| [1]Aaseth J, Boivin G, Andersen O. Osteoporosis and trace elements-- an overview. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2012;26(2-3):149-152.[2]编写组组长夏维波.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2017)[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2017,10(5): 413-444.[3]Donoso O, Pino AM, Seitz G, et al. Osteoporosis-associated alteration in the signalling status of BMP-2 in human MSCs under adipogenic conditions. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(7):1267-1277.[4]Liu H, Xia X, Li B. Mesenchymal stem cell aging: Mechanisms and influences on skeletal and non-skeletal tissues. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015;240(8):1099-1106.[5]Mundy G, Garrett R, Harris S, et al. Stimulation of bone formation in vitro and in rodents by statins. Science. 1999;286(5446):1946-1949.[6]罗明,黄宏兴,黄红,等. Hedgehog信号通路与骨质疏松症[J].中国骨伤, 2014, 27(2): 169-172.[7]Yao E, Chuang PT. Hedgehog signaling: From basic research to clinical applications. J Formos Med Assoc. 2015;114(7):569-576.[8]Ehlen HW, Buelens LA, Vortkamp A. Hedgehog signaling in skeletal development. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2006;78(3):267-279.[9]田发明. 辛伐他汀对大鼠骨质疏松性骨折及BMSCs成骨分化的影响[D]. 石家庄:河北医科大学, 2011.[10]刘家寅,刘光源,田发明,等.辛伐他汀通过p38MAPK信号通路诱导BMSCs成骨分化的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2016, 22(2): 125-130.[11]张磊,张柳,田发明,等.辛伐他汀对大鼠BMSCs成骨诱导Wnt信号传导通路相关因子mRNA表达的影响[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2009, 23(11):1371-1375.[12]曹华,高建华,刘小龙,等. 大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分离鉴定方法及生物学特性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(9):1357-1361.[13]Kim WK, Meliton V, Bourquard N, et al. Hedgehog signaling and osteogenic differentiation in multipotent bone marrow stromal cells are inhibited by oxidative stress. J Cell Biochem. 2010;111(5): 1199-1209.[14]Montgomery SR, Nargizyan T, Meliton V, et al. A novel osteogenic oxysterol compound for therapeutic development to promote bone growth: activation of hedgehog signaling and osteogenesis through smoothened binding. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(8):1872-1885.[15]Lin FX, Du SX, Liu DZ, et al. Naringin promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells by up-regulating Foxc2 expression via the IHH signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(11):5098-5107.[16]Gao L, Li S, Li Y. Exendin-4 promotes the osteogenic differentiation of osteoblasts via the Hedgehog/Gli1 signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10(1):315-324.[17]Chen JK, Taipale J, Cooper MK, et al. Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling by direct binding of cyclopamine to Smoothened. Genes Dev. 2002; 16(21):2743-2748.[18]Cousin W, Dani C, Peraldi P. Inhibition of the anti-adipogenic Hedgehog signaling pathway by cyclopamine does not trigger adipocyte differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006; 349(2):799-803.[19]刘昊,张岩,刘家寅,等.辛伐他汀对骨髓基质干细胞特异性成骨分化基因表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(19):2777-2782.[20]迟博婧,刘光源,邢磊,等.Hedgehog信号通路调控骨形成及BMSCs成骨分化的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2016,30(12): 1545-1550.[21]张岩,刘昊,邢磊,等.辛伐他汀干预卵巢切除大鼠骨密度和生物力学性能的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(7):981-986.[22]Zanette DL, Lorenzi JC, Panepucci RA, et al. Simvastatin modulates mesenchymal stromal cell proliferation and gene expression. PLoS One. 2015;10(4):e0120137.[23]Chuang SC, Chen CH, Fu YC, et al. Estrogen receptor mediates simvastatin-stimulated osteogenic effects in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015;98(3):453-464.[24]Niu J, Ding G, Zhang L. Effects of simvastatin on the osteogenic differentiation and immunomodulation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(6):8237-8240.[25]Song C, Dang G, Jia H, et al. Simvastatin induces osteoblastic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2003;35(5):533-536.Tai IC, Wang YH, Chen CH, et al. Simvastatin enhances Rho/actin/ cell rigidity pathway contributing to mesenchymal stem cells' osteogenic differentiation. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10: 5881-5894. |
.jpg)
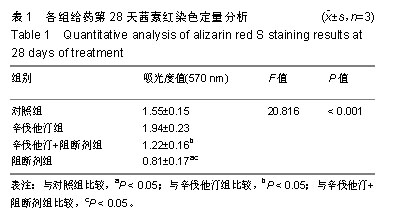
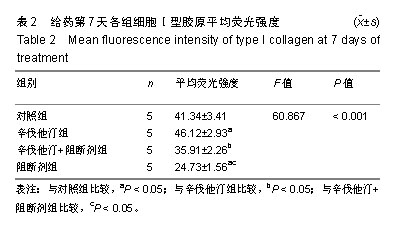
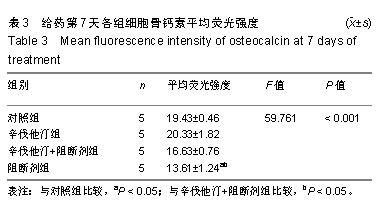
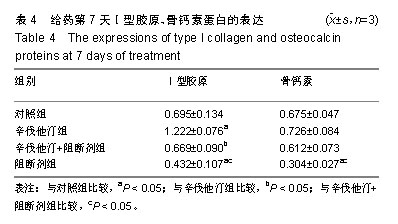
.jpg)
.jpg)