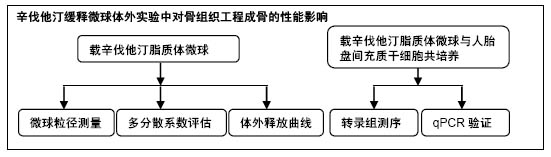
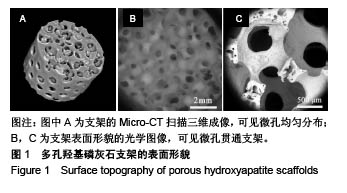
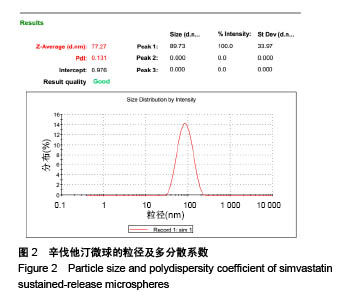
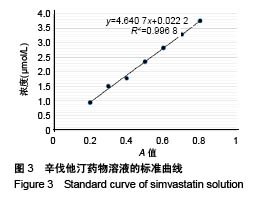
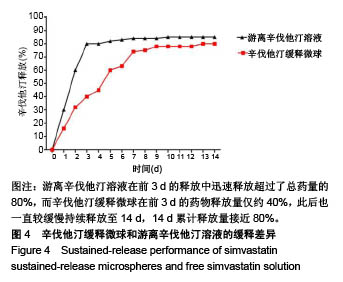
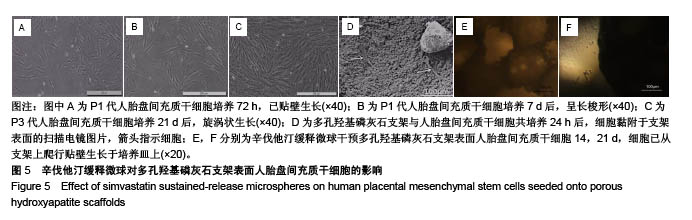
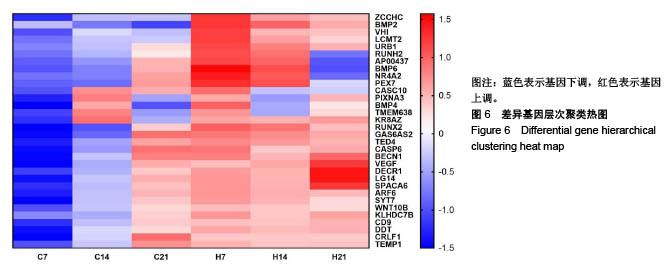
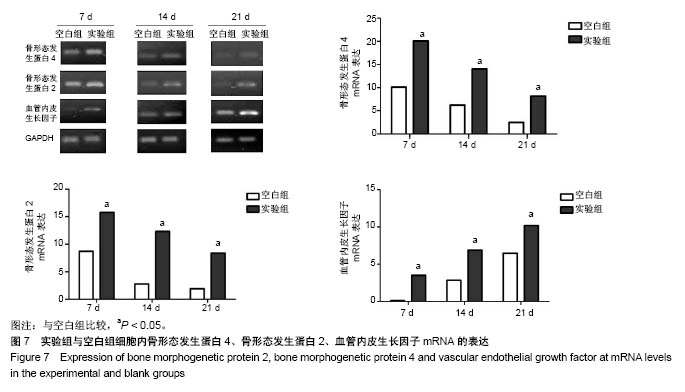
| [1] Killeen AC,Rakes PA,Schmid MJ,et al.Impact of local and systemic alendronate on simvastatin-induced new bone around periodontal defects.J Periodontol. 2012;83(12): 1463-1471. [2] Jiang L,Sun H,Yuan A,et al. Enhancement of osteoinduction by continual simvastatin release from poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-hydroxyapatite-simvastatin nano-fibrous scaffold. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2013;9(11):1921-1928. [3] Mundy G,Garrett R,Harris S,et al.Stimulation of Bone Formation in Vitro and in Rodents by Statins. Science. 1999; 286(5446):1946-1949. [4] Webber MA,Mahmud W,Lightfoot JD,et al.Rhabdomyolysis and compartment syndrome with coadministration of risperidone and simvastatin.J Psychopharmacol. 2004;18(3): 432. [5] Law M,Rudnicka AR.Statin safety: a systematic review.Am J Cardiol.2006;97(8):S52-52S60. [6] Ochoa L,Igartua M,Hernández RM,et al. Novel extended-release formulation of lovastatin by one-step melt granulation: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Eur J Pharm Biopharm.2011;77(2):306-312. [7] 邱晓明,甄平,李松凯.聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物载药微球制备工艺研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(10):1599-1604. [8] 朱林,王聿栋,董艳梅,等.缓释米诺环素的介孔纳米生物玻璃载药系统[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2018,50(2):249-255. [9] 宋效庆,刘红,陈天杰,等.淫羊藿苷/载明胶纳米复合物-PLGA缓释系统的制备及工艺优化[J].吉林大学学报(医学版), 2018, 60(2):438-443.[10] Davison NL,Luo X,Schoenmaker T,et al.Submicron-scale surface architecture of tricalcium phosphate directs osteogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Eur Cell Mater. 2014; 27(20):281.[11] Li J,Wang Q,Zhi W,et al.Immobilization of salvianolic acid B-loaded chitosan microspheres distributed three-dimensionally and homogeneously on the porous surface of hydroxyapatite scaffolds. Biomed Mater. 2016; 11(5):055014. [12] Li J,Zhi W,Xu T,et al.Ectopic osteogenesis and angiogenesis regulated by porous architecture of hydroxyapatite scaffolds with similar interconnecting structure in vivo.Regen Biomater. 2016;3(5):285-297. [13] Zhang B,He L,Han Z,et al.Enhanced osteogenesis of multilayered pore-closed microsphere-immobilizated hydroxyapatite scaffold via sequential delivery of osteogenic growth peptide and BMP-2.J Mater Chem B.2017;5(41). DOI: 10.1039/C7TB01970J[14] 邵苗苗,刘钟西,许诺,等.