、骨再生和炎症进展方面都能发挥一定的作用,为骨性疾病相关的组织工程研究提供了新的方向。
白藜芦醇(Piceatannol,3,4,3,5-四羟基-反式-二苯乙烯)是一种植物副产品。KUSUYAMA等[51]发现白藜芦醇作为一种脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂可抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂分化,促进成骨分化。研究发现10 μmol/L的白藜芦醇可有效抑制ST2细胞分化诱导的脾酪氨酸激酶磷酸化。在成脂条件下,白藜芦醇显著抑制油红O染色显示的脂滴外观和成脂标记物Fabp4,Pparg2,C/ebpa和C/ebpb的表达。在成骨条件下,基质矿化和碱性磷酸酶活性均被白藜芦醇显著促进,骨钙素、Runx2、无远端同源盒5(Dlx5)等成骨标记基因表达明显增加,同时发现晚期抑制脾酪氨酸激酶不影响成脂或成骨分化。这些结果表明脾酪氨酸激酶在骨髓间充质干细胞分化的早期具有重要作用。慢性痛风骨组织中存在的尿酸单钠盐微晶可以激活专业吞噬细胞中的NLRP3(核苷酸结合结构域和富含亮氨酸的重复区,包含受体蛋白3家族)炎症体[62]。ALLAEYS等[63]发现尿酸单钠盐也可被非专业吞噬细胞摄取,如表达NLRP3的成骨细胞,尿酸单钠盐不增加成骨细胞的死亡和晚期凋亡,但减少其增殖并降低其矿化能力。将白藜芦醇作用于尿酸单钠盐激活的成骨细胞中发现白藜芦醇可将尿酸单钠盐诱导的空泡形成减少58%,表明脾酪氨酸激酶参与了这一过程。
燧石症是一种颅面疾病,以上颌骨和下颌骨破坏为主要特征,SH3结构域结合蛋白2(SH3BP2)的功能突变是纤维性炎性病变引起的过度骨吸收的原因[64]。第2代脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂安托普汀尼(Entospletinib,GS-9973)对脾酪氨酸激酶的选择性高于R406并且在小鼠血浆中的半衰期更长。YOSHIMOTO等[65]发现与对照组相比用GS-9973处理的Sh3bp2KI/KI小鼠(燧石症小鼠)下颌骨表面的蚀坑形成减少,牙槽骨损失也被抑制。进一步研究表明,对Sh3bp2KI/KI小鼠应用GS-9973在治疗颅盖骨损失方面也是有效的,在改善全身骨损失方面是部分有效的,并且发现皮质骨对脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂更加敏感。在细胞水平上,GS-9973治疗抑制了破骨细胞的形成,说明在抑制巨噬细胞炎症的情况下破骨细胞分化的减少是Sh3bp2KI/KI小鼠骨破坏改善的主要原因。以上研究表明,脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂GS-9973的应用可以改善Sh3bp2KI/KI小鼠的炎症和骨破坏,抗脾酪氨酸激酶疗法是一种潜在的燧石症患者的药物治疗策略,特别是在疾病的侵袭性和破坏性阶段。
有研究证明Janus激酶(Janus kinase,Jak)抑制剂在关节炎动物模型治疗中有成效,且低剂量Jak抑制剂在中重度类风湿性关节炎患者临床治疗中已开展应用[66]。LLOP-GUEVARA等[67]发现在葡萄糖-6-磷酸异构酶诱导的小鼠慢性关节炎模型中,激酶抑制剂托法替尼(Jaki)和选择性脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂PRT062607(Syki)联合使用比单独使用Jaki更好地改善了破坏性和非缓解性关节炎。双重Jaki+Syki治疗小鼠的所有关节临床和组织病理学评分大幅下降,超过70%小鼠的关节炎在治疗3周后完全康复;双重激酶抑制降低了Th1/Th17细胞因子级联以及关节细胞的功能和分化能力,尤其是破骨细胞和成纤维样滑膜细胞。抗肿瘤坏死因子治疗也是临床上使用的一种标准的抗风湿性生物方法,可防止极早期急性葡萄糖-6-磷酸异构酶关节炎的发展,但抗肿瘤坏死因子(依那西普)治疗仅能够阻止疾病进展,不能改善或逆转疾病[68]。研究表明,双重Jaki+Syki的治疗效果比抗肿瘤坏死因子治疗持续时间更长,停止Jaki+Syki治疗后减少的Treg和NK细胞可迅速恢复到正常水平,将潜在的不利影响降至最低。以上研究表明,同时进行Jak+脾酪氨酸激酶抑制比单一Jak抑制和肿瘤坏死因子阻断有更好的疗效,为目前单一Jak抑制或抗肿瘤坏死因子治疗效果不佳的类风湿性关节炎患者提供了一个新的治疗策略。
脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂在近些年的研究较为广泛,在临床中也逐步应用,但研究重点主要在炎性疾病相关方面,这提示可以从脾酪氨酸激酶及其信号通路着手研究其与骨破坏和骨修复相关方面,开发新型脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂,从而为临床药物治疗提供新思路。脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(骨相关)化学结构,见表3。
| [1] YANAGI S, INATOME R, TAKANO T, et al. Syk expression and novel function in a wide variety of tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;288(3):495-498. [2] LOW SA, KOPECEK J. Targeting polymer therapeutics to bone. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64(12):1189-204. [3] CHEN X, WANG Z, DUAN N, et al. Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(2):99-107. [4] MOCSAI A, RULAND J, TYBULEWICZ VL. The SYK tyrosine kinase:a crucial player in diverse biological functions. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10(6):387-402. [5] WANG L, DUKE L, ZHANG PS, et al. Alternative splicing disrupts a nuclear localization signal in spleen tyrosine kinase that is required for invasion suppression in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2003;63(15):4724-4730. [6] PALACIOS EH, WEISS A. Distinct roles for Syk and ZAP-70 during early thymocyte development. J Exp Med. 2007;204(7):1703-1715. [7] ZIEGENFUSS JS, BISWAS R, AVERY MA, et al. Draper-dependent glial phagocytic activity is mediated by Src and Syk family kinase signalling. Nature. 