[1] ALESSANDRO P, CONSUELO C, ELPIDA P, et al.Engineering of Chitosan-Hydroxyapatite-Magnetite Hierarchical Scaffolds for Guided Bone Growth.Materials(Basel).2019;12:1-13.
[2] LI G, QIN S, ZHANG D, et al.Preparation of antibacterial degummed silk fiber/nano-hydroxyapatite/polylactic acid composite scaffold by degummed silk fiber loaded silver nanoparticles.Nanotechnology.2019;30(29):295101.
[3] 王天云,张青,朱良均,等.利用电化学法结合丝素膜调控羟基磷灰石沉积及其形貌[J].浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2018, 44(2):209-214.
[4] KULPETCHDARA K, LIMPICHAIPANIT A, RANDORN C, et al. Influence of the Nano Hydroxyapatite Powder on Thermally Sprayed HA Coatings onto Stainless Steel.Surf Coat Technol. 2016;306:181-186.
[5] VILARDELL AM, CINCA N, GARCIA-GIRALT N, et al. Functionalized coatings by cold spray: An in vitro study of micro- and nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite compared to porous titanium.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2018;87:41-49.
[6] KEYNOOSH B, ABBASI KB, ABDOLLAH A.Characterization of sol-gel derived silver/fluor-hydroxyapatite composite coatings on titanium substrate.Surf Coat Technol.2018;352:522-528.
[7] QADIR M, LI Y, WEN C.Ion-substituted calcium phosphate coatings by physical vapor deposition magnetron sputtering for biomedical applications: A review.Acta Biomater.2019;89:14-32.
[8] AMANDA B, KATARZYNA S, ELŻBIETA M, et al.Biological effect of hydrothermally synthesized silica nanoparticles within crystalline hydroxyapatite coatings for titanium implants.Mater Sci Eng C.2018;92:88-95.
[9] TÜRK S, ALTıNSOY I, EFE GÇ, et al.Biomimetic synthesis of Ag, Zn or Co doped HA and coating of Ag, Zn or Co doped HA/fMWCNT composite on functionalized Ti.Mate Sci Eng C. 2019;99:986-998.
[10] WANG J, GONG X, HAI J, et al.Synthesis of silver-hydroxyapatite composite with improved antibacterial properties.Vacuum.2018;152(61):132-137.
[11] VILLERET B, DIEU A, STRAUBE M, et al. Silver Nanoparticles Impair Retinoic Acid-Inducible Gene I-Mediated Mitochondrial Antiviral Immunity by Blocking the Autophagic Flux in Lung Epithelial Cells.ACS Nano.2018;12:1188-1202.
[12] JALAL M, ANSARI M, ALZOHAIRY MA, et al. Anticandidal activity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles: effect on growth, cell morphology, and key virulence attributes of Candida species.Int J Nanomedicine.2019;14:4667-4679.
[13] DASTJERDI R, MONTAZER M. A review on the application of inorganic nano-structured materials in the modification of textiles: Focus on anti-microbial properties.Colloids Surf.B. 2010;79:5-18.
[14] SIMCHI A, TAMJID E, PISHBIN F, et al.Recent progress in inorganic and composite coatings with bactericidal capability for orthopaedic applications. Nanomed.Nanotechnol.Biol Med. 2011;7(1):22-39.
[15] HAJIPOUR MJ, FROMM KM, ASHKARRAN AA, et al. Antibacterial properties of nanoparticles.Trends Biotechnol. 2012;30(10):499-511.
[16] JOANNA K, EWA G, KWIATKOWSKA-RÓżYCKA D. Substituted Hydroxyapatites with Antibacterial Properties. BioMed Res Int.2014;2014:1-15.
[17] ZIELEWICZ J. A Review on Potential Role of Silver Nanoparticles and Possible Mechanisms of their Actions on Bacteria.Drug Res.2017;11(2):70-76.
[18] ZHANG XF, LIU ZG, SHEN W, et al.Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties, Applications, and Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci.2016;17(9):1534.
[19] EHSAN R, ARAN R, CORMAC MG, et al.Adverse effects of nanosilver on human health and the environment.Acta Biomater.2019;94:145-159.
[20] REN L, PAN Y, LIANG Q, et al. Synthesis of Dental Resin Matrix Containing Silver Nanoparticles.J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2019;19:5774-5782.
[21] BAHAR K, NAHIDEH A, MORTEZA M, et al.A Review on Potential Role of Silver Nanoparticles and Possible Mechanisms of their Actions on Bacteria.Drug Res (Stuttg). 2017;67:70-76.
[22] 叶伟杰,陈楷航,蔡少龄,等.纳米银的合成及其抗菌应用研究进展[J].材料工程,2017,45(9):22-30.
[23] KEYHOOSH B, ABBASI KB, ABDOLLAH A.Characterization of sol-gel derived silver/fluor-hydroxyapatite composite coatings on titanium substrate.Surf Coat Technol.2018;352:522-528.
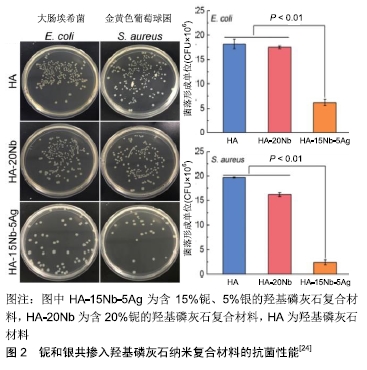
[24] WEI P, FANG J, FANG L, et al. Novel niobium and silver toughened hydroxyapatite nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical and biological properties for load-bearing bone implants.Appl Mater Today.2019;15:531-542.
[25] GENG Z, CUI Z, LI Z, et al.Strontium incorporation to optimize the antibacterial and biological characteristics of silver-substituted hydroxyapatite coating.Mater Sci Eng C. 2016;58:467-77.
[26] CHI W, ZOU J, AI F, et al. Research of Cu-Doped Hydroxyapatite Microbeads Fabricated by Pneumatic Extrusion Printing.Materials(Basel).2019;12:1-11.
[27] GABBAY J, BORKOW G. Copper, an Ancient Remedy Returning to Fight Microbial, Fungal and Viral Infections.Curr Chem Biol.2009;3:272-278.
[28] RENL, MA Z, LI M, et al.Antibacterial properties of Ti-6Al-4V-xCu alloys.Mater Sci Technol.2014;30:699-705.
[29] LIU J, LI F, LIU C, et al.Effect of Cu content on the antibacterial activity of titanium–copper sintered alloys.Mater Sci Eng C. 2014;35:392-400.
[30] SCHMIDT MG, TUURI RE, DHARSEE A, et al.Antimicrobial copper alloys decreased bacteria on stethoscope surfaces. Am.J.Infect.Control.2017;45:642-647.
[31] VINCENT M, DUVAL RE, HARTEMANN P, et al.Contact killing and antimicrobial properties of copper.J Appl Microbiol. 2017;124(5):1032-1046.
[32] 何立伟,高珊.铜的毒性、抗菌性及促进创伤愈合功效研究进展[J].毒理学杂志,2017,31(6):425-429.
[33] DIN MI, ARSHAD F, HUSSAIN Z, et al.Green Adeptness in the Synthesis and Stabilization of Copper Nanoparticles: Catalytic, Antibacterial, Cytotoxicity, and Antioxidant Activities. Nanoscale Res Lett.2017;12:638.
[34] 王琦,卢珊,胡长鹰.纳米铜食品抗菌包装材料的研究进展[J].包装工程,2019,40(5):64-71.
[35] GHOSH R, SWART O, WESTGATE S, et al.Antibacterial copper-hydroxyapatite composite coatings via electrochemical synthesis.Langmuir.2019;35:1-28.
[36] SHEDBALKAR U, SINGH R, WADHWANI S, et al.Microbial synthesis of gold nanoparticles: Current status and future prospects.Adv.Colloid Interface Sci.2014;209:40-48.
[37] ORTIZ-BENÍTEZ EA, VELÁZQUEZ-GUADARRAMA N, DURÁN FIGUEROA NV, et al.Antibacterial mechanism of gold nanoparticles on Streptococcus pneumoniae. Metallomics. 2019;11:1265-1276.
[38] XING X, MA W, ZHAO X, et al. Interaction between Surface Charge-Modified Gold Nanoparticles and Phospholipid Membranes.Langmuir, 2018;34:12583-12589.
[39] XIE Y, LIU Y, YAN J, et al.Gold Nanoclusters for Targeting Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus In Vivo.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.2018;57:3958-3962.
[40] CUI Y, ZHAO Y, TIAN Y, et al.The molecular mechanism of action of bactericidal gold nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Biomaterials.2012;33:2327-33.
