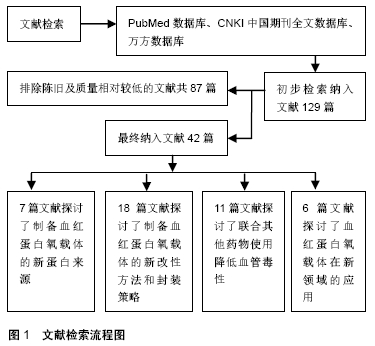
2.1 多源化血红蛋白制备血红蛋白氧载体方面的研究
2.1.1 成人与胎儿血红蛋白 胎儿血红蛋白具有较高的氧亲和力,可能降低血红蛋白氧载体的氧化毒性。SIMONS等[2]直接比较了重组胎儿血红蛋白(rHbF)和重组成人血红蛋白(rHbA)的功能特性和氧化反应性;结果发现,二者的自氧化速率、与过氧化氢反应速率、一氧化氮清除速率、亚硝酸盐还原酶活性均无明显差异;重组胎儿血红蛋白在低过氧化氢水平下损伤较小,并且具有较慢的内在血红素损失率;重组成人血红蛋白易被还原,不易被脂质过氧化物破坏,对磷脂酰胆碱脂质体损伤小。因此,二者作为血红蛋白来源各有优点。
2.1.2 无脊椎动物血红蛋白 以哺乳动物血红蛋白为基础的血红蛋白氧载体的研究进展缓慢,促使研究人员将目光转移到了无脊椎动物血红蛋白(Ecs)上。ZIMMERMAN等[3]在体外采用氧化速率、生理pH值下的离解、热稳定性、携氧能力等指标,直接比较了6种少毛纲动物的无脊椎动物血红蛋白;陆生蚯蚓血红蛋白和赤子爱胜蚓血红蛋白具有高的热稳定性和低聚物稳定性,同时也表现出相对较低的氧化速率;陆生蚯蚓血红蛋白的氧亲和力最低,对陆生蚯蚓血红蛋白和赤子爱胜蚓血红蛋白的主序列进行后续比对,揭示了D亚基界面中几个重要的氨基酸取代,这可能是导致氧亲和力发生这种显著变化的原因。上述结果表明陆生蚯蚓血红蛋白和赤子爱胜蚓血红蛋白是有潜力的潜在血液替代品,它们具有抗氧化和变性的能力,但还需要进行更多的实验来确定它们的安全性、有效性以及它们不同的氧亲和力在体内的影响。
2.1.3 β-亚基突变的血红蛋白 血红蛋白的α-亚基具有电子传递途径,能够通过等离子体抗氧化剂加速还原高价铁,而血红蛋白的β-亚基不具有该功能[4]。SILKSTONE等[5]利用海兔肌红蛋白与人类血红蛋白的β-亚基同样缺乏酪氨酸残基的特点,设计了一个能够产生多种苯丙氨酸到酪氨酸突变的模型;研究发现,产生βF41Y突变的肌红蛋白在没有影响其运载氧气的条件下降低了自氧化速率。COOPER等[6]将不同的单一酪氨酸突变插入到血红蛋白的α-亚基和β-亚基中,结果显示都能不同程度的增加Fe4+的还原速率,并且βT84Y、αL91Y和βF85Y这3个突变增强了抗坏血酸盐将高铁血红蛋白还原成携氧血红蛋白的速率。SILKSTONE等[7]研究进一步指出,某些酪氨酸突变有可能使血红蛋白在其功能铁氧化还原状态下保持更长寿命,其能够将高铁血红蛋白还原成携氧血红蛋白的作用值得深入研究。
2.1.4 鳄鱼来源的血红蛋白 大多数血红蛋白氧载体是从过期的人血中提取血红蛋白制成的,其来源有一定的限制。因此,从新的血红蛋白源中寻找创建血红蛋白氧载体的新方法可以克服这些限制。ROAMCHARERN等[8]通过戊二醛一步聚合,制备改性的无基质鳄鱼血红蛋白,得到高分子量的聚鳄鱼血红蛋白(Poly-cHb);然后对其理化性质进行了研究,并与聚人血红蛋白(Poly-hHb)进行了比较;研究发现,聚鳄鱼血红蛋白较聚人血红蛋白保持着更高的氧亲和力,且与原生人血红蛋白非常相似;并且聚鳄鱼血红蛋白有更好的巴氏灭菌能力,这可能有助于寻找新的血红蛋白源,用于血红蛋白氧载体的开发。
2.2 血红蛋白的化学修饰新进展
2.2.1 与腺苷及其衍生物交联 SIMONI等[9]利用药物交联的概念,开发了一种血红蛋白氧载体。它由纯化的血红蛋白与腺苷及其衍生物进行交联,并与还原型谷胱甘肽结合;在该组合物中,通过ATP激活嘌呤能受体产生一氧化氮和前列环素(PGI2)来调节血管张力,还可通过谷胱甘肽来降低等电点来阻断血红蛋白的外渗,减少其心血管毒性。