2008;453(7197):935-939. [8] AU-YEUNG BB, DEINDL S, HSU LY, et al. The structure, regulation, and function of ZAP-70. Immunol Rev. 2009;228(1):41-57. [9] TURNER M, SCHWEIGHOFFER E, COLUCCI F, et al. Tyrosine kinase SYK: essential functions for immunoreceptor signalling. Immunol Today. 2000;21(3):148-154. [10] FLORENCIO-SILVA R, SASSO GR, SASSO-CERRI E, et al. Biology of bone tissue: structure, function, and factors that influence bone cells. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:421746. [11] ROSS FP, CHRISTIANO AM. Nothing but skin and bone. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(5): 1140-1149. [12] SHI C, WU T, HE Y, et al. Recent advances in bone-targeted therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2020;207:107473. [13] CLARKE B. Normal bone anatomy and physiology. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3 Suppl 3:S131-S139. [14] LEE K, SEO I, CHOI MH, et al. Roles of mitogen-activated protein kinases in osteoclast biology. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(10):3004. [15] SOBACCHI C, SCHULZ A, COXON FP, et al. Osteopetrosis: genetics, treatment and new insights into osteoclast function. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2013;9(9):522-536. [16] RACHNER TD, KHOSLA S, HOFBAUER LC. Osteoporosis:now and the future. The Lancet. 2011;377(9773):1276-1287. [17] SCHETT G, GRAVALLESE E. Bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis:mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(11):656-664. [18] LE GOFF B, BERTHELOT JM, MAUGARS Y, et al. Osteoclasts in RA: diverse origins and functions. Joint Bone Spine. 2013;80(6):586-591. [19] EDWARDS JR, MUNDY GR. Advances in osteoclast biology:old findings and new insights from mouse models. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(4):235-243. [20] OKAMOTO K, NAKASHIMA T, SHINOHARA M, et al. Osteoimmunology: the conceptual framework unifying the immune and skeletal systems. Physiol Rev. 2017;97(4):1295-1349. [21] TAKAYANAGI H. New immune connections in osteoclast formation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192:117-123. [22] GYORI DS, MOCSAI A. Osteoclast signal transduction during bone metastasis formation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:507. [23] TAKAYANAGI H. Osteoimmunology: shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(4):292-304. [24] ABTAHIAN F, GUERRIERO A, SEBZDA E, et al. Regulation of blood and lymphatic vascular separation by signaling proteins SLP-76 and Syk. Science. 2003;299(5604): 247-251. [25] CSETE D, SIMON E, ALATSHAN A, et al. Hematopoietic or osteoclast-specific deletion of syk leads to increased bone mass in experimental mice. Front Immunol. 