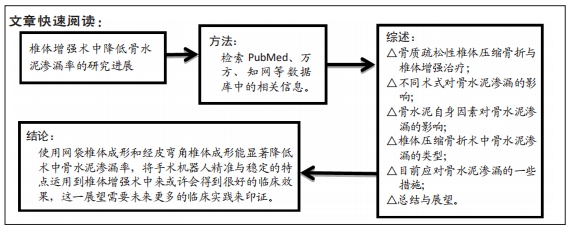
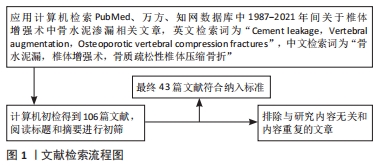
[1] LEWIECKI EM, JESSE DO, JACQUELINE VO, et al.Healthcare Policy Changes in Osteoporosis Can Improve Outcomes and Reduce Costs in the United States. JBMR Plus. 2019;3(9):110-115.
[2] 印平,马远征,马迅,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的治疗指南[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(6):643-648.
[3] 王复案,陈允震.骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折诊疗现状及其对策[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(5):590-594+599.
[4] Van MJ, Bastian L, Boonen S, et al. A randomized trial of balloon kyphoplasty and nonsurgical management for treating acute vertebral compression fractures: vertebral body kyphosis correction and surgical parameters. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(12):971-983.
[5] GALIBERT P, DERAMOND H, ROSAT P, et al. Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty. Neuro-Chirurgie. 1987;33(2):166-168.
[6] 张帅,王清,杨进,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术骨水泥椎管内渗漏发生率及相关危险因素分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(24): 2244-2249.
[7] HIWATASHI A, WESTESSON PLA, YOSHIURA T, et al. Kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty produce the same degree of height restoration. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30(4):669-673.
[8] STEVEN RG, RUDOLPH AB, LEDLIE J. Balloon Kyphoplasty for Symptomatic Vertebral Body Compression Fractures Results in Rapid, Significant, and Sustained Improvements in Back Pain, Function, and Quality of Life for Elderly Patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31(19):2213-2220.
[9] WOO BJ, GWAK HS, KIM S, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for patients with metastatic compression fractures of the thoracolumbar spine: clinical and radiological factors affecting functional outcomes. Spine J. 2016;16(3):355-364.
[10] CHANDRA RV, MAINGARD J, ASADI H, et al. Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures: What Are the Latest Data? Am J Neuroradiol. 2018;39(5):798-806.
[11] WANG F, WANG LF, MIAO DC, et al. Which one is more effective for the treatment of very severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: PVP or PKP? J Pain Res. 2018;18(29):2625-2631.
[12] TAYLOR RS, TAYLOR RJ, PETER F. Balloon Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty for Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Comparative Systematic Review of Efficacy and Safety. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31(23):264-264.
[13] LAREDO JD, HAMZE B. Complications of percutaneous vertebroplasty and their prevention. Skeletal Radiol. 2004;33(9)493-505.
[14] SEMAAN H, OBRI T, BAZERBASHI M, et al. Clinical outcome and subsequent sequelae of cement extravasation after percutaneous kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty: a comparative review. Acta Radiol. 2018;59(7):861-868.
[15] YOON ST, QURESHI AA, HELLER JG, et al. Kyphoplasty for salvage of a failed vertebroplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: case report and surgical technique. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18(7):129-134.
[16] KIM MJ, DEREK PL, MATTHEW H, et al. Vertebroplasty Versus Kyphoplasty: Biomechanical Behavior Under Repetitive Loading Conditions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(18):2079-2084.
[17] ALHASHASH M, SHOUSHA M, BARAKAT AS, et al. Effects of polymethyl-methacrylate cement viscosity and bone porosity on cement leakage and new vertebral fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty: a prospective study. Global Spine J. 2019;9(7):754-760.
[18] GUO D, YU M, ZHANG S, et al. Novel surgical strategy for treating osteoporotic vertebral fractures with cord compression. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(6):1082-1092.
[19] HE CJ, LIU GD. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of bone filling mesh container and simple percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Pain Physician. 2018;21(3):259-268.
[20] KLINGLER JH, SIRCAR R, DEININGER MH, et al. Vesselplasty: a new minimally invasive approach to treat pathological vertebral fractures in selected tumor patients - preliminary results. Rofo. 2013;185(4):340-350.