[41] ZHENG Y, LIU W, QIN Z, et al. Mercaptopyrimidine- Conjugated Gold Nanoclusters as Nanoantibiotics for Combating Multidrug-Resistant Superbugs.Bioconjug Chem. 2018;29:3094-3103.
[42] KIM H, MONDAL S, JANG B, et al.Biomimetic synthesis of metal–hydroxyapatite (Au-HAp, Ag-HAp, Au-Ag-HAp): Structural analysis, spectroscopic characterization and biomedical application.Ceram Int.2018;44:20490-20500.
[43] BAHERJEE S, BAGCHI S, BHANDARY S, et al.A facile vacuum assisted synthesis of nanoparticle impregnated hydroxyapatite composites having excellent antimicrobial properties and biocompatibility.Ceram Int. 2018;44: 1066-1077.
[44] RUDE RK, GRUBER HE, NORTON HJ, et al.Dietary magnesium reduction to 25% of nutrient requirement disrupts bone and mineral metabolism in the rat.Bone. 2005;37: 211-219.
[45] MAIER JAM, BERNARDINI D, RAYSSIGUIER Y, et al.High concentrations of magnesium modulate vascular endothelial cell behaviour in vitro.Biochim Biophys Acta.2004;1689:6-12.
[46] ZICHE M, MORBIDELLI L. Nitric Oxide and Angiogenesis. Circulation.2002;105:2133-2135.
[47] XUE W, DAHLQUIST K, BANERIEE A, et al.Synthesis and characterization of tricalcium phosphate with Zn and Mg based dopants.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2008;19:2669-2677.
[48] LANDI E, LOGROSCINO G, PROETTI L, et al.Biomimetic Mg-substituted hydroxyapatite: from synthesis to in vivo behaviour.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2008;19:239-247.
[49] GAYATHRI B, MUTHUKUMARASAMY N, DHAYALAN V, et al. Magnesium incorporated hydroxyapatite nanoparticles: Preparation,characterization, antibacterial and larvicidal activity. Arabian J Chem.2018;11:645-654.
[50] COELHO CC, ARAUJO R, QUADROS PA, et al.Antibacterial bone substitute of hydroxyapatite and magnesium oxide to prevent dental and orthopaedic infections.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2019;97:529-538.
[51] LEUNG Y, NG A, XU X, et al.Mechanisms of antibacterial activity of mgo: non-ros mediated toxicity of mgo nanoparticles towards escherichia coli.Small. 2014;10:1171-1183.
[52] HE Y, INGUDAM S, REED S, et al. Study on the mechanism of antibacterial action of magnesium oxide nanoparticles against foodborne pathogens.J Nanobiotechnol.2016;14:1-9.
[53] FENG H, WANG G, JIN W, et al.Systematic study of inherent anti-bacterial properties of magnesium-based biomaterials. ACS Appl Mater.Interfaces.2016;8:1-35.
[54] LI Y, LIU G, ZHAI Z, et al. Antibacterial properties of magnesium in vitro and in an in vivo model of implant-associated methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014;58:7586-7591.
[55] SAIDAK Z, MARIE PJ. Strontium signaling: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications in osteoporosis. Pharmacol Ther.2012;136:216-226.
[56] RAVI ND, BALU R, KUMAR TSS.Strontium-Substituted Calcium Deficient Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Antibacterial Properties.J Am Ceram Soc.2012;95:2700-2708.
[57] BRAUER DS, KARPUKHINA N, KEDIA G, et al.Bactericidal strontium-releasing injectable bone cements based on bioactive glasses.J R Soc Interface.2013;10(78):20120647.
[58] LIN Y, YANG Z, CHENG J, et al.Synthesis,Charactcrization and Antibacterial Property of Strontium Half and Totally Substituted Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles. J Wuhan Univ Technol.2008;23(4):475-479.
[59] YAMAGUCHI M. Role of nutritional zinc in the prevention of osteoporosis.Mol Cell Biochem.2010;338(1-2):241-254.
[60] XIONG K, ZHANG J, ZHU Y. Zinc doping induced differences in the surface composition, surfacemorphology and osteogenesis performance of the calcium phosphate cementhydration products.Mater.Sci.Eng.C.2019;105:1-9.
[61] REBECCA C, JOSé CM, Suelen S, et al.Does the incorporation of zinc into calcium phosphate improve bone repair?A systematic review.Ceram Int.2018;44:1240-1249.
[62] OFUDJE EA, ADEOGUN AI, IDOWU MA, et al.Synthesis and characterization of Zn-Doped hydroxyapatite: scaffold application, antibacterial and bioactivity studies.Heliyon. 2019;5:e01716.