2019;10:937. [26] NAKAMURA T, IMAI Y, MATSUMOTO T, et al. Estrogen prevents bone loss via estrogen receptor alpha and induction of Fas ligand in osteoclasts. Cell. 2007; 130(5):811-823. [27] ZOU W, KITAURA H, REEVE J, et al. Syk, c-Src, the alphavbeta3 integrin, and ITAM immunoreceptors, in concert, regulate osteoclastic bone resorption. J Cell Biol. 2007;176(6):877-888. [28] MOCSAI A, HUMPHREY MB, VAN ZIFFLE JA, et al. The immunomodulatory adapter proteins DAP12 and Fc receptor gamma-chain (FcRgamma) regulate development of functional osteoclasts through the Syk tyrosine kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(16):6158-6163. [29] LEE EJ, KIM JL, GONG JH, et al. Inhibition of osteoclast activation by phloretin through disturbing alphavbeta3 integrin-c-Src pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:680145. [30] FACCIO R, TEITELBAUM SL, FUJIKAWA K, et al. Vav3 regulates osteoclast function and bone mass. Nat Med. 2005;11(3):284-290. [31] LAU KW, SHENG MH. A novel miR17/protein tyrosine phosphatase-oc/EphA4 regulatory axis of osteoclast activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2018;650:30-38. [32] TAIRA T, SAITO Y, NIKI T, et al. DJ-1 has a role in antioxidative stress to prevent cell death. E Rep. 2004;5(2):213-218. [33] KIM HS, NAM ST, MUN SH, et al. DJ-1 controls bone homeostasis through the regulation of osteoclast differentiation. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):1519. [34] CAI X, XING J, LONG CL, et al. DOK3 Modulates bone remodeling by negatively regulating osteoclastogenesis and positively regulating osteoblastogenesis. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32(11):2207-2218. [35] PERUZZI G, MOLFETTA R, GASPARRINI F, et al. The adaptor molecule CIN85 regulates Syk tyrosine kinase level by activating the ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway. J Immunol. 2007;179(4):2089-2096. [36] KIM JY, PARK SH, BAEK JM, et al. Harpagoside Inhibits RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis via Syk-Btk-PLCgamma2-Ca(2+) Signaling Pathway and Prevents Inflammation-Mediated Bone Loss. J Nat Prod. 2015;78(9):2167-2174. [37] HARA S, NAGAI-YOSHIOKA Y, YAMASAKI R, et al. Dectin-1-mediated suppression of RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by glucan from baker’s yeast. J Cell Physiol. 2020; 236(7):5098-5107. [38] WAGENER M, HOVING JC, NDLOVU H, et al. Dectin-1-Syk-CARD9 signaling pathway in TB immunity. Front Immunol. 2018;9:225. [39] FUJITA S, MUKAI T, MITO T, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of tankyrase induces bone loss in mice by increasing osteoclastogenesis. Bone. 2018;106:156-166. [40] KIM MK, KIM B, KWON JO, et al. ST5 positively regulates osteoclastogenesis via Src/Syk/calcium signaling pathways. Mol Cells. 2019;42(11):810-819. [41] JIA Y, TAO Y, LV C, et al. Tetrandrine enhances the ubiquitination and degradation of Syk through an AhR-c-src-c-Cbl pathway and consequently inhibits osteoclastogenesis and bone destruction in arthritis. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(2): 38. [42] JIA Y, MIAO Y, YUE M, et al. Tetrandrine attenuates the bone erosion in collagen-induced arthritis rats by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis via spleen tyrosine kinase. FASEB J. 2018;32(6):3398-3410. [43] VAZQUEZ-GOMEZ G, ROCHA-ZAVALETA L, RODRIGUEZ-SOSA M, et al. Benzo[a]pyrene activates an AhR/Src/ERK axis that contributes to CYP1A1 induction and stable DNA adducts formation in lung cells. Toxicol Lett. 2018;289:54-62. [44] LEE B, IWANIEC UT, TURNER RT, et al. RIP140 in monocytes/macrophages regulates osteoclast differentiation and bone homeostasis. JCI Insight. 