2.2.2 与人血浆白蛋白组合 人血浆白蛋白是血浆中一种带负电的蛋白,其与内皮细胞之间存在静电排斥作用,因此人血浆白蛋白的血管通透性不到血红蛋白的1/100[10]。普遍认为以血红蛋白为核心、人血浆白蛋白为外壳的血红蛋白氧载体Hb-HSA3,具有较低的渗透风险。HARUKI等[11]将一种名为HemoAct的Hb-HSA3输入到大鼠体内,其与注射人血浆白蛋白具有相同的生理反应,且无血管收缩作用,注射后仅出现轻微的平均动脉压变化。IWASAKI等[12]用Hb-HSA3溶液替代大鼠20%的血液,发现其与对照组、人血浆白蛋白组的血液循环和气体平衡的生理反应基本相同,平均动脉压和心率保持6 h不变,说明Hb-HSA3未产生血管收缩作用,对大鼠没有急性毒性或不良反应。GEKKA等[13]研究显示,将HemoAct输入到缺血再灌注损伤大鼠模型中,由于HemoAct外壳的白蛋白具有负电荷和高静电斥力,有效抑制了血红蛋白的外渗,在该模型中观察到其神经保护作用,并且没有出现血压升高的情况。
2.2.3 零链聚合血红蛋白 零链聚合是一种新技术,使每个血红蛋白四聚体分子之间形成伪多肽类键完成聚合,有效的保留了血红蛋白结构完整性,限制了可能导致血红素快速暴露或释放的构象变化,从而限制了其参与循环系统内的氧化事件。WOLLOCKO等[14]研究证明,零链聚合血红蛋白(OxyVita?Hb)的高分子球状结构具有分子内和分子间的伪肽键,即使存在高浓度的展开化合物,也能高度对抗分子展开和血红素释放;同时还指出该结构将增加其稳定性,并可能阻止因暴露血红素和游离铁导致的芬顿反应(过氧化氢与二价铁离子的混合溶液将很多已知的有机化合物如羧酸、醇、酯类氧化为无机态),从而限制氧化损伤;即使OxyVita?Hb转化为被氧化的状态,也不会导致聚合物的分子解离,再次说明其具有极强的稳定性。
2.2.4 利用纳米二氧化硅吸附 DEVINEAU等[15]使用了一种与封装相反的策略,他们将血红蛋白直接吸附在二氧化硅纳米颗粒表面。实验发现,血红蛋白对二氧化硅纳米颗粒具有很强的亲和力,能有效吸附在二氧化硅纳米颗粒上,吸附后氧亲合力明显增加;二氧化硅纳米颗粒对血红蛋白四聚体结构具有保护作用,同时纳米颗粒还能促进血红蛋白的增长。
2.2.5 与右旋糖酐偶联 WANG等[16]将牛血红蛋白与高碘酸盐氧化的右旋糖酐偶联,制备了一种右旋糖酐-牛血红蛋白偶联物(Dex-bHb);并用4,4’-二硫基联吡啶可逆性保护牛血红蛋白的重要功能残基Cys-93(β),以避免Cys-93(β)与高碘酸盐氧化的右旋糖酐反应;实验发现,与右旋糖酐偶联稳定了牛血红蛋白的R态,使右旋糖酐-牛血红蛋白偶联物的氧平衡曲线较牛血红蛋白左移(P50减小),氧亲和力提高,并且降低了牛血红蛋白自氧化速率。ZHANG等[17]在金色叙利亚仓鼠出血休克的模型上进一步研究了右旋糖酐-牛血红蛋白偶联物在体内的生物有效性和器官保护效果。研究表明,右旋糖酐-牛血红蛋白偶联物具有良好的血液相容性,不影响红细胞聚集和溶血,能有效恢复微循环血流灌注,对各脏器均有保护作用;右旋糖酐-牛血红蛋白偶联物有望成为一种安全有效的血液代用品。
2.3 新的封装策略
2.3.1 聚多巴胺包封 聚多巴胺(PDA)是一种非常理想的封装材料,它具有如下几个特点:能简单高效的附着在多种机体表面,还可以清除自由基[18];具有良好的血液和生物相容性[19];自发氧化过程中会释放电子,因此具有氧化还原特性[20]。王权[21]研究论证了聚多巴胺用于血红蛋白表面修饰的可行性,建立了聚多巴胺表面修饰技术,多巴胺盐酸的初始浓度为9.76 g/L,缓冲液种类为0.1 mol/L Tris-HCl缓冲液,反应体系pH值为8.5,反应温度为4 ℃,反应时间为210 min,发现酚羟基在聚多巴胺对血红蛋白表面修饰过程中起着关键性作用,并且聚多巴胺的表面修饰过程对血红蛋白结构和生物活性无影响。WANG等[22]利用聚多巴胺为外壳封装血红蛋白,血红蛋白的官能团几乎没有发生化学反应,从而保留了血红蛋白的结构和活性;采用Fe3+还原抗氧化能力实验,结果表明聚多巴胺-血红蛋白具有将Fe3+还原为Fe2+的能力;WANG等[23]后续还证明了在体外聚多巴胺-血红蛋白有清除自由基和活性氧的能力,能抑制过氧化氢诱导的细胞凋亡,以及较高的氧亲和力,与血液组分的相互作用低,细胞毒性低。因此,采用聚多巴胺涂层封装是一种有效策略。