[21] BAROUD G, CROOKSHANK M, BOHNER M. High-Viscosity Cement Significantly Enhances Uniformity of Cement Filling in Vertebroplasty: An Experimental Model and Study on Cement Leakage. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(22):2562-2568.
[22] NOBORU T, ATSUSHI K, SHUJI K, et al. Relationship between cement distribution pattern and new compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJR. Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189(6):348-352.
[23] CHEN WC, TSAI SUNG HL, GOYAL A, et al. Comparison between vertebroplasty with high or low viscosity cement augmentation or kyphoplasty in cement leakage rate for patients with vertebral compression fracture: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2020;10(9):1-11.
[24] 姚海燕,李青,赵成毅,等.PVP术中椎间盘骨水泥渗漏的危险因素及对策[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2016,8(3):133-140.
[25] MARC JN, SANDER PJM, ARIAN RE, et al. A Clinical Comparative Study on Low Versus Medium Viscosity PolyMethylMetAcrylate Bone Cement in Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Viscosity Associated With Cement Leakage. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(20):1037-1044.
[26] SARACEN A, KOTWICA Z. Complications of percutaneous vertebroplasty. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(24):3850-3850.
[27] MICHAEL G, TUAN LV, ELIE F, et al. Rare complication of a percutaneous technique: intradural cement leakage and its surgical treatment. World Neurosurg. 2018;7(45):97.
[28] MATHIS JM. Percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty: which one do I choose? Skeletal Radiol. 2006;35(9):629-631.
[29] HSIEH MK, KAO FC, CHIU PY, et al. Risk factors of neurological deficit and pulmonary cement embolism after percutaneous vertebroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(9):483-490.
[30] BERLEMANN U, HULME PA, KREBS J, et al. Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: A Systematic Review of 69 Clinical Studies. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(17):1983-2001.
[31] KOTWICA Z, SARACEN A. Early and long-term outcomes of vertebroplasty for single osteoporotic fractures. Neurologiai Neurochirurgia Polska. 2011;45(5):431-435.
[32] TANG BP, CUI LB, CHEN XM, et al. Risk Factors for Cement Leakage in Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: An Analysis of 1456 Vertebrae Augmented by Low-Viscosity Bone Cement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;46(4):216-222.
[33] CARAAN NA, WINDHAGER R, WEBB J, et al. Role of fast-setting cements in arthroplasty: A comparative analysis of characteristics. World J Orthop. 2017; 8(12):881-890.
[34] 李玉伟,崔红领,王海蛟.应用可弯曲骨水泥注入器单侧穿刺行经皮椎体成形术的可行性及疗效[J]. 中华放射学杂志,2017,51(4): 293-298.
[35] CHENG YH, LIU YM. Percutaneous curved vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Int Med Res. 2019;47(6):2424-2433.
[36] 杨惠林,刘强,唐海.经皮椎体后凸成形术的规范化操作及相关问题的专家共识[J].中华医学杂志,2018,98(11):808-812.
[37] 钟远鸣,万通,钟锡锋,等.弯角与单侧椎弓根入路椎体成形治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折有效性与安全性的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(3):456-462.
[38] 苏允裕,章晓云.骨水泥分布形态对PKP治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩骨折疗效的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(11):1178-1180.
[39] ZUO XH, ZHU XP, BAO HG, et al. Network meta-analysis of percutaneous vertebroplasty, percutaneous kyphoplasty, nerve block, and conservative treatment for nonsurgery options of acute/subacute and chronic osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs) in short-term and long-term effects. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(29):11544-11544.
[40] 孙海波,景晓珊,唐海,等.椎体成形术中注入不同剂量骨水泥治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效分析[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2019, 14(5):361-365.
[41] VERLAAN JJ, SOMERS I, DHERT WJ, et al.Clinical and radio logical results 6 years after treatment of traumatic thoraco lumbar burst fractures with pedicle screw instrumentation and balloon assisted endplate reduction. Spine J. 2015;15(6):1172-1178.
[42] DE GENDT EEA, KUPERUS JS, FOPPEN W, et al. Clinical,ra diological,and patient-reported outcomes 13 years after pedicle screw fixation with balloon-assisted endplate re duction and cement injection. Europ Spine J. 2020;29(4):914-921.
[43] YUAN W, CAO WH, MENG XT, et al. Learning Curve of Robot-Assisted Percutaneous Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. World Neurosurg. 2020;138(10):323-329. |