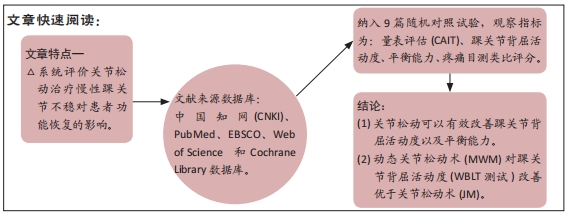
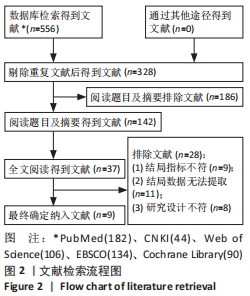
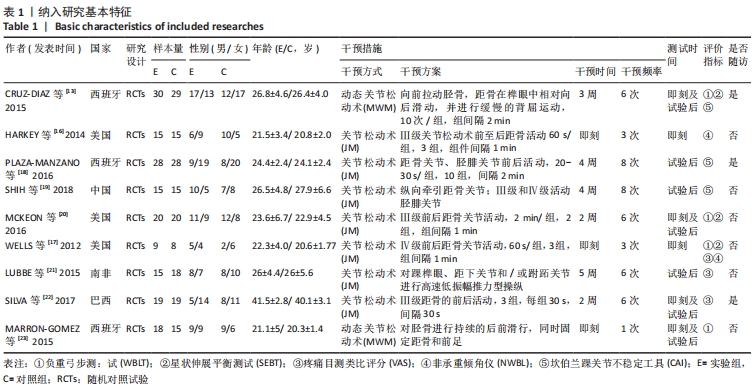
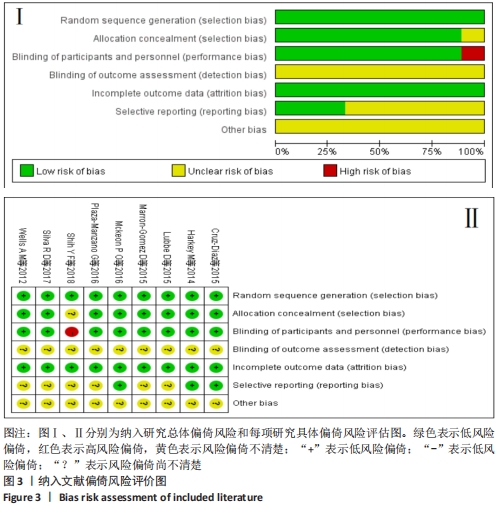
[1] DOHERTY C, DELAHUNT E, CAULFIELD B, et al. The incidence and prevalence of ankle sprain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective epidemiological studies. Sports Med. 2014;44(1):123-140.
[2] GRIBBLE PA, BLEAKLEY CM, CAULFIELD BM, et al. Evidence review for the 2016 International Ankle Consortium consensus statement on the prevalence, impact and long-term consequences of lateral ankle sprains. Br J Sports Med. 2016; 50(24):1496-1505.
[3] WHALAN M, LOVELL R, MCCUNN R, et al. The incidence and burden of time loss injury in Australian men’s sub-elite football (soccer): A single season prospective cohort study. J Sci Med Sport. 2019;22(1):42-47.
[4] DEITCH JR, STARKEY C, WALTERS SL, et al. Injury risk in professional basketball players: a comparison of Women’s National Basketball Association and National Basketball Association athletes. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34(7):1077-1083.
[5] DELAHUNT E, BLEAKLEY CM, BOSSARD DS, et al. Clinical assessment of acute lateral ankle sprain injuries (ROAST): 2019 consensus statement and recommendations of the International Ankle Consortium. Br J Sports Med. 2018;52(20):1304-1310.
[6] 侯宗辰,敖英芳,胡跃林,等.慢性踝关节不稳患者足底压力特征及相关因素分析[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2021,53(2):279-285.
[7] KANNUS P, RENSTROM P. Treatment for acute tears of the lateral ligaments of the ankle. Operation, cast, or early controlled mobilization. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73(2):305-312.