2017;2(7):e90517. [45] GUNTUR AR, ROSEN CJ. The skeleton:a multi-functional complex organ:new insights into osteoblasts and their role in bone formation: the central role of PI3Kinase. J Endocrinol. 2011;211(2):123-130. [46] CHAVES NETO AH, QUEIROZ KC, MILANI R, et al. Profiling the changes in signaling pathways in ascorbic acid/beta-glycerophosphate-induced osteoblastic differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(1):71-77. [47] SU CM, CHIANG YC, HUANG CY, et al. Osteopontin promotes oncostatin m production in human osteoblasts:implication of rheumatoid arthritis therapy. J Immunol. 2015;195(7):3355-3364. [48] PACIFICI R. The role of IL-17 and TH17 cells in the bone catabolic activity of PTH. Front Immunol. 2016;7:57. [49] TSAI CH, LIU SC, WANG YH, et al. Osteopontin inhibition of miR-129-3p enhances IL-17 expression and monocyte migration in rheumatoid arthritis. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017;1861(2):15-22. [50] YOSHIDA K, HIGUCHI C, NAKURA A, et al. Spleen tyrosine kinase suppresses osteoblastic differentiation through MAPK and PKCα. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;411(4):774-779. [51] KUSUYAMA J, KAMISONO A, CHANGHWAN S, et al. Spleen tyrosine kinase influences the early stages of multilineage differentiation of bone marrow stromal cell lines by regulating phospholipase C gamma activities. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(3):2549-2559. [52] MAZHARIAN A, THOMAS SG, DHANJAL TS, et al. Critical role of Src-Syk-PLC{gamma}2 signaling in megakaryocyte migration and thrombopoiesis. Blood. 2010;116(5):793-800. [53] GOETZKE R, SECHI A, DE LAPORTE L, et al. Why the impact of mechanical stimuli on stem cells remains a challenge. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(18):3297-3312. [54] KUSUYAMA J, SEONG C, MAKAREWICZ NS, et al. Low intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) maintains osteogenic potency by the increased expression and stability of Nanog through spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) activation. Cell Signal. 2019;62: 109345. [55] BOYLE ST, SAMUEL MS. Mechano-reciprocity is maintained between physiological boundaries by tuning signal flux through the Rho-associated protein kinase. Small GTPases. 2016;7(3):139-146. [56] KUSUYAMA J, NAKAMURA T, OHNISHI T, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes bone morphogenic protein 9-induced osteogenesis and suppresses inhibitory effects of inflammatory cytokines on cellular responses via Rho-associated kinase 1 in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(9):14657-14669. [57] MUKAI T, ISHIDA S, ISHIKAWA R, et al. SH3BP2 cherubism mutation potentiates TNF-alpha-induced osteoclastogenesis via NFATc1 and TNF-alpha-mediated inflammatory bone loss. