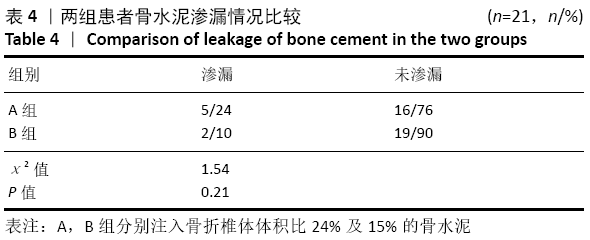
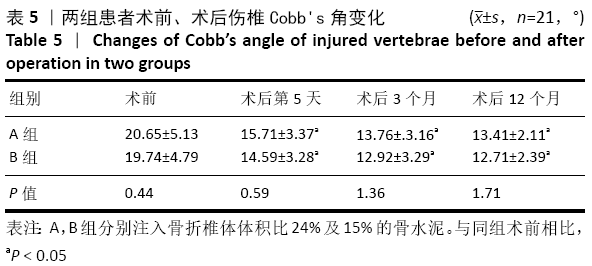
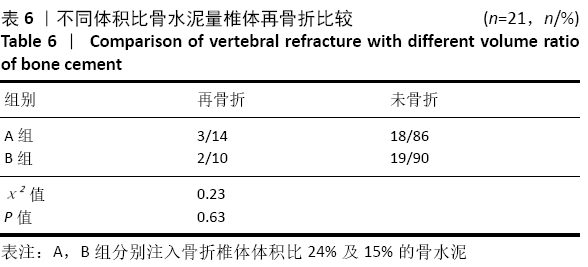
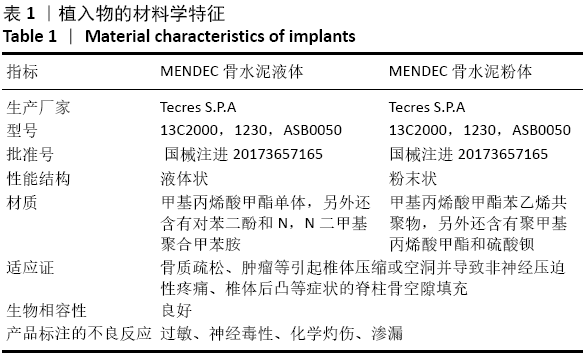
[1] 李楠,张贵林,何达,等.骨水泥的分布与剂量对椎体成形术疗效影响的研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(1):66-68.
[2] LI YA, LIN CL, CHANG MC, et al. Subsequent vertebral fracture after vertebroplasty: incidences and analysis of risk factors. Spine. 2012; 37(3): 179-183.
[3] NIEUWENHUIJSE MJ, BOLLEN L,VAN ERKEL AR, et al. Optimal intravertebral cement volume in percutaneous vertebroplasty for Painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine. 2012; 37(20): 1747-1755.
[4] LA MAIDA GA, GIARRATANA LS, ACERBI A, et al. Cement leakage: safety of minimally invasive surgical techniques in the treatment of myeloma vertehral lesions. Eur Spine J. 2012;1:61-68.
[5] LIEBSCHNER MA, ROSENBERG WS, KEAVENY TM. Effects of bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebroplasty. Spine. 2001; 26(14) :1547-1554.
[6] YANG B, FANG SB, LI CS, et al. Digital Three-Dimensional Model of Lumbar region 4-5 and Adjacent Structures Based on a virtual Chinese human. Orthop Surg. 2013;5(2):130-134.
[7] 杨波,方世兵,唐雷,等.数值化虚拟腰椎的三维重建及可视化研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2013,33(1):71-75.
[8] 中国医师协会骨科学分会脊柱创伤专业委员会.急性症状性骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折椎体强化术临床指南[J].中华创伤杂志, 2019,35(6):481-489.
[9] 杨惠林,刘强,唐海,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折患者抗骨质疏松规范治疗专家共识[J].中华医学杂志,2018,98(11):803-807.
[10] WANG G, YANG H, CHEN K. Osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with an intravertebral cleft treated by percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(11):1553-1557.
[11] 杨惠林,胡侦明,邱贵兴,等.经皮椎体成形术治疗的相关建议[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2015,8(5):375-376.
[12] KALLMES DF, COMSTOCK BA, HEAGERTY PJ, et al. A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic spinal fractures. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361(6):569-579.
[13] BUCHBINDER R, OSBORNE RH, EBELING PR, et al. A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(6):557-568.
[14] KLAZEN CA , LOHLE PN , DE VRIES J ,et al. Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet . 2010; 376 (9746): 1085-1092.