[63] PREDOI D, ICONARU SL, PREDOI MV, et al.Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Zinc-Doped Hydroxyapatite Colloids and Dispersion Stability Using Ultrasounds. Nanomaterials (Basel).2019;9:1-22.
[64] WAKAMURA M. Photocatalysis by calcium hydroxyapatite modifiedby Ti(IV).Fujitsu Sci.Tech.J.2005;41(2):181-190.
[65] LOPES FS, OLIVEIRA JR, MILANI J, et al.Biomineralized diamond-like carbon films incorporating titanium dioxide nanoparticles improved bioactivity properties and reduced biofilm formation.Mater Sci Eng C.2017;81:373-379.
[66] LI Y, ZHANG W, NIU J, et al.Mechanism of Photogenerated Reactive Oxygen Species and Correlation with the Antibacterial Properties of Engineered Metal-Oxide Nanoparticles.ACS Nano.2012;6(6):5164-5173.
[67] MACFARLANE J W, JENKINSON H F, SCOTT T B. Sterilization of microorganisms on jet spray formed titanium dioxide surfaces.Appl.Catal.B.2011;(106):181-185.
[68] DAPU S, EL CA, CHRISTOFILOPOULOS P, et al.The potential role of cobalt ions released from metal prosthesis on the inhibition of Hv1 proton channels and the decrease in Staphyloccocus epidermidis killing by human neutrophils. Biomaterials.2011;32(7):1769-1777.
[69] WU C, ZHOU Y, FAN W, et al.Hypoxia-mimicking mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds with controllable cobalt ion release for bone tissue engineering.Biomaterials. 2012;33(7):2076-2085.
[70] KULANTHAIVEL S, ROY B, AGARWAL T, et al.Cobalt doped Proangiogenic Hydroxyapatite for Bone Tissue Engineering Application. Mater Sci Eng C.2015;58:648.
[71] AJDUKOVIĆ ZR, MIHAJILOV-KRSTEV TM, IGNJATOVIĆ NL, et al.In Vitro Evaluation of Nanoscale Hydroxyapatite-Based Bone Reconstructive Materials with Antimicrobial Properties.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2016;16(2):1420-1428.
[72] DINA R, KRISTINE V B, ALBERT H, et al.Insights into the mode of action of chitosan as an antibacterial compound.Appl Environ Microbiol.2008;74(12):3764-3773.
[73] COSTA EM, SILVA S, TAVARIA FK, et al.Insights into chitosan antibiofilm activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.J Appl Microbiol.2017;122:1547-1557.
[74] LU Y, LI M, LI L, et al.High-activity chitosan/ nanohydroxyapatite/zoledronic acid scaffolds for simultaneous tumor inhibition, bone repair and infection eradication.Mater Sci Eng C.2018;82:225-233.
[75] YAN Y, ZHANG X, LI C, et al.Preparation and characterization of chitosan-silver/hydroxyapatite composite coatings onTiO2 nanotube for biomedical applications.Appl.Surf.Sci. 2015;332: 62-69.
[76] RODRIGUEZ GM, GARDNER R, KAUR N, et al.Utilization of Fe3+ -acinetoferrin analogs as an iron source by Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Biometals 2008;21:93-103.
[77] KANEKO Y, THOENDEL M, OLAKANMI O, et al.The transition metal gallium disrupts Pseudomonas aeruginosa iron metabolism and has antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity. J Clin Invest.2007;117(4):877-888.
[78] MELNIKOV P, TEIXEIRA AR, MALZAC A, et al. Gallium-containing hydroxyapatite for potential use in orthopedics.Mater Chem Phys.2009;117(1):86-90.
[79] LIU W, GOLSHAN N H, DENG X, et al.Selenium nanoparticles incorporated into titania nanotubes inhibit bacterial growth and macrophage proliferation. Nanoscale. 2016;8(34):15783-15794.
[80] NASTULYAVICHUS A, KUDRYASHOV S, SMIRNOV N, et al. Antibacterial coatings of Se and Si nanoparticles.Appl Surf Sci.2018;469:220-225.
[81] PRIYADARSHINI B, ANJANEYULU U, VIJAYALAKSHMI U. Preparation and characterization of sol-gel derived Ce4+ doped hydroxyapatite and its in vitro biological evaluations for orthopedic applications.Mater Des.2017;119:446-455.
|