牙髓干细胞在组织工程研究中的进展和应用前景[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(13):2126-2132. [15] 杨超,申才良.诱导多能干细胞治疗颈节段脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].安徽医科大学学报,2018,53(2):323-326.[16] Bernardo AS, Hay CW, Docherty K. Pancreatic transcription factors and their role in the birth, life and survival of the pancreatic beta cell.Mol Cell Endocrinol.2008;294(1):1-9. [17] Xie J,Peng C,Zhao Q,et al. Osteogenic Differentiation and Bone Regeneration of the iPSC-MSCs Supported by a Biomimetic Nanofibrous Scaffold.Acta Biomater. 2016;29: 365-379. [18] Jaiswal N,Haynesworth SE,Caplan AI,et al.Osteogenic differentiation of purified, culture-expanded human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. J Cell Biochem. 2015;64(2): 295-312. [19] 伍佳,温永梅,吕欣荣,等.人胎盘来源间充质干细胞的生物学性能及体外生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(5):755-759. [20] Li J,Xu T,Wang Q,et al.Integrating surface topography of stripe pattern on pore surface of 3-dimensional hydroxyapatiye scaffolds.Mater Lett.2016;169:148-152. [21] Maciel-Oliveira N, Bradaschia-Correa V, Arana-Chavez VE. Early alveolar bone regeneration in rats after topical administration of simvastatin. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011;112(2):170-179.[22] Kwon YD,Yang DH,Lee DW.A Titanium Surface-Modified with Nano-Sized Hydroxyapatite and Simvastatin Enhances Bone Formation and Osseintegration.J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2015; 11(6):1007. [23] Gentile P,Nandagiri VK,Daly J,et al.Localised controlled release of simvastatin from porous chitosan-gelatin scaffolds engrafted with simvastatin loaded PLGA-microparticles for bone tissue engineering application.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2016;59:249-257.[24] Zhang HX,Xiao GY,Wang X,et al.Biocompatibility and osteogenesis of calcium phosphate composite scaffolds containing simvastatin-loaded PLGA microspheres for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(10): 3250-3258.. [25] Liu T,Gao Y,Sakamoto K,et al.BMP-2 promotes differentiation of osteoblasts and chondroblasts in Runx2-deficient cell lines. J Cell Physiol.2010;211(3):728-735. [26] Wang Z,Gerstein M,Snyder M.RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10(1):57-63. [27] Ferreira CL, Abreu FAMD, Silva GAB, et al. TGF-β1 and BMP-4 carried by liposomes enhance the healing process in alveolar bone.Arch Oral Biol.2013;58(6):646-656. [28] Pullisaar H, Reseland JE, Haugen HJ, et al. Simvastatin coating of TiO? scaffold induces osteogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;447(1):139-144. |