[15] CLARK W, BIRD P, GONSKI P, et al. Safety and efficacy of vertebroplasty for acute painful osteoporotic fractures (VAPOUR): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet . 2016; 388 (10052): 1408-1416.
[16] WARDLAW D, CUMMINGS SR, VAN MEIRHAEGHE J, et al. Efficacy and safety of balloon kyphoplasty compared with non-surgical care for vertebral compression fracture (FREE): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2009; 373 (9668): 1016-1024.
[17] SAXENA BP, SHAH BV, JOSHI SP. Outcome of percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty in vertebral compression fractures. Indian J Orthop. 2015; 49(4):458-464.
[18] ZAPAŁOWICZ K, RADEK M. Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of painful vertebral compression fractures: effect on local kyphosis and one-year outcomes in pain and disability. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2015; 49(1):11-15.
[19] CHEN AT,COHEN DB,SKOLASKY RL. Impact of nonoperative treatment, vertebroplasty, and kyphoplasty on survival and morbidity after vertebral compression fracture in the medicare population. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 2013; 95(19):1729-1736.
[20] 黎双庆,杨波,杨逸禧,等.经皮穿刺椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性严重椎体压缩性骨折[J].中国微创外科杂志,2015,15(9):818-821.
[21] 陈建常,王鑫,马在松,等.骨质疏松患者PVP/PKP术后新发椎体压缩性骨折相关危险因素[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(10): 902-907.
[22] KAUFMANN TJ,TROUT AT,KALLMES DF. The effects of cement volume on clinical outcome of percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27 (9) :1933-1937.
[23] 苟永胜,李海波,何小翠,等.骨水泥注射量与经皮椎体后凸成形术后疗效的临床随机对照研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015, 30(5):473-476.
[24] LUO J, DAINES L, CHARALAMBOUS A, et al. Vertebroplasty: only small cement volumes are required to normalize stress distributions on the vertebral bodies.Spine. 2009;34(26):2865-2873.
[25] YAN L , CHANG Z , XU Z, et al. Biomechanical effects of bone cement volume on the endplates of augmented vertebral body: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(1): 79-84.
[26] 江晓兵,黄伟权,庞智晖,等. 基于Mimics软件计算椎体强化术后椎体内骨水泥体积及骨水泥/推体体积比的新方法[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(3):238-243
[27] MOUSAVI P, ROTH S, FINKELSTEIN J, et al. Volumetric quantification of cement leakage following percutaneous vertebroplasty in metastatic and osteoporotic vertebrae. J Neurosurg. 2003;99 (1 Suppl): 56-59.
[28] KOMEMUSHI A, TANIGAWA N,KARIYA S, et al. percutaneous vertebroplasty for compression fracture:analysis of verterbral body by CT volumetry. Acta Radiol. 2005;46(3):276-279.
[29] JIN YJ, YOON SH, PARK KW, et al. The volumetric analysis of cement in vertebroplasty: relationship with clinical outcome and complications. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(2):E761-E762.
[30] NIEUWENHUIJSE MJ, BOLLEN L, VAN ERKEL AR, et al. Optimal intravertebral cement volume in percutaneous vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(20):1747-1755.
[31] KWON HM, LEE SP, BAEK JW, et al. Appropriate cement volume in vertebroplasty: a multivariate analysis with short-term follow-up. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2016;12(2):128-134.
[32] 唐龙,杨波,章波,等.数字骨科学在微创治疗严重OVCF中临床应用[J].中国数字医学,2015,10(1):61-63.
[33] 杨惠林.经皮椎体强化术的临床应用[J].骨科,2017,8(3):161-162.
[34] SONG D, MENG B, GAN M, et al. The incidence of secondary vertebral fracture of vertebral augmentation techniques versus conservative treatment for painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a systematic review and meta analysis. Acta Radiol. 2015;56(8):970-979.
[35] TAYLOR RS, FRITZELL P, TAYLOR RJ. Balloon kyphoplasty in the management of vertebral compression fractures: an updated systematic review and meta-Analysis. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(8): 1085-1100.
[36] TROUT AT, KALLMES DF. Does vertebroplasty cause incident vertebral fractures?A review of available data. AJNR Am JNeuroradiol. 2006; 27(7):1397-1403.
[37] POLIKEIT A, NOHE LP, FERGUSON SJ. The effect of cement augmentation on the load transfer in an osteoporotic functional spinal unit: finite-element analysis. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(10): 991-996.
[38] 张煜,张绍东.椎体成形术后手术椎体再塌陷的危险因素[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2016,26(5):459-462. |