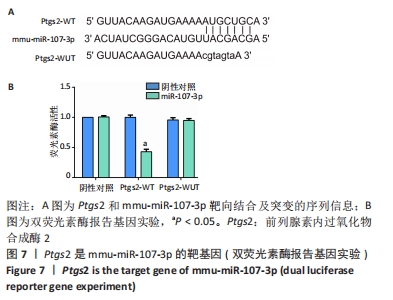
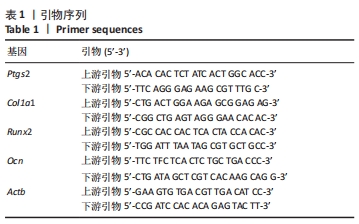
[1] KO NY, CHEN LR, CHEN KH. The Role of Micro RNA and Long-Non-Coding RNA in Osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(14):4886.
[2] KOMORI T. Runx2, an inducer of osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018;149(4):313-323.
[3] WANG LJ, CAI HQ. Let-7b downgrades CCND1 to repress osteogenic proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells: An implication in osteoporosis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020;36(10):775-785.
[4] YANG Y, YUJIAO W, FANG W, et al. The roles of miRNA, lncRNA and circRNA in the development of osteoporosis. Biol Res. 2020;53(1):40.
[5] GARCIA J, DELANY AM. MicroRNAs regulating TGFβ and BMP signaling in the osteoblast lineage. Bone. 2021;143:115791.
[6] ZHAI F, SONG N, MA J, et al. FGF18 inhibits MC3T3‑E1 cell osteogenic differentiation via the ERK signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(4):4127-4132.
[7] HUANG X, WANG X, ZHANG Y, et al. Absorption and utilisation of epimedin C and icariin from Epimedii herba, and the regulatory mechanism via the BMP2/Runx2 signalling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;118:109345.
[8] COSTA-SILVA J, DOMINGUES D, LOPES FM. RNA-Seq differential expression analysis: An extended review and a software tool. PLoS One. 2017;12(12):e0190152.
[9] LI W. Volcano plots in analyzing differential expressions with mRNA microarrays. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2012;10(6):1231003.
[10] HUANG DA W, SHERMAN BT, LEMPICKI RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 2009;4(1):44-57.
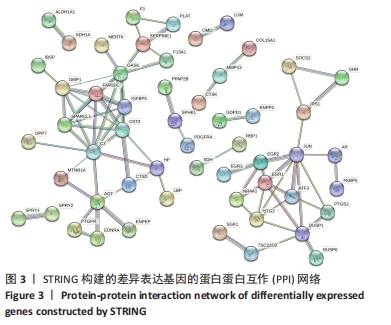
[11] SZKLARCZYK D, MORRIS JH, COOK H, et al. The STRING database in 2017: quality-controlled protein-protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(D1):D362-D368.
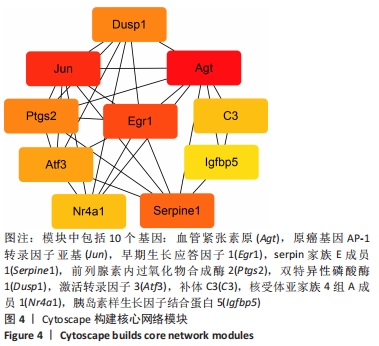
[12] SHANNON P, MARKIEL A, OZIER O, et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003; 13(11):2498-2504.
[13] CHIN CH, CHEN SH, WU HH, et al. cytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol. 2014;8 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S11.
[14] AGARWAL V, BELL GW, NAM JW, et al. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife. 2015;4:e05005. .
[15] XIONG Y, CHEN L, YAN C, et al. The lncRNA Rhno1/miR-6979-5p/BMP2 Axis Modulates Osteoblast Differentiation. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(9):1604-1615.
[16] YANG C, NILSSON L, CHEEMA MU, et al. Chitosan/siRNA nanoparticles targeting cyclooxygenase type 2 attenuate unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced kidney injury in mice. Theranostics. 2015;5(2):110-123.
