中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (10): 1489-1494.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3052
• 组织工程骨材料Tissue-engineered bone • 上一篇 下一篇
骨形态发生蛋白9复合胶原基骨修复材料体外成骨性能与体内修复骨缺损
庄传记1,陈文昭2,江新民1
- 1景德镇市第二人民医院骨科,江西省景德镇市 333000;2南昌大学第一附属医院骨科,江西省南昌市 330006
Osteogenesis in vitro and bone defect repair in vivo of bone morphogenetic protein 9 composite collagen based bone repair material
Zhuang Chuanji1, Chen Wenzhao2, Jiang Xinmin1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Second People’s Hospital of Jingdezhen, Jingdezhen 333000, Jiangxi Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
骨形态发生蛋白:属于转化生长因子β超家族成员,因具有较强的诱导骨形成能力而得名,在人类中具有促成骨作用的主要有骨形态发生蛋白2、骨形态发生蛋白4、骨形态发生蛋白6与骨形态发生蛋白7,其中骨形态发生蛋白2与骨形态发生蛋白7目前已被临床用于促进脊柱融合。近些年的研究显示,骨形态发生蛋白成员中的骨形态发生蛋白9同样具有诱导骨形成与成骨分化的能力。
碱性磷酸酶:几乎存在于人体的任何组织,但主要集中于骨、肝脏、胆管、肾脏等,是成骨分化早期的重要标志性基因。
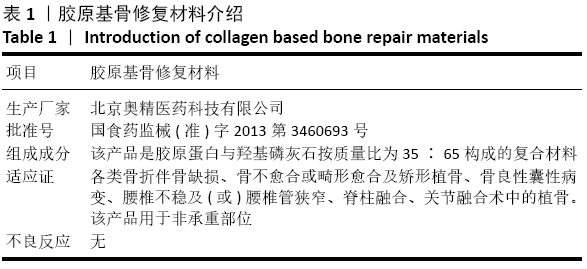
背景:胶原基骨修复材料具备良好的骨传导性、骨诱导性、降解性、机械性能与生物相容性,目前已被广泛应用于临床骨修复中,但其诱导成骨效果仍不及自体骨。
目的:将骨形态发生蛋白9(bone morphogenetic protein 9,BMP-9)复合于胶原基骨修复材料中,观察其诱导成骨的能力。
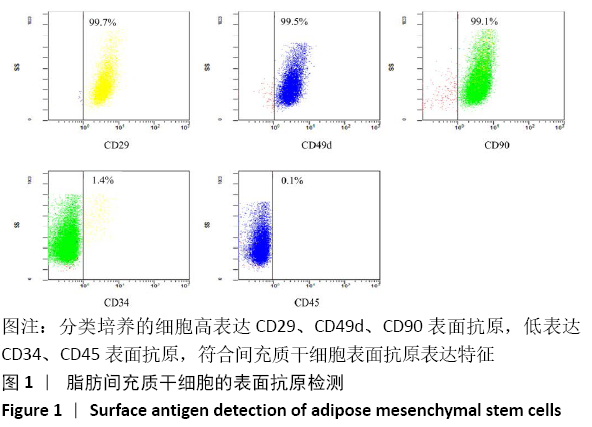
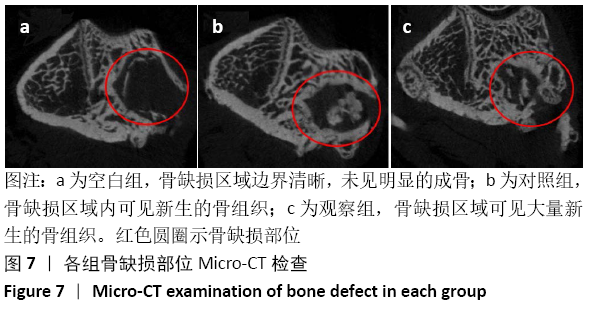
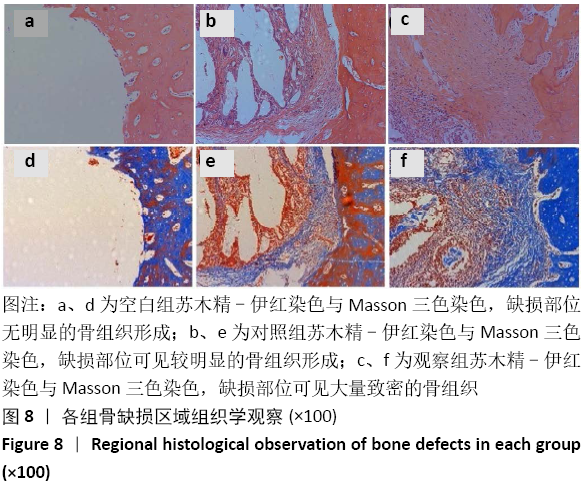
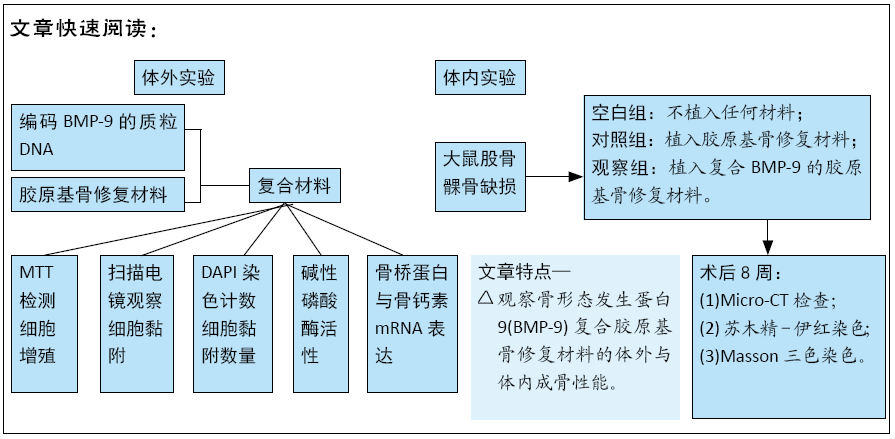
方法:将编码BMP-9的质粒DNA负载到胶原基骨修复材料中,构建复合BMP-9的胶原基骨修复材料。①体外实验:将SD大鼠脂肪间充质干细胞分别接种于复合BMP-9的胶原基骨修复材料与胶原基骨修复材料中,利用MTT法检测细胞增殖,扫描电镜观察细胞黏附,DAPI染色后计数细胞黏附数量,碱性磷酸酶活力试剂盒检测成骨诱导后细胞中的碱性磷酸酶活性,qRT-PCR检测成骨诱导后细胞中的骨桥蛋白与骨钙素mRNA表达量;②体内实验:在15只SD大鼠右后肢股骨内上髁制作直径3 mm、深3 mm的骨缺损,空白组不植入任何材料,对照组植入胶原基骨修复材料,观察组植入复合BMP-9的胶原基骨修复材料,术后8周取材,分别进行Micro-CT检查与组织学观察。实验方案经南昌大学实验动物科学中心伦理委员会批准。
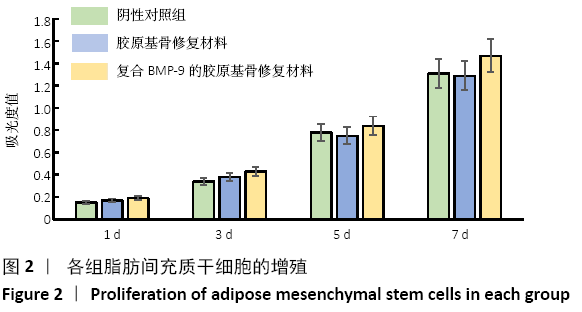