[8] LOUDON JK, REIMAN MP, SYLVAIN J. The efficacy of manual joint mobilisation/manipulation in treatment of lateral ankle sprains: a systematic review. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48(5):365-370.
[9] COOKE MW, LAMB SE, MARSH J, et al. A survey of current consultant practice of treatment of severe ankle sprains in emergency departments in the United Kingdom. Emerg Med J. 2003;20(6):505-507.
[10] MULLIGAN BR. Mobilizations with movement. J Man Manip Ther. 1993;1(4):154-156.
[11] ELLY HENGEVELD. Maitland’s Peripheral Manipulation.Butterworth-Heinemann, 2005.
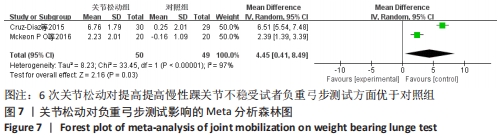
[12] MCKEON PO, BOOI MJ, BRANAM B, et al. Lateral ankle ligament anesthesia significantly alters single limb postural control. Gait Posture. 2010; 32(3):374-377.
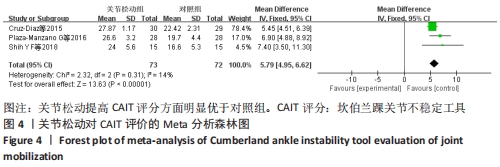
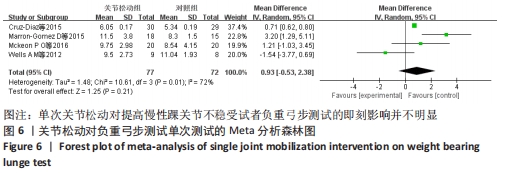
[13] CRUZ-DIAZ D, LOMAS VEGA R, OSUNA-PEREZ MC, et al. Effects of joint mobilization on chronic ankle instability: a randomized controlled trial. Disabil Rehabil. 2015;37(7):601-610.
[14] 赵彦,李平,陆矫,等.血流限制训练对肌骨疼痛康复效果的Meta分析[J].体育与科学,2020, 41(6):65-74.
[15] 耿治中,裴子文,言功立,等.肌内效贴对延迟性肌肉酸痛影响的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(35):5733-5740.
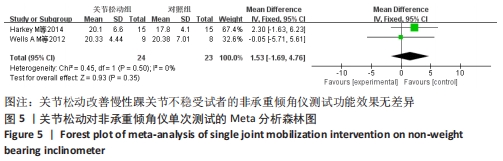
[16] HARKEY M, MCLEOD M, VAN SCOIT A, et al. The immediate effects of an anterior-to-posterior talar mobilization on neural excitability, dorsiflexion range of motion, and dynamic balance in patients with chronic ankle instability. J Sport Rehabil. 2014;23(4):351-359.
[17] WELLS AM. Effects of Joint Mobilization on Ankle Dorsiflexion Range of Motion, Dynamic Postural Control and Self-Reported Patient Outcomes in Individuals with Chronic Ankle Instability. The University of Toledo. 2012.
[18] PLAZA-MANZANO G, VERGARA-VILA M, VAL-OTERO S, et al. Manual therapy in joint and nerve structures combined with exercises in the treatment of recurrent ankle sprains: A randomized, controlled trial. Man Ther. 2016;26: 141-149.
[19] SHIH YF, YU HT, CHEN WY, et al. The effect of additional joint mobilization on neuromuscular performance in individuals with functional ankle instability. Phys Ther Sport. 2018;30:22-28.
[20] MCKEON PO, WIKSTROM EA. Sensory-Targeted Ankle Rehabilitation Strategies for Chronic Ankle Instability. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2016;48(5):776-784.
[21] LUBBE D, LAKHANI E, BRANTINGHAM JW, et al. Manipulative therapy and rehabilitation for recurrent ankle sprain with functional instability: a short-term, assessor-blind, parallel-group randomized trial. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2015;38(1):22-34.