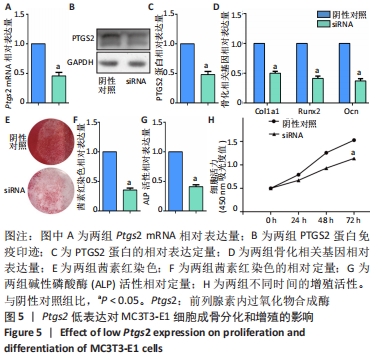
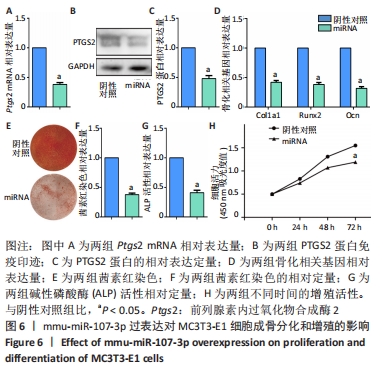
[17] GREGORY CA, GUNN WG, PEISTER A, et al. An Alizarin red-based assay of mineralization by adherent cells in culture: comparison with cetylpyridinium chloride extraction. Anal Biochem. 2004;329(1):77-84.
[18] PISZCZEK P, RADTKE A, EHLERT M, et al. Comprehensive Evaluation of the Biological Properties of Surface-Modified Titanium Alloy Implants. J Clin Med. 2020;9(2):342.
[19] ROSEN CJ. The Epidemiology and Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis//Endotext (FEINGOLD KR, ANAWALT B, BOYCE A, et al. eds). South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.Copyright © 2000-2021, MDText.com, Inc., 2000.
[20] 白璧辉,谢兴文,李鼎鹏,等.我国近5年来骨质疏松症流行病学研究现状[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(2):253-258.
[21] 中华医学会物理医学与康复学分会,中国老年学和老年医学学会骨质疏松康复分会.原发性骨质疏松症康复干预中国专家共识[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2019,41(1):1-7.
[22] AN J, YANG H, ZHANG Q, et al. Natural products for treatment of osteoporosis: The effects and mechanisms on promoting osteoblast-mediated bone formation. Life Sci. 2016;147:46-58.
[23] KIM JM, LIN C, STAVRE Z, et al. Osteoblast-Osteoclast Communication and Bone Homeostasis. Cells. 2020;9(9):2073.
[24] 中华医学会放射学分会骨关节学组,中国医师协会放射医师分会肌骨学组,中华医学会骨科学分会骨质疏松学组,等. 骨质疏松的影像学与骨密度诊断专家共识[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(9):1249-1256.
[25] ZHU S, ZHU Y, WANG Z, et al. Bioinformatics analysis and identification of circular RNAs promoting the osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on titanium treated by surface mechanical attrition.Peer J. 2020;8:e9292.
[26] MAJIDINIA M, SADEGHPOUR A, YOUSEFI B. The roles of signaling pathways in bone repair and regeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(4):2937-2948.
[27] EKEGREN CL, EDWARDS ER, DE STEIGER R, et al. Incidence, Costs and Predictors of Non-Union, Delayed Union and Mal-Union Following Long Bone Fracture. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15(12):2845.
[28] BLACKWELL KA, RAISZ LG, PILBEAM CC. Prostaglandins in bone: bad cop, good cop?. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010;21(5):294-301.
[29] WHEATLEY BM, NAPPO KE, CHRISTENSEN DL, et al. Effect of NSAIDs on Bone Healing Rates: A Meta-analysis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019;27(7):e330-e336.
[30] GEORGE MD, BAKER JF, LEONARD CE, et al. Risk of Nonunion with Nonselective NSAIDs, COX-2 Inhibitors, and Opioids. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(14):1230-1238.
[31] LONG J, LEWIS S, KUKLO T, et al. The effect of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors on spinal fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84(10):1763-1768.
[32] GE DW, WANG WW, CHEN HT, et al. Functions of microRNAs in osteoporosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(21):4784-4789.
|