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(12):2618-2635. [58] TAN RZ, LI JC, LIU J, et al. BAY61-3606 protects kidney from acute ischemia/reperfusion injury through inhibiting spleen tyrosine kinase and suppressing inflammatory macrophage response. FASEB J. 2020. doi: 10.1096/fj.202000261RRR. [59] TAN RZ, WANG C, DENG C, et al. Quercetin protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting Mincle/Syk/NF-kappaB signaling maintained macrophage inflammation. Phytother Res. 2020;34(1):139-152. [60] 陈玉凤.Syk介导的JNK和NLRP3的活化在糖尿病心肌病中的作用的研究[D]. 天津:天津医科大学,2017. [61] PANDORI WJ, LIMA TS, MALLYA S, et al. Toxoplasma gondii activates a Syk-CARD9-NF-kappaB signaling axis and gasdermin D-independent release of IL-1beta during infection of primary human monocytes. PLoS Pathog. 2019;15(8):e1007923. [62] LIU D, ZENG X, LI X, et al. Advances in the molecular mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome activators and inactivators. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;175:113863. [63] ALLAEYS I, MARCEAU F, POUBELLE PE. NLRP3 promotes autophagy of urate crystals phagocytized by human osteoblasts. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(6):R176. [64] MATSUMOTO Y, ROTTAPEL R. Bone dynamics and inflammation: lessons from rare diseases. Immunol Med. 2020;43(2):61-64. [65] YOSHIMOTO T, HAYASHI T, KONDO T, et al. Second-generation syk inhibitor entospletinib ameliorates fully established inflammation and bone destruction in the cherubism mouse model. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(8):1513-1519. [66] CHARLES-SCHOEMAN C, BURMESTER G, NASH P, et al. Efficacy and safety of tofacitinib following inadequate response to conventional synthetic or biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(7):1293-1301. [67] LLOP-GUEVARA A, PORRAS M, CENDON C, et al. Simultaneous inhibition of JAK and SYK kinases ameliorates chronic and destructive arthritis in mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:356. [68] MATSUMOTO I, ZHANG H, YASUKOCHI T, et al. Therapeutic effects of antibodies to tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6 and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 immunoglobulin in mice with glucose-6-phosphate isomerase induced arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(3):R66. |
| [1] | 谭新访, 郭艳幸, 秦晓飞, 张斌清, 赵东亮, 潘琨琨, 李瑜卓, 陈皓宇. 顺轴疲劳运动对兔髌股关节软骨损伤的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [2] | 许新忠, 吴钟汉, 余水生, 赵 耀, 徐春归, 张 鑫, 郑嵋戈, 荆珏华. 斯氏针置入股骨头不同方式的生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1313-1317. |
| [3] | 魏国强, 李云峰, 王 一, 牛晓芬, 车丽芳, 王海燕, 李志军, 史国鹏, 白 灵, 莫 凯, 张晨晨, 许阳阳, 李筱贺. 非均匀材料股骨在不同负荷情况下的生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1318-1322. |
| [4] | 李 获, 王 鹏, 高健明, 蒋浩然, 鲁晓波, 彭 江. 股骨头坏死血运重建与内部微观结构改变的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1323-1328. |
| [5] | 李 睿, 史 文, 杨士彩, 吕林蔚, 张春秋. 夹板外固定与散巴布剂对桡骨骨折模型兔骨愈合的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1329-1333. |
| [6] | 袁加斌, 朱宗东, 唐孝明, 魏 丹, 谭 波, 肖成伟, 赵淦琳炜, 廖 锋. 难复性股骨转子间骨折的解剖分型与复位策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1341-1345. |
| [7] | 张吉超, 董跃福, 牟志芳, 张 震, 李冰言, 徐祥钧, 李佳意, 任 梦, 董万鹏. 骨关节炎患者在不同步态角度下膝关节内部生物力学变化的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [8] | 刘 峰, 冯 毅. 步态周期下不同克氏针张力带治疗髌骨横行骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1367-1371. |
| [9] | 姚晓玲, 彭建城, 许岳荣, 杨志东, 张顺聪. 可变角度零切迹前路椎间融合内固定系统治疗脊髓型颈椎病:30个月随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [10] | 姜欢畅, 张兆飞, 梁 德, 江晓兵, 杨晓东, 刘志祥. 单侧多方向弯曲与直行椎体成形治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性压缩骨折优势的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [11] | 遇呈祥, 刘乐洪, 李文博, 陈金石, 冉春雷, 王忠平. 脊柱和骨盆矢状位参数与椎体成形治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折预后的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1412-1417. |
| [12] | 薛亚东, 周新社, 裴立家, 孟繁宇, 李 键, 王金子. 自体髂骨块联合钛板重建Paprosky Ⅲ型髋臼骨缺损为假体提供坚强的初始固定#br#[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [13] | 庄至坤, 吴荣凯, 林行会, 龚志兵, 张前进, 魏秋实, 张庆文, 吴昭克. 稳定增强型内衬髋关节系统在偏瘫老年股骨颈骨折全髋关节置换中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [14] | 李灿辉, 吴征杰, 曾焰辉, 何影浩, 司徒晓鹏, 杜雪莲, 洪 石, 何家雄. 骨科手术机器人辅助与传统透视下经皮骶髂螺钉置入的优劣分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1434-1438. |
| [15] | 朱 婵, 韩栩珂, 姚承佼, 周 倩, 张 强, 陈 秋. 人体唾液成分与骨质疏松/骨量低下[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
文章对脾酪氨酸激酶及其信号通路在骨重塑过程中的作用进行概述,讨论脾酪氨酸激酶及其信号通路在成骨细胞和破骨细胞中的作用,并总结脾酪氨酸激酶相关的骨性和炎性疾病以及可能用于治疗这些疾病的脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂。文章旨在加深对脾酪氨酸激酶在骨重塑中作用的理解,推进骨修复和骨再生相关组织工程研究,以支持开发治疗骨破坏的新型药物及生物材料。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2021年3月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2000年1月至2021年3月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed及中国知网数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“脾酪氨酸激酶、骨、破骨细胞、成骨细胞、抑制剂”,英文检索词为“syk,bone,
osteoclast,osteoblast,inhibitor”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 综述及研究原著。
1.1.6 检索策略 以PubMed数据库为例,见图1。
1.1.7 检索文献量 初检文献英文240篇,中文8篇。
1.2 纳入与排除标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①与骨重塑相关的文献;②与脾酪氨酸激酶有关的研究;③研究内容与组织再生相关。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①与主题相关性不高的文献;②证据等级较低、质量较低的文献;③研究内容重复的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估 根据排除标准,通过阅读题目和摘要进行筛选,排除与研究目的和研究内容相关性差、质量较低及重复性文献180篇,最终纳入68篇文献,其中英文文献67篇和中文文献1篇。
1.4 数据的提取 文献数据由陈艺元提取并成文;牛卫东审校及修改,分别描述脾酪氨酸激酶的发现与结构、骨和骨重塑、脾酪氨酸激酶及其抑制剂在破骨细胞和成骨细胞中的作用和临床现状。文献筛选流程图,见图2。
文章通过查阅文献发现脾酪氨酸激酶相关研究重点主要在炎症、肿瘤、动脉粥样硬化等其他疾病方面,在骨及骨重塑方面的研究仍有待深入。脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂的研究方向主要为自身免疫与炎症,极少与骨及骨重塑相关,现已有研究表明脾酪氨酸激酶是潜在的骨性疾病治疗靶点,脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂作为一种有前途的研究方向应继续进行探索。同时作者查阅文献过程中发现虽然近些年脾酪氨酸激酶及其抑制剂在各方面的研究进展迅速,但只有较少进入到临床应用阶段,主要原因是部分脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂对脾酪氨酸激酶的选择性较低,因此提高脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂的选择性也是今后研究的重点。同时应更加深入探索脾酪氨酸激酶抑制剂分子的作用机制,提高其临床应用价值。
脾酪氨酸激酶在骨重塑方面的相关研究有望为促进骨组织再生提供新的思路和方向,推进骨再生和骨修复相关组织工程研究,以支持开发治疗骨破坏的新型药物及生物材料。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程

文题释义:
脾酪氨酸激酶:即Syk,是一种非受体型酪氨酸激酶,主要位于细胞质中,也存在于细胞核中,由3个串联的Src同源性2(SH2)结构域和一个C-末端酪氨酸激酶结构域组成,在细胞的形态发生、生长、迁移和存活中起着关键作用。
骨重塑:是通过更新骨来维持机械强度和矿物质平衡的过程,包括不断去除离散的旧骨,新合成的蛋白质基质取代这些旧骨并矿化形成新骨。重塑过程吸收旧骨并形成新骨,防止微损伤的积累。
文章综述脾酪氨酸激酶及其信号通路在骨重塑中的作用,为进一步研究和临床治疗骨相关疾病提供思路。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||