[22] SILVA RD, TEIXEIRA LM, MOREIRA TS, et al. Effects of Anteroposterior Talus Mobilization on Range of Motion, Pain, and Functional Capacity in Participants With Subacute and Chronic Ankle Injuries: A Controlled Trial. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2017;40(4):273-283.
[23] MARRON-GOMEZ D, RODRIGUEZ-FERNANDEZ AL, MARTIN-URRIALDE JA. The effect of two mobilization techniques on dorsiflexion in people with chronic ankle instability. Phys Ther Sport. 2015;16(1):10-15.
[24] MORAES MR, CAVALCANTE ML, LEITE JA, et al. Histomorphometric evaluation of mechanoreceptors and free nerve endings in human lateral ankle ligaments. Foot Ankle Int. 2008;29(1):87-90.
[25] WU X, SONG W, ZHENG C, et al. Morphological study of mechanoreceptors in collateral ligaments of the ankle joint. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:92.
[26] WANKHADE UG, UMASHANKAR MK, REDDY BS. Functional Outcome of Lumbar Discectomy by Fenestration Technique in Lumbar Disc Prolapse - Return to Work and Relief of Pain. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016;10(3):RC09-13.
[27] HUBBARD TJ, HERTEL J. Mechanical contributions to chronic lateral ankle instability. Sports Med. 2006;36(3):263-277.
[28] ROIJEZON U, CLARK NC, TRELEAVEN J. Proprioception in musculoskeletal rehabilitation. Part 1: Basic science and principles of assessment and clinical interventions. Man Ther. 2015;20(3): 368-377.
[29] HAAVIK H, MURPHY B. The role of spinal manipulation in addressing disordered sensorimotor integration and altered motor control. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2012;22(5):768-776.
[30] ROSEN AB, JOHNSTON M, CHUNG S, et al. The reliability and validity of a digital version of the Cumberland Ankle Instability Tool. Disabil Rehabil. 2021;43(12):1738-1741.
[31] GREEN T, REFSHAUGE K, CROSBIE J, et al. A randomized controlled trial of a passive accessory joint mobilization on acute ankle inversion sprains. Phys Ther. 2001;81(4):984-994.
[32] HOCH MC, STATON GS, MEDINA MCKEON JM, et al. Dorsiflexion and dynamic postural control deficits are present in those with chronic ankle instability. J Sci Med Sport. 2012;15(6):574-579.
[33] VICENZINO B, BRANJERDPORN M, TEYS P, et al. Initial changes in posterior talar glide and dorsiflexion of the ankle after mobilization with movement in individuals with recurrent ankle sprain. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2006;36(7):464-471.
[34] 邓宇,李新春,梁荣光.正常踝关节及常见病变的影像学诊断[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2009,3(1):71-81.
[35] 高丕明,罗小兵,虞亚明,等.慢性踝关节不稳患者三维步态动力学特征[J].中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(3):182-186.
[36] DE RIDDER R, WILLEMS TM, VANRENTERGHEM J, et al. Effect of a Home-based Balance Training Protocol on Dynamic Postural Control in Subjects with Chronic Ankle Instability. Int J Sports Med. 2015;36(7):596-602.
[37] HOCH MC, FARWELL KE, GAVEN SL, et al. Weight-Bearing Dorsiflexion Range of Motion and Landing Biomechanics in Individuals With Chronic Ankle Instability. J Athl Train. 2015;50(8):833-839.
[38] 张旭,张虹.发散式冲击波联合关节松动技术治疗冻结期肩周炎的效果[J].中国老年学杂志, 2021;41(7):1448-1451.
[39] DONAHUE M, SIMON J, DOCHERTY CL. Critical review of self-reported functional ankle instability measures. Foot Ankle Int. 2011;32(12):1140-1146.
[40] 张阳,王强,宋旭,等.功能性踝关节不稳者的动态平衡能力研究[J].体育科学,2016,36(9): 54-58+83.
|