2.3.2 纳米粒子封装 LU等[24]制备了一种采用聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物-聚乙二醇纳米粒子封装的血红蛋白氧载体,其粒径约200 nm,并且稳定性和携氧能力良好,保留了血红蛋白的生物学和结构特征;其在体外的黏度与血液相近,对红细胞聚集、溶血和凝血无明显影响;他们还通过控制出血小鼠模型,证明了它们在体内抗自氧化的能力,这些均表明聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物-聚乙二醇纳米粒子封装的血红蛋白有作为血红蛋白氧载体的潜力。LI等[25]制备了由含有亲水性聚乙二醇链、疏水性聚己内酯和聚乳酸链组成的杂三嵌段共聚物纳米颗粒,并合成了一系列分子量不同的聚乙二醇-聚己内酯-聚乳酸-聚乙二醇共聚物,优化了聚合物与血红蛋白的配比;在急性贫血大鼠模型上证实了该聚合物封装的血红蛋白纳米颗粒能够有效缓解休克症状,并能降低短期死亡率。
2.3.3 仿红细胞形态微粒 YU等[26]采用葡聚糖与血红蛋白、氢氧化钙(Ca(OH)2)共沉淀法制备了红细胞型微粒子,并进行了戊二醛交联,得到了一个两面凹盘状的微粒;采用紫外-可见吸收和电化学技术研究了微粒子的载释氧性能;作者证明了Ca(OH)2-Hb微粒氧吸收值是自由血红蛋白的7倍,并且在5 ℃到50 ℃的不同温度下与氧气的结合和释放性能都保持不变。
2.4 联合其他药物使用降低血管毒性
2.4.1 血红蛋白氧载体的血管毒性 血红蛋白氧载体不具有功能完备的细胞膜结构及相应的酶体系。游离的血红蛋白与血管内皮细胞合成的一氧化氮发生快速的不可逆反应,作为血管活性物质的一氧化氮被清除[27]。这不仅导致毛细血管收缩,产生体循环和肺动脉高压,还导致内皮细胞功能紊乱和血小板功能活化[28]。血管收缩和血小板的激活又将导致血栓形成[29],这可能是血红蛋白氧载体引发血管收缩相关的心血管并发症和死亡率增加的潜在因素。
2.4.2 联合使用一氧化氮的动物实验 通过输入或吸入一氧化氮补偿血红蛋白氧载体消耗的内源性一氧化氮,来减轻血红蛋白氧载体的不良反应,是简单易行的策略。HBOC-201是一种含有强抗氧化剂N-乙酰胆碱的血红蛋白氧载体。NIGAM等[30]验证实验表明:当硝酸甘油与HBOC-201分别通过单独静脉注射到动物模型体内时,硝酸甘油补充的一氧化氮可以有效降低因输入HBOC-201而引起的平均动脉压升高。VOELKER等[31]研究发现,在急性呼吸窘迫综合征大鼠模型中,输入一种HBOC(Hemoglobin glutamerer-200)可诱导肺动脉高压和预防低血压,而后吸入一氧化氮能够逆转肺动脉高压。
2.4.3 联合使用一氧化氮的临床试验 MARRAZZO等[32]记录了一位87岁的严重贫血患者,在输入HBOC-201之前和输入期间均吸入一氧化氮,在HBOC-201输注过程中,通过测定离心后总高铁血红蛋白和血浆高铁血红蛋白的百分比,评估与一氧化氮吸入有关的HBOC-201输注毒性和失活;研究发现,一氧化氮和HBOC-201的联合使用维持了72%的血红蛋白携氧能力,可以预防HBOC-201介导的全身和肺部高血压危象,改善心输出量、动脉血氧含量、乳酸清除率,并降低血管加压素的需求。PAYEN[33]研究发现,患者在输入血红蛋白氧载体之前,先短时间内吸入高剂量(0.008%)吸入型一氧化氮,输入血红蛋白氧载体期间再给予低剂量(0.002%)吸入型一氧化氮,患者血液动力学及毒性监则数据与6个月后随访情况相同。这些无疑是通过补充体外来源的一氧化氮来增加血红蛋白氧载体使用安全性的有力证据。