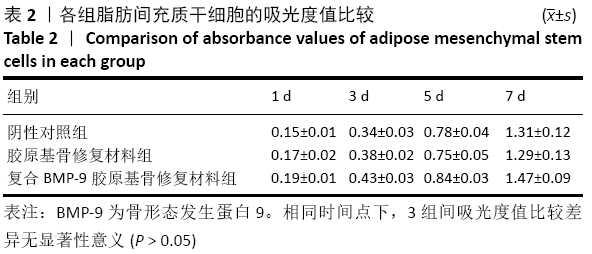
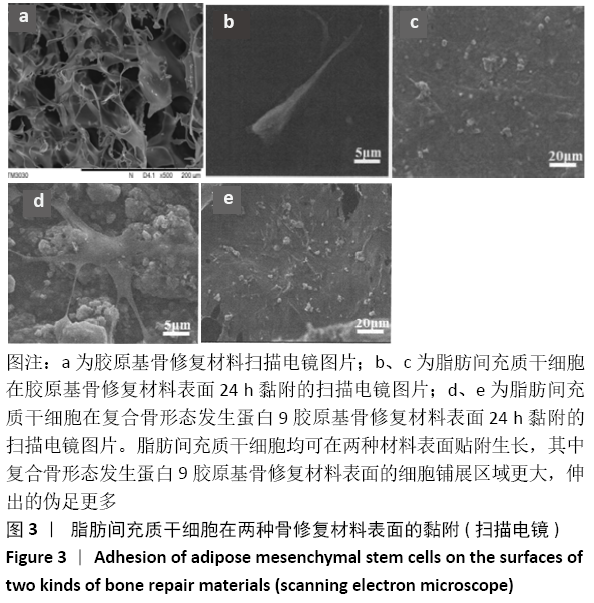
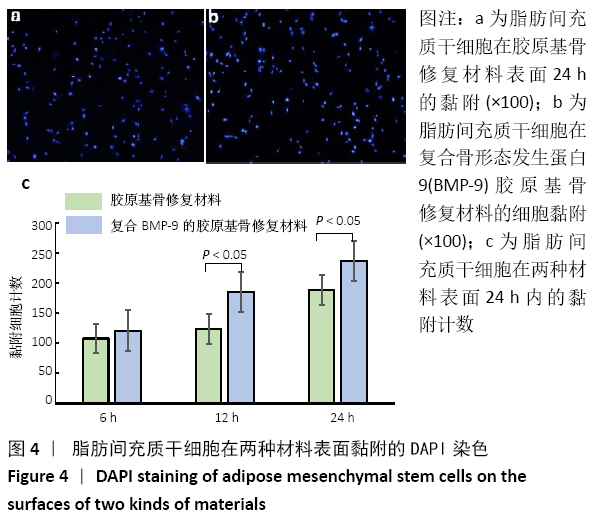
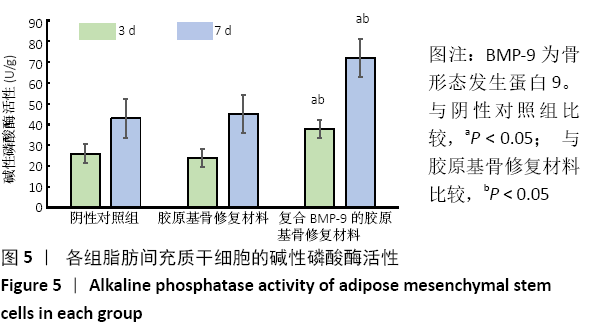
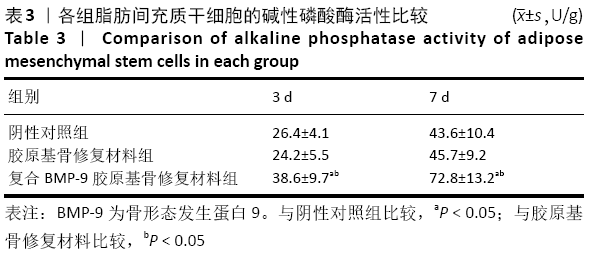
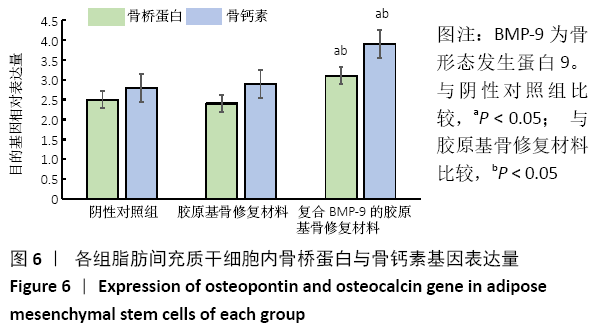
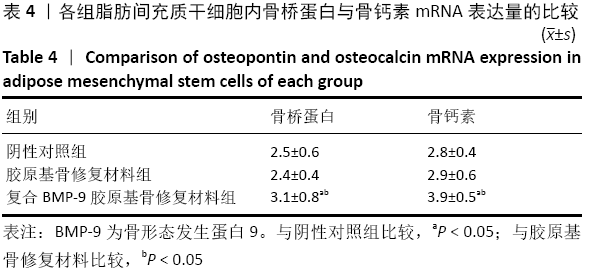
结果与结论:①体外实验显示,复合BMP-9胶原基骨修复材料中培养1,3,5,7 d的细胞增殖与胶原基骨修复材料比较差异无显著性意义(P﹥0.05);②体外共培养24 h后,在复合BMP-9胶原基骨修复材料表面黏附的细胞较多,并伸出较多的伪足,黏附细胞计数与铺展情况优于胶原基骨修复材料;③体外成骨诱导3,7 d后,复合BMP-9胶原基骨修复材料表面细胞的碱性磷酸酶活性高于胶原基骨修复材料(P < 0.05),成骨诱导7 d后的骨桥蛋白与骨钙素mRNA表达量高于胶原基骨修复材料(P < 0.05);④体内实验Micro-CT检查显示,观察组新骨生成量高于对照组、空白组(P < 0.05),对照组高于空白组(P < 0.05);⑤体内实验苏木精-伊红与Masson三色染色显示,观察组的骨修复效果优于对照组、空白组,对照组优于空白组;⑥结果表明,BMP-9可进一步提高胶原基骨修复材料的骨诱导性能。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4297-9304 (庄传记)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: