中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (19): 3103-3109.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0271
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇 下一篇
氨甲环酸减少胸腰椎后路融合围术期出血量的Meta分析
钟的桂,王文豪,吕 阳,陈善创,麦秀钧,黄永明,黄永铨,侯秋科,苏海涛
- 广州中医药大学第二附属医院,广东省中医院,广东省广州市 510120
Tranexamic acid reduces perioperative blood loss in thoracolumbar posterior fusion: a meta-analysis
Zhong De-gui, Wang Wen-hao, Lü Yang, Chen Shan-chuang, Mai Xiu-jun, Huang Yong-ming, Huang Yong-quan, Hou Qiu-ke, Su Hai-tao
- the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of TCM, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
氨甲环酸:是抗纤维蛋白溶解药物中的一种,由赖氨酸衍生物合成,通过吸附在纤维蛋白赖氨酸结合位点,竞争性抑制阻止纤溶酶与纤维蛋白结合,抑制纤维蛋白溶解,从而减少术中、术后失血和隐性失血,临床中在髋膝关节置换围术期使用较为常见,可减少创伤及手术所致出血量来降低死亡率。
胸、腰椎后路融合:是临床中运用最广的胸腰椎入路。除了进达胸、腰椎间盘外,此入路还能暴露脊椎的所有后部成分:棘突、椎板、椎间小关节和椎弓根,此入路经由后正中线,可向近侧及远侧延伸。严重退变性胸、腰椎管狭窄通常需要后路减压植骨融合手术治疗,术中需要广泛的椎板减压、椎体间或椎旁融合并辅助椎弓根螺钉固定,术中出血多,操作复杂,手术时间长,并且大量的失血通常需要输血治疗。
摘要
背景:有研究报道胸腰椎后路融合围术期运用氨甲环酸可减少围手术期出血量,但这些研究普遍病例数较少。因而,有必要对国内外氨甲环酸减少胸腰椎后路融合术后出血量的临床研究进行系统评价和分析。
目的:探讨氨甲环酸减少胸腰椎后路融合围术期出血量的疗效和安全性。
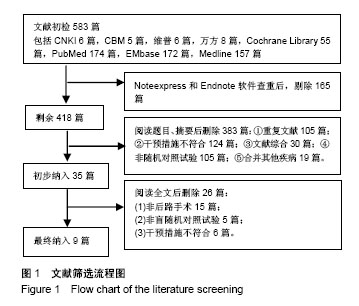
方法:计算机全面检索Cochrane Library,PubMed,EMbase,Medline 4个外文数据库和在中国期刊全文数据库、中国生物医学文献、万方、维普等4个中文数据库中关于氨甲环酸在胸腰椎后路融合术中作用的随机对照研究,通过阅读全文对文献进行方法学质量评价,运用RevMan 5.3软件进行异质性分析,再进行Meta分析合并效应量。
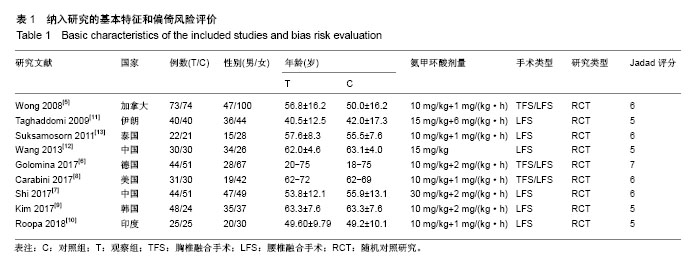
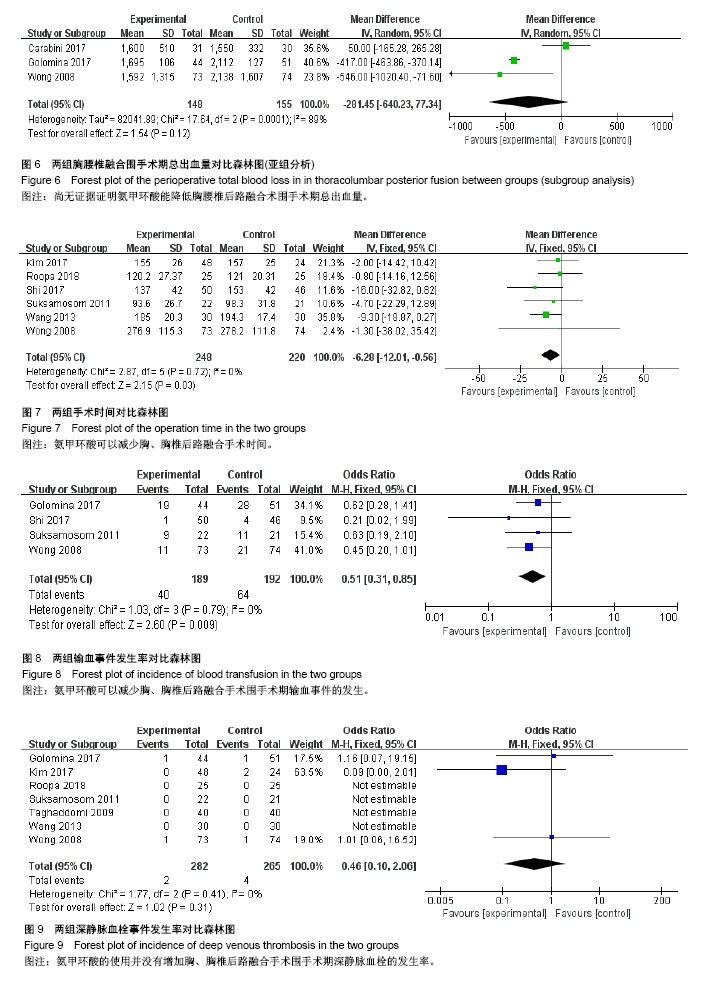
结果与结论:共计纳入9个研究,其中氨甲环酸组患者363例,对照组341例,Meta分析结果显示:对比同等剂量安慰剂,在胸腰椎后路融合术中静滴氨甲环酸可降低术中出血量(MD=-50.57,95%CI:-78.69至-22.44),降低术后引流量(MD=-109.45,95%CI:-124.50至-94.39),减少围手术期输血需求(OR=0.51,95%CI:0.31-0.85),也降低了手术操作时间(MD=-6.28,95%CI:-12.01至-0.56),且并未增加深静脉血栓事件的发生率(OR=0.46,95%CI:0.10-2.06),氨甲环酸还可降低腰椎后路融合围手术期总出血量(MD=-184.53,95%CI:-224.66至-144.40)。结果证实,在胸腰椎后路融合术中静滴氨甲环酸可减少术中、术后出血量和输血,具有较好的疗效和安全性,由于纳入文章病例数不多,仍需大样本、多中心随机对照试验的进一步去证实。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-7377-6370(钟的桂)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-7377-6370(钟的桂)
中图分类号:

.jpg)