2.4.4 联合使用替唑生坦 TAVERN等[34]发现,使用L-NNA(一氧化氮合酶抑制剂)阻断内皮一氧化氮合酶,随后输入HBOC-201没有进一步增加平均动脉压或体循环阻力,但诱导平均肺动脉压和肺循环阻力升高,而且清除活性氧不能降低肺血管的升压反应。这表明HBOC-201还通过肺血管系统的另一途径发挥其血管收缩作用;使用替唑生坦(内皮素受体拮抗剂)阻断内皮素受体,可阻止HBOC-201诱导的全身和肺血管的升压反应;因此他们指出:未来的研究应该关注合并输入长效内皮素受体拮抗剂。
2.5 血红蛋白氧载体新的应用领域
2.5.1 血红蛋白氧载体具有快速释氧的特性 由于游离的血红蛋白不具有完整的细胞结构,在不同条件下,其释氧速率均快于红细胞[35]。即使给人体输入低浓度游离的血红蛋白,也可能迅速释放大量氧气[36]。利用这一特性,血红蛋白氧载体可能作为治疗药物应用于一些新的领域。
2.5.2 提高伤口愈合能力 FUKUI等[37]在糖尿病小鼠模型双侧背部,用圆形皮肤刀创建2个直径为6 mm的皮肤伤口,然后通过静脉注射脂质体包裹的高氧血红蛋白h-LEH;结果发现,h-LEH处理的糖尿病小鼠伤口愈合速度与正常小鼠相似;与生理盐水处理的糖尿病小鼠相比,愈合速度增加,炎症细胞因子显著减少,表面灌注增加;结果表明,损伤后早期h-LEH(2 mL/kg)可能通过降低缺氧、增加表面灌注、抑制炎症、加速原位细胞增殖和蛋白质合成等机制,将糖尿病小鼠的皮肤伤口愈合加速到与正常小鼠相当的水平。
2.5.3 治疗癌症和肿瘤 YQ23是一种基于血红蛋白的氧载体。QI等[38]建立了裸鼠原位异种肝移植瘤模型,随后使用顺铂和YQ23进行化疗;通过观察YQ23联合顺铂化疗对肝癌细胞增殖的影响;实时活体内显像显示,YQ23在异位肝癌模型肿瘤组织中蓄积,维持时间长达3 d。免疫荧光光谱分析表明,给药后36 h内YQ23主要分布于原位肝癌模型的肝脏和膀胱;联合化疗对YQ23具有剂量和时间依赖性,YQ23给药对原位肝癌模型的顺铂化疗有显著的致敏作用;二氢叶酸还原酶下调可能是YQ23致敏顺铂化疗的原因之一;因此,顺铂联合YQ23化疗可能是肝癌治疗的一种潜在治疗策略。KAWAGUCHI等[39]在小鼠结肠癌模型的研究中发现,输注h-LEH能显著改善肿瘤的氧合,防止肿瘤血管生成,从而抑制肿瘤生长。
2.5.4 辅助治疗葡萄酒斑 Hb-Vs是一种将纯化和浓缩的血红蛋白溶液包裹在磷脂双层膜中的细胞颗粒。RIKIHISA等[40]将Hb-Vs作为光敏剂,在染料激光治疗(波长为595 nm)葡萄酒色斑(即呈现为红色胎记的毛细血管畸形)时使用;实验发现小尺寸的Hb-Vs(250 nm)分布在血液的血浆相,并倾向于在微血管的边缘区域流动,这正是激光治疗所需要的;静脉注射Hb-Vs可引起微血管扩张,使微血管含有更多的血红蛋白吸收激光光子并产生热量,用Hb-vs染料激光治疗可有效破坏血管壁。因此,Hb-Vs的这些特性可能有助于增强染料激光治疗葡萄酒色斑的效果。
2.5.5 移植器官的灌注 MATTON等[41]在使用基于血红蛋白氧载体作为灌注液的常温机械灌注期间,与使用红细胞的常温机械灌注相比,血管流量改善,肝ATP浓度增加,胆汁产量增加。基于上述研究和血红蛋白氧载体的一些独特特性,如低温下的可用性和使用能力,DE VRIES等[42]已经启动了一项临床试验,用体外机器灌注研究高危供肝的生存能力;到目前为止,在双低温机灌注后成功移植了6个高危供肝,随后进行控制氧合复温和常温机械灌注,每个阶段使用相同的HBOC-201灌注溶液;所有接受者均存活,临床表现良好,移植物存活率100%。因此,有理由认为基于HBOC-201的灌注溶液是一种可行的替代红细胞的肝脏原位机器灌注方法。