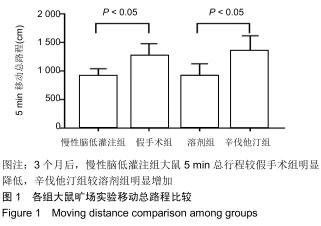
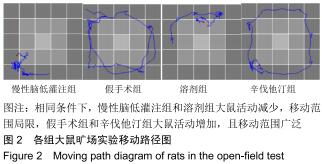
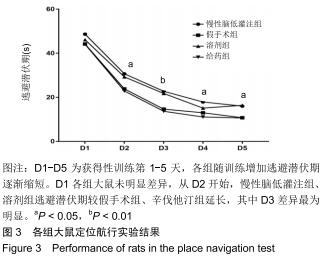
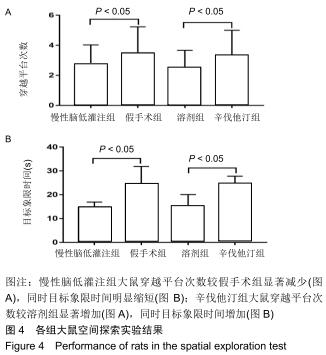
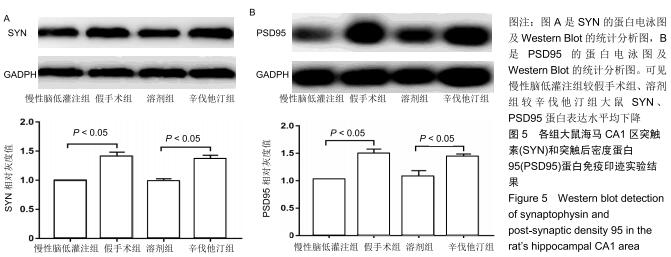
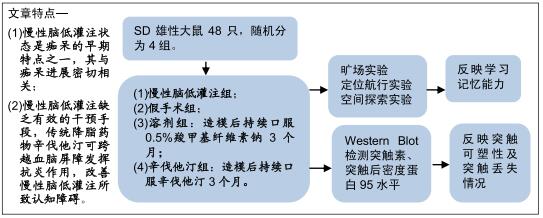
|
[1] ZHOU M, WANG H, ZENG X, et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet.2019;394(10204): 1145-1158.
[2] VÖLGYI K, GULYÁSSY P, TODOROV MI, et al. Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion Induced Synaptic Proteome Changes in the rat Cerebral Cortex. Mol Neurobiol.2018;55(5):4253-4266.
[3] LIANG S, ZHANG J, ZHANG Q, et al. Longitudinal tracing of white matter integrity on diffusion tensor imaging in the chronic cerebral ischemia and acute cerebral ischemia. Brain Res Bull. 2019;154:135-141.
[4] CORRIVEAU RA, BOSETTI F, EMR M, et al. The Science of Vascular Contributions to Cognitive Impairment and Dementia (VCID): A Framework for Advancing Research Priorities in the Cerebrovascular Biology of Cognitive Decline. Cell Mol Neurobiol.2016;36(2):281-288.
[5] APPLETON JP, SCUTT P, SPRIGG N, et al. Hypercholesterolaemia and vascular dementia. Clin Sci (Lond).2017;131(14):1561-1578.
[6] TRIGIANI LJ, ROYEA J, TONG XK, et al. Comparative benefits of simvastatin and exercise in a mouse model of vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. FASEB J 2019;33(12):13280-13293.
[7] FANG SC, XIE H, CHEN F, et al.Simvastatin ameliorates memory impairment and neurotoxicity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Neuroscience. 2017;355:200-211.
[8] CHAN D, BINKS S, NICHOLAS JM, et al. Effect of high-dose simvastatin on cognitive, neuropsychiatric, and health-related quality-of-life measures in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis: secondary analyses from the MS-STAT randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol.2017;16(8):591-600.
[9] SWIGER KJ, MANALAC RJ, BLUMENTHAL RS, et al.Statins and cognition: a systematic review and meta-analysis of short- and long-term cognitive effects. Mayo Clin Proc.2013;88(11):1213-1221.
