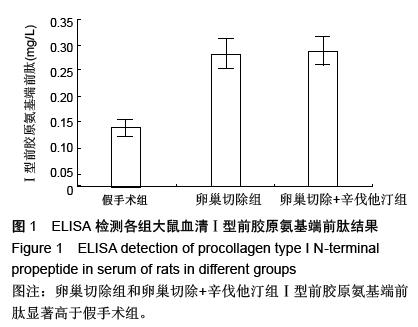
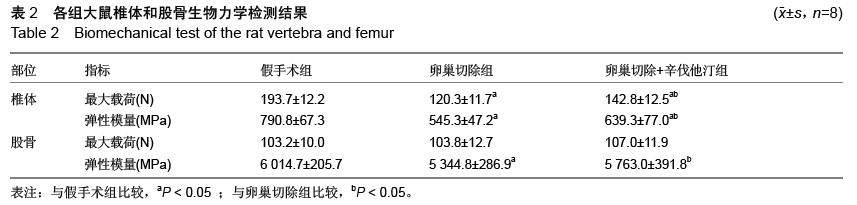
| [1] Cao Y, Mori S, Mashiba T, et al.Raloxifene, estrogen and alendronate affect the processes of fracture repair differently in ovariectomized rats. J Bone Miner Res. 2002; 17 (12) : 2237-2246.
[2] Manabe T, Mori S, Mashiba T, et al. Eel calcitonin (elcatonin) suppressed callus remodeling but did not interfere with fracture healing in the femoral fracture model of cynomolgus monkeys. J Bone Miner Metab. 2009;27(3): 295-302.
[3] Mundy G, Garrett R, Harris S, et al.Stimulation of bone formation in vitro and in rodents by statins. Science. 1999;286(5446):1946-1949.
[4] Oxlund H, Andreassen TT. Simvastatin treatment partially ovariectomy- induced bone loss while increasing cortical bone formation. Bone. 2004; 34(4): 609-618.
[5] Van StaaTP,WegmanS,deVresF,etal.Use of statins and risk of fractures.JAMA.2001; 285(14):1850-1855.
[6] Von Stechow D, Fish S, Yahalom D, et al.Does simvastatin stimulate bone formation in vivo?BMC MusculoskeletDisord. 2003; 4:8.
[7] 田发明,张柳,孟亚强,等.辛伐他汀对大鼠骨量及骨髓基质干细胞增殖、分化的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志. 2007; 13(8): 580-585.
[8] Sehmisch S, Galal R, Kolios L, et al. Effects of low-magnitude, high-frequency mechanical stimulation in the rat osteopenia model. Osteoporos Int. 2009; 20(12): 1999-2008.
[9] Khan K, Sharan K, Swarnkar G, et al.Positive skeletal effects of cladrin, a naturally occurring dimethoxydaidzein, in osteopenic rats that were maintained after treatment discontinuation. Osteoporos Int. 2013; 24(4):1455-1470.
[10] Oliver RA, Yu Y, Yee G, et al. Poor histological healing of a femoral fracture following 12 months of oestrogen deficiency in rats. Osteoporos Int. 2013; 24(10): 2581-2589.
[11] Durão SF, Gomes PS, Colaço BJ, et al. The biomaterial- mediated healing of critical size bone defects in the ovariectomized rat. Osteoporos Int.2014; 25(5): 1535-1545.
[12] Qiu C, Liu X, Wang J, et al. Estrogen increases the transcription of human α2-Heremans-Schmid- glycoprotein by an interplay of estrogen receptor α and activator protein-1. Osteoporos Int. 2014; 25(4): 1357-1367.
[13] Luo Y, Zhang L, Wang WY, et al. Alendronate retards the progression of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration in ovariectomized rats. Bone.2013; 55(2): 439-448.
[14] Yang N, Cui Y, Tan J, et al. Local injection of a single dose of simvastatin augments osteoporotic bone mass in ovariectomized rats. J Bone Miner Metab. 2014; 32(3): 252-260.
