中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (23): 3768-3772.doi: 10.12307/2022.681
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇
两种肾虚证型去势模型大鼠骨小梁微观结构及骨代谢的差异
何兴鹏1,郑利钦1,李鹏飞2,3,悦桂阳1,李志鸿4,吴敏辉1,林梓凌5,6
- 1广州中医药大学第一临床医学院,广东省广州市 510405;2暨南大学附属江门中医院,广东省江门市 529000;3江门市中心医院,广东省江门市 529030;4广州中医药大学国际学院,广东省广州市 510405;5广州中医药大学第一附属医院创伤骨科,广东省广州市 510405;6广州中医药大学岭南医学研究中心,广东省广州市 510405
Differences of trabecular microstructure and bone metabolism in two types of kidney-deficiency ovariectomized rats
He Xingpeng1, Zheng Liqin1, Li Pengfei2, 3, Yue Guiyang1, Li Zhihong4, Wu Minhui1, Lin Ziling5, 6
- 1First School of Clinical Medicine of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine; 2Jiangmen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Affiliated to Jinan University; 3Jiangmen Central Hospital; 4International College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine; 5Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine; 6Lingnan Medical Research Center of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine
摘要:

文题释义:
骨小梁:骨内微结构,是骨皮质在松质骨内的延伸部分,在骨髓腔内呈现不规则的立体网状结构,具有承载负荷、在骨小梁之间及骨小梁与皮质骨之间传导及分散应力载荷的作用,是一个影响骨强度的主要因素。骨小梁具有一定的数目、质量、方向和厚度等,其形态计量学参数可客观准确地衡量骨小梁的生物性能,为骨质疏松症等疾病的评价和预防提供可靠依据。
骨代谢指标:应用于骨质疏松以及代谢性骨病的评估指标,是由成骨细胞或破骨细胞分泌的酶和激素,以及骨基质的胶原蛋白或非胶原蛋白代谢产物。骨代谢生化指标可及时反映骨转换状态,灵敏度高、特异性强,用于骨质疏松诊断分型、预测骨折风险、抗骨质疏松治疗疗效评价以及代谢性骨病的诊断与鉴别诊断。
背景:目前去势大鼠是成熟可靠的骨质疏松症动物模型,对肾阳虚证、肾阴虚证大鼠模型的建立与相关观察指标也已有比较详细的研究,但对肾阳虚证、肾阴虚证骨质疏松的“病证结合”大鼠模型研究还有待完善。交感-副交感神经功能测定是判断阴虚、阳虚证型的一个特异性指标,但用来分析两种肾虚证型骨骼系统相关指标方面仍存在不足,“病证结合”需要更多的实验依据和观察指标。
目的:比较分析肾阳虚证和肾阴虚证骨质疏松大鼠骨小梁微观结构参数及血清中骨代谢指标的差异。
方法:手术摘除20只SD雌性大鼠双侧卵巢建立去势骨质疏松模型,10周后随机分为肾阳虚组、肾阴虚组,每组10只。肾阳虚组去势大鼠臀部肌肉注射氢化可的松注射液,肾阴虚组去势大鼠灌胃甲状腺片混悬药液,均1次/d,连续14 d,造模成功后采用Micro-CT扫描获取大鼠左侧股骨感兴趣区域骨微结构参数,ELISA法检测大鼠血清中骨形成及骨吸收相关指标。
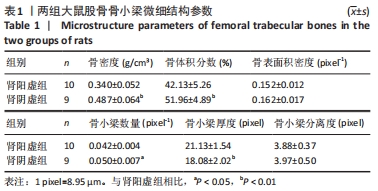
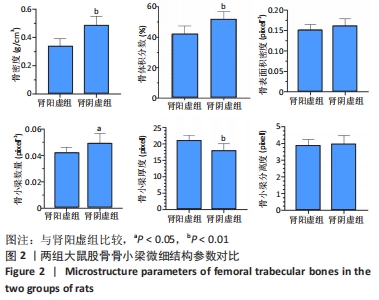
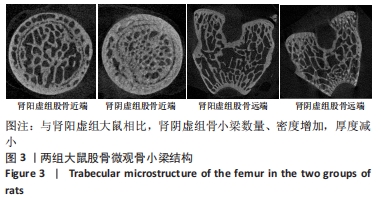
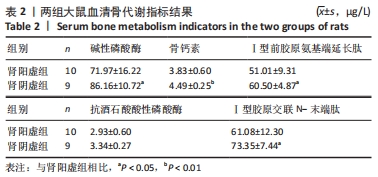
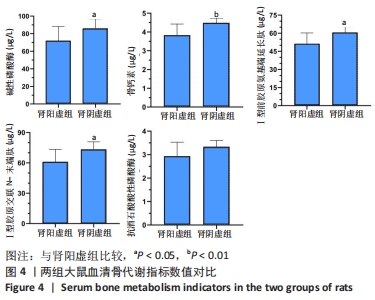
结果与结论:①成功建立两种肾虚证型去势骨质疏松大鼠病证结合模型;②与肾阳虚组大鼠相比,肾阴虚组大鼠骨小梁骨密度及骨体积分数明显升高,骨小梁数量增加,骨小梁厚度减小,血清各项骨形成、骨吸收指标明显升高,提示肾阴虚组大鼠骨代谢过程明显加快;③结果表明,肾阳虚、肾阴虚证型去势骨质疏松大鼠骨小梁微观结构及骨代谢指标存在明显差异,其机制仍需进一步研究。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7363-9962 (何兴鹏)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: