[1] 王礼宁,马勇,郑苏阳,等.蛇床子素对NFATc1基因表达及破骨细胞分化的影响[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2018,11(5): 475-483.
[2] BOSE S, SARKAR N. Natural medicinal compounds in bone tissue engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2020;38(4):404-417.
[3] 何家扬.骨愈灵胶囊治疗Colles骨折34例临床观察[J].新中医,2013, 45(9):61-62.
[4] 王晓军.骨愈灵胶囊治疗骨质疏松性桡骨远端骨折效果分析[J].航空航天医学杂志,2012,23(10):1229-1230.
[5] 胡南.骨愈灵胶囊对上肢骨折患者术后疼痛、肿胀、骨折愈合的影响[J].医药前沿,2015,5(14):155-156.
[6] 何郁泉.骨愈灵胶囊治疗骨质疏松症及各类型骨折临床疗效观察[C].骨质疏松研究与防治文集.1994.
[7] 刘继平.骨愈灵胶囊主要药效及毒理学研究[D].西安:陕西中医药大学, 2008.
[8] 丁桂芝,李榕,周勇.骨愈灵胶囊治疗骨质疏松症32例疗效观察[J].医药导报,1994,(5):212-213.
[9] 高武兴.骨愈灵胶囊治疗骨质疏松症68例临床疗效观察[J].内蒙古中医药,2013,32(27):19-20.
[10] 吴永光.骨愈灵胶囊治疗骨质疏松症临床疗效观察[J].湖北中医杂志, 2012,34(6):32.
[11] 孙静. 蛇床子素促成骨作用及代谢多态性研究[D].天津:天津医科大学, 2019.
[12] ZHAO Y, XU Y, ZHENG H, et al. QingYan formula extracts protect against postmenopausal osteoporosis in ovariectomized rat model via active ER-dependent MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt signal pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;268:113644.
[13] NOGUCHI T, EBINA K, HIRAO M, et al. Apolipoprotein E plays crucial roles in maintaining bone mass by promoting osteoblast differentiation via ERK1/2 pathway and by suppressing osteoclast differentiation via c-Fos, NFATc1, and NF-κB pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503(2):644-650.
[14] ZHAO H, YANG Y, WANG Y, et al. MicroRNA-497-5p stimulates osteoblast differentiation through HMGA2-mediated JNK signaling pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):515.
[15] BROWN KK, HEITMEYER SA, HOOKFIN EB, et al. P38 MAP kinase inhibitors as potential therapeutics for the treatment of joint degeneration and pain associated with osteoarthritis. J Inflamm (Lond). 2008;5:22.
[16] JO YJ, LEE HI, KIM N, et al. Cinchonine inhibits osteoclast differentiation by regulating TAK1 and AKT, and promotes osteogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2021; 236(3):1854-1865.
[17] KOT A, ZHONG ZA, ZHANG H, et al. Sex dimorphic regulation of osteoprogenitor progesterone in bone stromal cells. J Mol Endocrinol. 2017;59(4):351-363.
[18] MUKHERJEE A, LARSON EA, KLEIN RF, et al. Distinct actions of akt1 on skeletal architecture and function. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e93040.
[19] MUKHERJEE A, ROTWEIN P. Selective signaling by Akt1 controls osteoblast differentiation and osteoblast-mediated osteoclast development. Mol Cell Biol. 2012;32(2):490-500.
[20] MUKHERJEE A, WILSON EM, ROTWEIN P. Selective signaling by Akt2 promotes bone morphogenetic protein 2-mediated osteoblast differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30(4):1018-1027.
[21] AMJADI-MOHEB F, AKHAVAN-NIAKI H. Wnt signaling pathway in osteoporosis: Epigenetic regulation, interaction with other signaling pathways, and therapeutic promises. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(9): 14641-14650.
[22] Liu Y, Wang X, Chang H, et al. Mongolian Medicine echinops prevented postmenopausal osteoporosis and induced ER/AKT/ERK pathway in BMSCs. Biosci Trends. 2018;12(3):275-281.
[23] 刘景陶,柳耀花.计算机分子模拟技术及人工智能在药物研发中的应用[J].科技创新与应用,2018(2):46-47.