[15] Tan J, Yang N, Fu X, et al. Single-dose local simvastatin injection improves implant fixation via increased angiogenesis and bone formation in an ovariectomized rat model.Med Sci Monit. 2015;21: 1428-1439.
[16] Wang JW, Xu SW, Yang DS, et al. Locally applied simvastatin promotes fracture healing in ovariectomizedrat. Osteoporos Int. 2007;18(12): 1641-1650.
[17] Chen PY, Sun JS, Tsuang YH, et al. Simvastatin promotes osteoblast viability and differentiation viaRas/Smad/ERK/BMP-2 signaling pathway. Nutr Res. 2010; 30(3):191-199.
[18] Kim IS,Jeong BC,Kim OS,et al.Lactone form 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitors(statins) stimulate the osteoblastic differentiation of mouse periodontal ligament cells via the ERK pathway. J Periodontal Res. 2011; 46(2): 204-213.
[19] Qiao LJ, Kang KL, Heo JS. Simvastatin Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells Via Canonical Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Mol Cells. 2011; 32(5):437-444.
[20] Miyazawa A, Matsuno T, Asano K, et al. Controlled release of simvastatin from biodegradable hydrogels promotes odontoblastic differentiation. Dent Mater J. 2015; 34(4):466-474.
[21] Seferos N, Pantopoulou A, Kotsiou A, et al. The influence of simvastatin in rats mandible and femur bone mass under Freund's adjuvant arthritis. Stomatologija. 2012;14(2):46-52.
[22] Chan MH, Mak TW, Chiu RW, et al. Simvastatin increases serum osteocalcin concentration in patients treated for hypercholesterolaemia.J ClinEndocrinolMetab. 2001; 86: 4556-4559.
[23] Meier CR, Schlienger RG, Kraenzlin ME, et al. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and the risk of fractures. JAMA. 2000; 283: 3205-3210.
[24] Maeda T, Matsunuma A, Kawane T, et al. Simvastatin promotes osteoblast differentiation and mineralization in MC3T3-E1 cells. BiochemBiophys Res Commun. 2001; 280: 874-877.
[25] Hernández JL, Olmos JM, Romaña G, et al. Bone mineral density in statin users: a population-based analysis from a Spanish cohort. J Bone Miner Metab. 2014; 32(2):184-191.
[26] Maritz FJ, Conradie MM, Hulley PA, et al. Effect of statins on bone mineral density and bone histomorphometry in rodents. Arterios-clerThrombVasc Biol.2001; 21(10): 1636-1641.
[27] 褚亚明,姜保国,张殿英,等.骨量、微结构及受力方向对去卵巢大鼠骨生物力学的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志.2007; 13(9): 651-654.
[28] Chen C,Liang MK,Zhang H, et al.Relationships between age-related biochemical markers of bone turnover and OPG, TGF-β1 and TGF-β2 in native Chinese women. Endocr Res. 2014;39(3):105-114.
[29] Bauer DC, Garnero P, Harrison SL, et al. Biochemical markers of bone turnover, hip bone loss, and fracture in older men: the MrOS study.J Bone Miner Res. 2009; 24(12):2032-2038.
[30] 邢学农,任安,杨静,等.Ⅰ型前胶原氨基端伸展肽在诊断骨质疏松症中的应用[J].安徽医科大学学报,1999,34(5): 361-363.
[31] Burshell AL, Möricke R, Correa-Rotter R,et al. Correlations between biochemical markers of bone turnover and bone density responses in patients with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis treated with teriparatide or alendronate.Bone. 2010;46(4):935-939.
[32] Boonyanurak P, Wilawan K. Levels of biochemical bone marker procollagen type I N-propeptide (PTIN) in Thai women aged 40-70 years. J Med Assoc Thai. 2009;92(7):873-877.
[33] 李铁军,文华军,丁中伟.辛伐他汀和吉非罗齐对高脂血症伴骨量减少患者骨代谢和骨密度的影响[J]. 局解手术学杂志,2011,20(1):57-59. |
.jpg)