[10] MCGUINNESS B, CRAIG D, BULLOCK R, et al.Statins for the prevention of dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;(1): CD003160.
[11] BHUVANENDRAN S, BAKAR SNS, KUMARI Y, et al. Embelin Improves the Spatial Memory and Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation in a Rat Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):14507.
[12] HE J, HUANG Y, DU G, et al. Lasting spatial learning and memory deficits following chronic cerebral hypoperfusion are associated with hippocampal mitochondrial aging in rats. Neuroscience. 2019;415: 215-229.
[13] FARKAS E, LUITEN PG, BARI F. Permanent, bilateral common carotid artery occlusion in the rat: a model for chronic cerebral hypoperfusion- related neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Rev. 2007;54(1): 162-180.
[14] ANISIMOVA AV, GUNCHENKO AS, IKONNIKOVA AY, et al. A clinical and genetic analysis of risk factors for the development of acute and chronic cerebral ischemia. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2019;119(3. Vyp. 2):62-67.
[15] DUNCOMBE J, KITAMURA A, HASE Y, et al. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion: a key mechanism leading to vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. Clin Sci (Lond).2017;131(19):2451-2468.
[16] 何婧,黄燕,杜果,等.慢性脑低灌注致模型大鼠学习记忆受损及海马α-突触核蛋白变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(20):3230-3236.
[17] WANG Z, FAN J, WANG J, et al. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induces long-lasting cognitive deficits accompanied by long-term hippocampal silent synapses increase in rats. Behav Brain Res. 2016; 301:243-252.
[18] KOLOS YA, GRIGORIYEV IP, KORZHEVSKYI DE. A synaptic marker synaptophysin. Morfologiia. 2015;147(1):78-82.
[19] FUNK AJ, MIELNIK CA, KOENE R, et al. Postsynaptic Density-95 Isoform Abnormalities in Schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull.2017;43(4): 891-899.
[20] DU SQ, WANG XR, XIAO LY, et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Vascular Dementia: What Can Be Learned from Animal Models of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion? Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54(5):3670-3682.
[21] CHU CS, TSENG PT, STUBBS B, et al. Use of statins and the risk of dementia and mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep.2018;8(1):5804.
[22] BUNT CW, HOGAN AJ. The Effect of Statins on Dementia and Cognitive Decline. Am Fam Physician.2017;95(3):151-152.
[23] GEIFMAN N, BRINTON RD, KENNEDY RE, et al. Evidence for benefit of statins to modify cognitive decline and risk in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Res Ther.2017;9(1):10.
[24] RICHARDSON K, SCHOEN M, FRENCH B, et al. Statins and cognitive function: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med.2013;159(10): 688-697.
[25] SCHULTZ BG, PATTEN DK, BERLAU DJ. The role of statins in both cognitive impairment and protection against dementia: a tale of two mechanisms. Transl Neurodegener.2018;7:5.
[26] CHATTERJEE S1, KRISHNAMOORTHY P, RANJAN P, et al. Statins and cognitive function: an updated review. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2015; 17(2):4.
[27] LI R, WANG TJ, LYU PY, et al. Effects of Plasma Lipids and Statins on Cognitive Function. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018;131(4):471-476.
[28] JALAL FY, YANG Y, THOMPSON JF, et al. Hypoxia-induced neuroinflammatory white-matter injury reduced by minocycline in SHR/SP.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2015;35(7):1145-1153.
[29] REUTER B, RODEMER C, GRUDZENSKI S, et al. Effect of simvastatin on MMPs and TIMPs in human brain endothelial cells and experimental stroke. Transl Stroke Res.2015;6(2):156-159.
[30] CARVALHO K, FAIVRE E, PIETROWSKI MJ, et al. Exacerbation of C1q dysregulation, synaptic loss and memory deficits in tau pathology linked to neuronal adenosine A2A receptor. Brain. 2019;142(11): 3636-3654.
[31] STIVAROS S,GARG S, TZIRAKI M, et al. Randomised controlled trial of simvastatin treatment for autism in young children with neurofibromatosis type 1 (SANTA). Mol Autism.2018;9:12.
|