[24] 刘景陶,刘映雪.分子对接在药物研发中的应用[J].科技创新与应用,2018(1):167-168.
[25] 叶小彤.基于生物信息学的中药蛋白质成分作用机制研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2017.
[26] WANACHEWIN O, POTHACHAROEN P, KONGTAWELERT P, et al. Inhibitory effects of sesamin on human osteoclastogenesis. Arch Pharm Res. 2017; 40(10):1186-1196.
[27] 李慧英,孟东方,阮志磊.骨碎补总黄酮对激素性股骨头坏死血钙、血磷及空骨陷窝率的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2016,31(12): 5352-5354.
[28] 王永胜,胡菁菁,卢育南,等.骨碎补总黄酮对去势大鼠骨质疏松的防治作用[J].中国卫生标准管理,2020,11(9):94-95.
[29] KIM EK, CHOI EJ. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1802(4):396-405.
[30] 陈建勇,王聪,王娟,等.MAPK信号通路研究进展[J].中国医药科学, 2011,1(8):32-34.
[31] YANG Y, FANG S. Small non-coding RNAs-based bone regulation and targeting therapeutic strategies. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017;456:16-35.
[32] XING LZ, NI HJ, WANG YL. Quercitrin attenuates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by regulating mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;89:1136-1141.
[33] TAK PP, FIRESTEIN GS. NF-kappaB: a key role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest. 2001;107(1):7-11.
[34] AN Y, ZHANG H, WANG C, et al. Activation of ROS/MAPKs/NF-κB/NLRP3 and inhibition of efferocytosis in osteoclast-mediated diabetic osteoporosis. FASEB J. 2019;33(11):12515-12527.
[35] ONO K, HAN J. The p38 signal transduction pathway: activation and function. Cell Signal. 2000;12(1):1-13.
[36] BA P, DUAN X, FU G, et al. Differential effects of p38 and Erk1/2 on the chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(1):63-68.
[37] XIAO L, ZHONG M, HUANG Y, et al. Puerarin alleviates osteoporosis in the ovariectomy-induced mice by suppressing osteoclastogenesis via inhibition of TRAF6/ROS-dependent MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(21):21706-21729.
