[1] 陆艳红,石晓兵.膝骨关节炎国内外流行病学研究现状及进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2012,20(6):81-84.
[2] 刘铭柏,刘少津,乔荣勤,等.口服养血方联合蜡疗治疗膝骨关节炎气血虚弱证的疗效观察及作用机制分析[J].中医正骨,2018,30(9):67-69, 72.
[3] 许蓓,林进.骨关节炎发病机制及治疗进展[J].浙江医学,2017, 39(21):1833-1835, 1851.
[4] ZHANG P, LIANG Y, HE J, et al. Timing of tourniquet release in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(17):e6786.
[5] PARVIZI J, DIAZ-LEDEZMA C. Total knee replacement with the use of a tourniquet: more pros than cons. Bone Joint J. 2013; 95-B(11 Suppl A):133-134.
[6] WANG K, NI S, LI Z, et al. The effects of tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(9): 2849-2857.
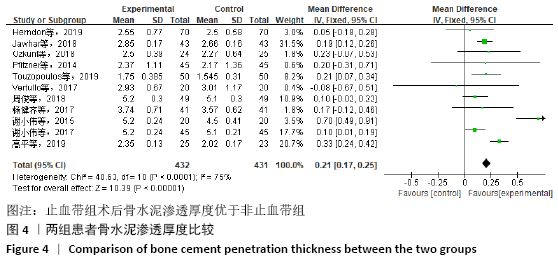
[7] TOUZOPOULOS P, VERVERIDIS A, MPOGIATZIS C, et al. The use of tourniquet may influence the cement mantle thickness under the tibial implant during total knee arthroplasty. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2019;29(4):869-875.
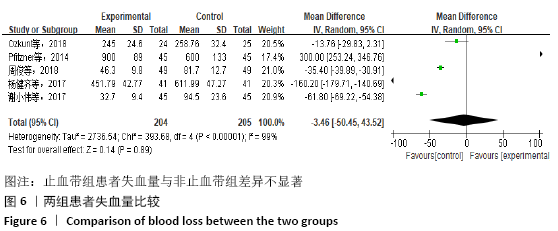
[8] PFITZNER T, VON ROTH P, VOERKELIUS N, et al. Influence of the tourniquet on tibial cement mantle thickness in primary total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(1):96-101.
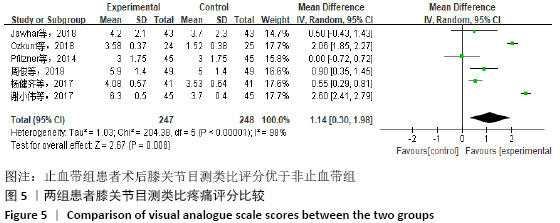
[9] Jawhar A, Stetzelberger V, Kollowa K, et al. Tourniquet application does not affect the periprosthetic bone cement penetration in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(7):2071-2081.
[10] LUTZ MJ, PINCUS PF, WHITEHOUSE SL, et al. The effect of cement gun and cement syringe use on the tibial cement mantle in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(3):461-467.
[11] MILLER MA, GOODHEART JR, IZANT TH, et al. Loss of cement-bone interlock in retrieved tibial components from total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Related Res. 2014;472(1):304-313.
[12] HERNDON CL, GROSSO MJ, SARPONG NO, et al. Tibial cement mantle thickness is not affected by tourniquetless total knee arthroplasty when performed with tranexamic acid. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(5):1526-1531.
[13] JAWHAR A, SKEIREK D, STETZELBERGER V, et al. Influence of the Tourniquet on Pain and Function in Total Knee Arthroplasty: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Z Orthop Unfall. 2019. doi: 10.1055/a-0983-3808.
[14] 顾培伦,董金波,王维山,等.人工全膝关节置换中是否应用气囊止血带止血:一项Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(15):2446-2452.
[15] VERTULLO CJ, NAGARAJAN M. Is cement penetration in TKR reduced by not using a tourniquet during cementation? A single blinded, randomized trial. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2017;25(1):2309499016684323.
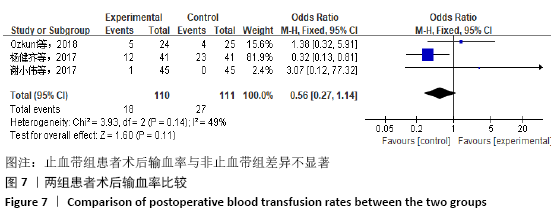
[16] OZKUNT O, SARIYILMAZ K, GEMALMAZ HC, et al. The effect of tourniquet usage on cement penetration in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study of 3 methods. Medicine. 2018;97(4): e9668.
