中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (27): 4337-4341.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0349
• 脊柱植入物 spinal implant • 上一篇 下一篇
经伤椎一侧置钉联合短节段5钉内固定治疗不稳定型胸腰椎骨折
常步青,冯 虎,于潮将,单鸿剑,胡孟子,李子昂,卜祥博,高 啸,蒋允昌
- 徐州医科大学附属医院骨科,江苏省徐州市 221000
Unilateral placement combined with short-segment five-screw fixation for unstable thoracolumbar fractures
Chang Bu-qing, Feng Hu, Yu Chao-jiang, Shan Hong-jian, Hu Meng-zi, Li Zi-ang, Bu Xiang-bo, Gao Xiao, Jiang Yun-chang
- Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
不稳定型胸腰椎骨折:不稳定脊柱损伤指骨折或脱位在愈合过程中易移位产生神经或脊髓症状的骨折。爆裂骨折、屈曲分离损伤、骨折脱位均破坏前、中、后柱,属不稳定损伤。
后纵韧带复合体:包括黄韧带、棘间韧带、棘上韧带和小关节囊。这些结构共同保证了脊柱的稳定性,并对轻微损伤具有一定的抵抗作用。后纵韧带复合体的损伤通常是手术治疗的指征之一。后纵韧带复合体状态的分类有:完整、破裂和未定型。
摘要
背景:胸腰椎骨折是最常见的脊柱骨折,中青年的胸腰椎骨折多由较大的外力造成,传统的长节段固定目前已被短节段的跨伤椎固定所取代,但是短节段固定易造成伤椎椎体高度的丢失,采用5钉三椎体固定近年逐渐成为主流的修复方式。
目的:探讨后路经伤椎一侧置钉联合短节段5钉内固定治疗不稳定型胸腰椎骨折的疗效。
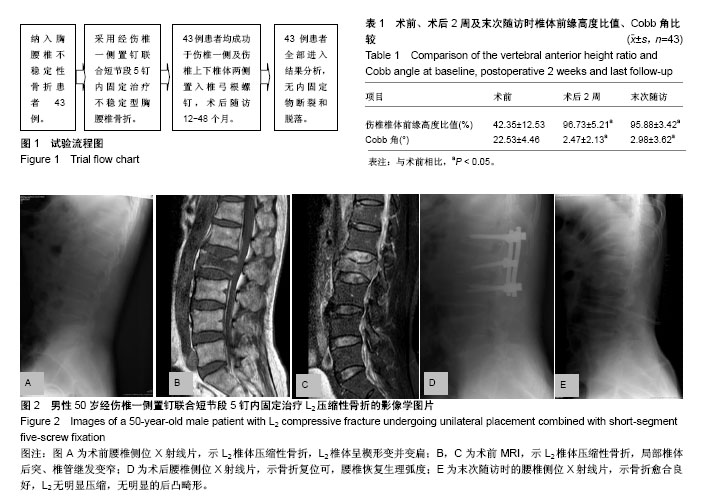
方法:回顾性分析徐州医科大学附属医院2012年1月至2015年12月采用后路经伤椎一侧置钉联合短节段5钉内固定治疗单节段胸腰椎骨折并获得1年以上随访的43例患者,根据术前、术后以及末次随访时的X射线片测量Cobb角,计算伤椎椎体前缘高度比值,观察内固定有无断裂、脱出,同时观察手术时间、出血量,采用目测类比评分评价术前术后疼痛。
结果与结论:①43例患者均顺利完成手术,手术时间为60-125 min,平均80 mim;术中出血为50-400 mL,平均160 mL;②与术前相比,术后2周及末次随访时的伤椎椎体前缘高度比值均显著增大(t=10.15,9.57,P < 0.05);末次随访时伤椎椎体前缘高度比值与术后2周相比,差异无显著性意义(t=0.42,P > 0.05);③与术前相比,术后2周及末次随访时的Cobb角均显著减小(t=8.46,7.81,P < 0.05);末次随访时的Cobb角与术后2周相比差异无显著性意义(t=0.93,P > 0.05);④术后2周的目测类比评分显著低于术前(P < 0.05);⑤所有患者均未发生内固定物断裂、脱出等并发症;⑥经伤椎一侧置钉联合短节段5钉内固定治疗不稳定型胸腰椎骨折可减小Cobb角,重建伤椎椎体前缘高度,且并发症较少,临床结果令人满意。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-3829-4732(常步青)
中图分类号:
.jpg)