[38] LEE JY, PARK SJ, KIM DA, et al. Muscle-derived lumican stimulates bone formation via integrin α2β1 and the downstream ERK signal. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:565826.
[39] JIN H , SHAO Z , WANG Q, et al. Sclareol prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss in vivo and inhibits osteoclastogenesis in vitro via suppressing NF-κB and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways. Food Funct. 2019;10(10):6556-6567.
[40] WANG W, BAI J, ZHANG W, et al. Protective effects of punicalagin on osteoporosis by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and inflammation via the nf-κb and mapk pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:696.
|

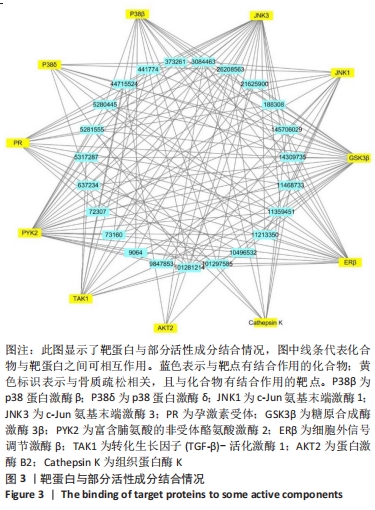
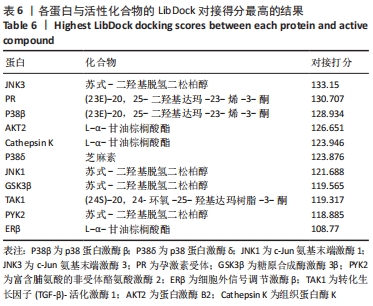
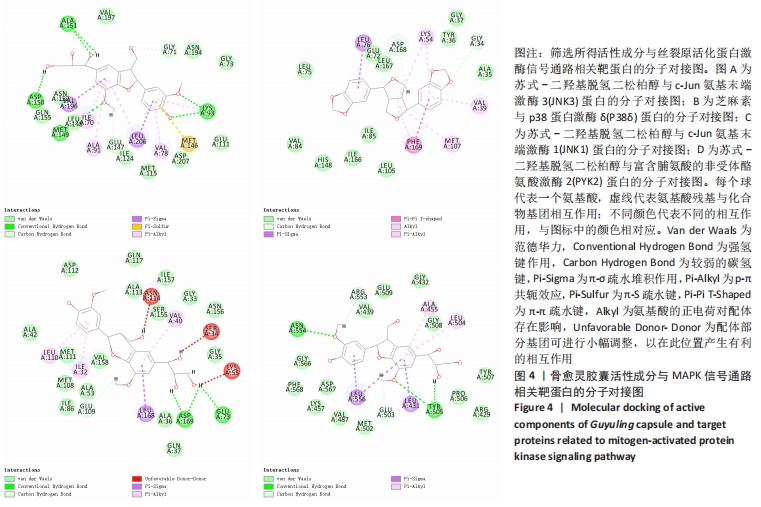


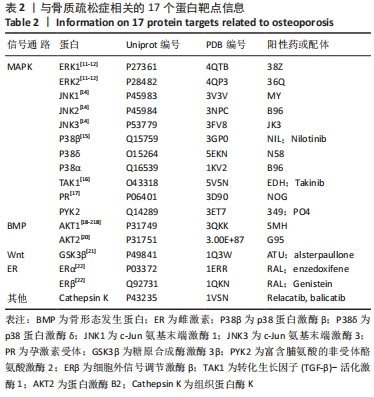
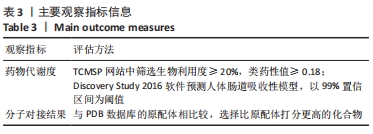

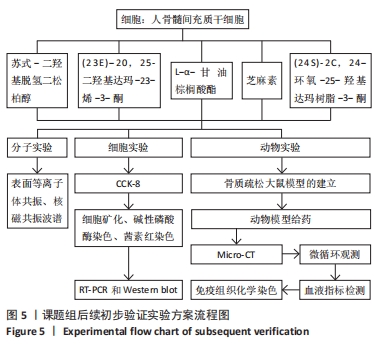 3.3 文章局限性及展望 由于中药复方中的中药有不同配比,活性成分含量也不同,分子对接无法确定成分的差异。文章将方剂中的活性成分作为天然化合物的分子库,借此寻找对骨质疏松症有治疗作用的药物。现有数据表明,通过网络药理学筛选得到的成分作为骨愈灵胶囊的主要药效成分可能仅有理论上的意义。计算机分子对接模拟是为了筛除与靶蛋白没有作用的单体,留下与靶蛋白有相互作用的活性单体,但是这种相互作用是激活还是抑制,以及这种相互作用的强度如何,都需要进一步实验验证。总之,实验运用生物信息学与分子对接方法预测骨愈灵胶囊治疗骨质疏松症的潜在活性成分、及其与骨质疏松症相关靶蛋白的结合情况,探究骨愈灵胶囊治疗骨质疏松症的可能分子机制,为进一步展开相关实验研究提供活性物质基础及思路。
3.3 文章局限性及展望 由于中药复方中的中药有不同配比,活性成分含量也不同,分子对接无法确定成分的差异。文章将方剂中的活性成分作为天然化合物的分子库,借此寻找对骨质疏松症有治疗作用的药物。现有数据表明,通过网络药理学筛选得到的成分作为骨愈灵胶囊的主要药效成分可能仅有理论上的意义。计算机分子对接模拟是为了筛除与靶蛋白没有作用的单体,留下与靶蛋白有相互作用的活性单体,但是这种相互作用是激活还是抑制,以及这种相互作用的强度如何,都需要进一步实验验证。总之,实验运用生物信息学与分子对接方法预测骨愈灵胶囊治疗骨质疏松症的潜在活性成分、及其与骨质疏松症相关靶蛋白的结合情况,探究骨愈灵胶囊治疗骨质疏松症的可能分子机制,为进一步展开相关实验研究提供活性物质基础及思路。