[17] 谢小伟,岳辰,黄泽宇,等.全膝关节置换术应用与不应用止血带的随机对照研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2017,25(17): 1572-1576.
[18] 杨健齐,魏鲁青,张健平,等.全膝关节置换术中止血带应用对假体骨水泥厚度影响的对照研究[J].重庆医学,2017, 46(6):782-785.
[19] 高平,李会波,白正武,等.TKA术中不使用止血带对早期假体稳定性及膝关节功能的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2019,34(12):1294-1296.
[20] 周俊,钭伟国,欧阳海清,等.全膝关节置换术中不应用止血带对患者术后的影响[J].中国乡村医药,2018,25(23):10-11, 13.
[21] 谢小伟.比较三种不同止血带方法:对初次全膝关节置换术患者早期康复及骨水泥厚度的影响[C].2015成都国际骨科论坛暨四川省医学会第19次骨科学术会议.2015.
[22] 顾培伦.全膝关节置换术中是否应用止血带Meta分析[D].石河子:石河子大学, 2018.
[23] 杨健齐.全膝关节置换术中止血带应用的研究进展[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2018,11(11):877-880.
[24] WANG FD, WANG YP, CHEN CF, et al. The incidence rate, trend and microbiological aetiology of prosthetic joint infection after total knee arthroplasty: a 13 years’ experience from a tertiary medical center in Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2018;51(6):717-722.
[25] EJAZ A, LAURSEN AC, KAPPEL A, et al. Faster recovery without the use of a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2014;85(4):422-426.
[26] 杜传超,邱海滨,张衡,等.关于全膝关节置换术中使用止血带利弊随机对照性研究的系统回顾及Meta分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(8):800-803.
[27] YI S, TAN J, CHEN C, et al. The use of pneumatic tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(10):1469-1476.
[28] 吴鑫杰,谭明生.充气式止血带在全膝关节置换术中应用的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(17):1601-1604.
[29] MAJKOWSKI RS, BANNISTER GC, MILES AW, et al. The effect of bleeding on the cement-bone interface. An experimental study. Clin Orthop Related Res. 1994;(299):293-297.
[30] MOHER D, SHAMSEER L, CLARKE M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. 2015; 4(1):1.
[31] HE S, ZHANG Y, LV N, et al. The effect of bone cement distribution on clinical efficacy after percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Medicine. 2019;98(50):e18217.
[32] Ledin H, Aspenberg P, Good L, et al. Tourniquet use in total knee replacement does not improve fixation, but appears to reduce final range of motion. Acta Orthop. 2012;83(5):499-503.
[33] MOLT M, HARSTEN A, TOKSVIG-LARSEN S, et al. The effect of tourniquet use on fixation quality in cemented total knee arthroplasty a prospective randomized clinical controlled RSA trial. Knee. 2014;21(2):396-401.
[34] BUCHER TA, BUTLER M, LEE C, et al. TKR without tourniquet: A laboratory study investigating the quality of the tibial cement mantle when using metaphyseal suction and cement gun. J Arthroscopy Joint Surg. 2015. doi:10.1016/j.jajs.2015.06.002.
[35] Srinivasan P, Miller MA, Verdonschot N, et al. Strain shielding in trabecular bone at the tibial cement-bone interface. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;66:181-186.
[36] OLIVECRONA C, LAPIDUS J, BENSON L, et al. Tourniquet time affects postoperative complications after knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2013;37(5):827-832.
[37] GILLANI S, CAO J, SUZUKI T, et al. The effect of ischemia reperfusion injury on skeletal muscle. Injury. 2012;43(6):670-675.
[38] MURATA I, NOZAKI R, OOI K, et al. Nitrite reduces ischemia/reperfusion-induced muscle damage and improves survival rates in rat crush injury model. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;72(6):1548-1554.
[39] ZHANG P, LIANG Y, HE J, et al. Timing of tourniquet release in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Medicine. 2017;96(17):e6786.
[40] NA YG, BAMNE AB, WON HH, et al. After early release of tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty, should it be reinflated or kept deflated? A randomized trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017; 25(9):2769-2777.
[41] KOVESI T, ROYSTON D. Pharmacological approaches to reducing allogeneic blood exposure. Vox Sanguinis. 2003;84(1):2-10.
[42] HU Y, LI Q, WEI BG, et al. Blood loss of total knee arthroplasty in osteoarthritis: an analysis of influential factors. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):325.
[43] CHEUY VA, FORAN JRH, PAXTON RJ, et al. Arthrofibrosis associated with total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(8):2604-2611.
|