中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (36): 5889-5895.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1899
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇 下一篇
机器人辅助与传统手法行单髁置换效果的Meta分析
高阳阳1,车先达1,韩鹏飞1,2,梁 斌3,李鹏翠4
- 1山西医科大学第二临床医学院,山西省太原市 030001;2长治市第二人民医院,山西省长治市 046000;3山西省汾阳医院,山西省吕梁市 033000;4山西医科大学第二医院骨与软组织损伤修复重点实验室,山西省太原市 030001
Clinical efficacy of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty between robotic-assisted and conventional manual methods: a meta-analysis
Gao Yangyang1, Che Xianda1, Han Pengfei1, 2, Liang Bin3, Li Pengcui4
- 1Second Clinical Medical College of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 2Second People’s Hospital of Changzhi, Changzhi 046000, Shanxi Province, China; 3Shanxi Fenyang Hospital, Lüliang 033000, Shanxi Province, China; 4Key Laboratory of Bone and Soft Tissue Injury Repair, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
单髁置换:是应用微创技术,使患者减少疼痛、早期活动、减少住院时间、迅速地进行康复、尽早恢复功能的一种手术。近年来由于手术技术、适应证选择、假体设计和手术器械的改进,目前微创单髁置换治疗膝关节单间室骨性关节炎在国内外得到了广泛的应用,临床效果良好。
机器人辅助:1992年骨科手术中机器人辅助技术被第一次使用,据统计目前15%-20%的膝关节单髁置换是在机器人辅助下进行的。一项前瞻性随机对照研究表明,与传统单髁置换相比,机器人辅助单髁置换在假体定位(矢状位、冠状位及轴向)的精度上较前者有明显改善。
摘要
背景:以往骨关节炎临床上终末期的主要治疗方式是关节置换,近年来随着保膝理念的盛行以及内固定材料和手术技术的不断发展,单髁置换这一微创技术在单间室骨关节炎的治疗中得到了广泛应用。
目的:通过Meta分析的方法系统比较机器人辅助技术与传统手法行骨关节炎单髁置换效果的差异。
方法:检索包括国内外于1999年至2019年3月已发表的临床对照研究,所检索的数据库包括Embase、PubMed、Central、Cinahl、PQDT、中国知网、维普、万方、Cochrane Library、CBM等。选择胫骨组件置入准确度、股骨组件置入准确度、胫股骨组件安全区、手术时间及并发症等作为结局指标,力求全面细致地比较机器人辅助技术与传统手法单髁置换的疗效差异。
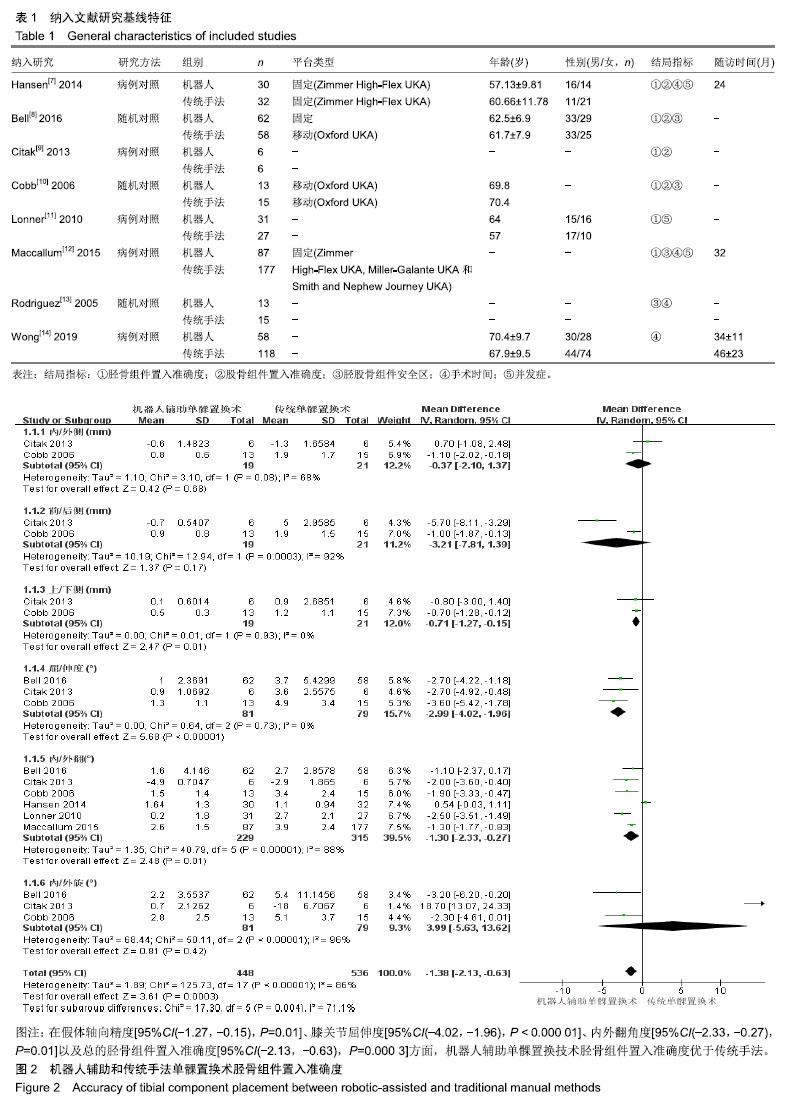
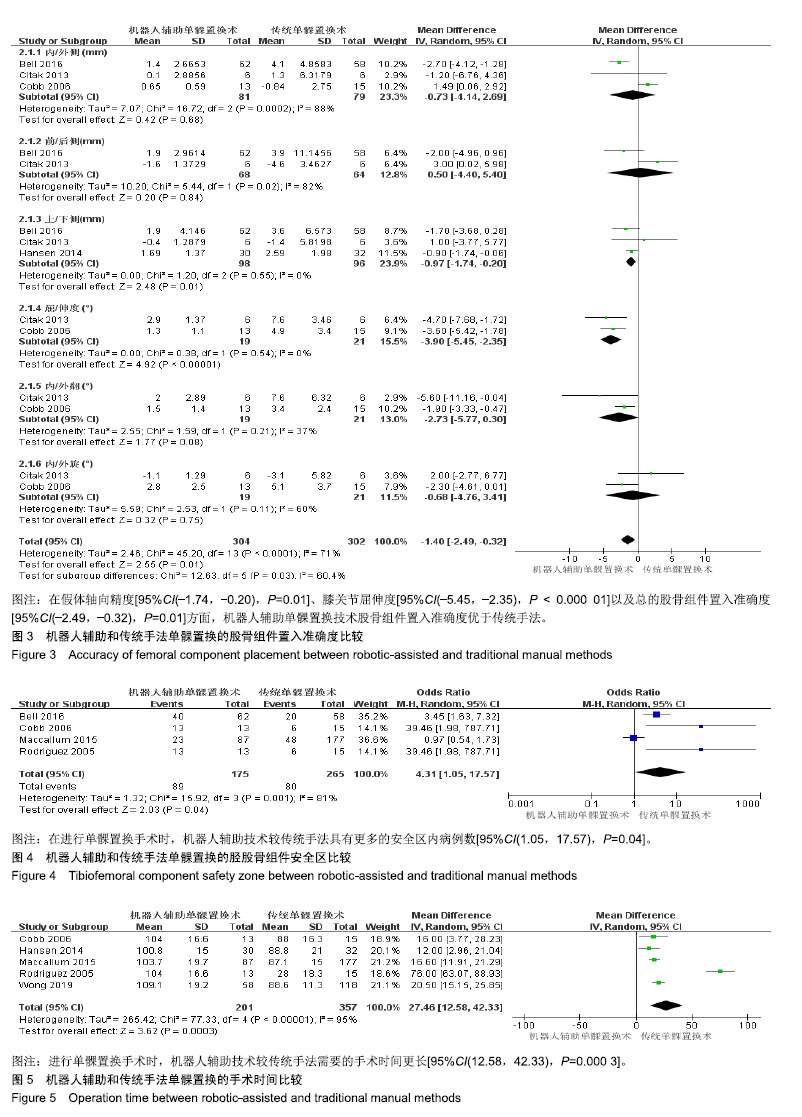
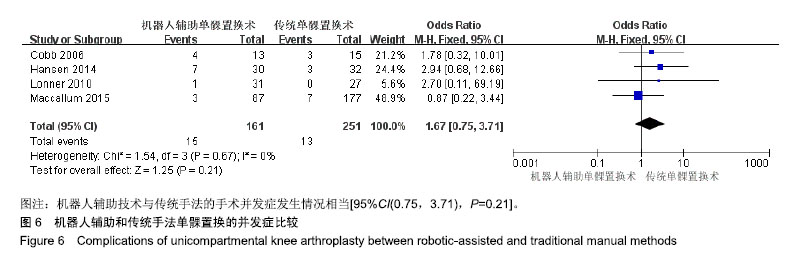
结果与结论:①依据以上检索策略,最终纳入8篇外文文献;②通过比较,发现机器人辅助单髁置换技术在胫骨组件置入准确度[95%CI(-2.13,-0.63),P=0.000 3]、股骨组件置入准确度[95%CI(-2.49,-0.32),P=0.01]、胫股骨组件安全区[95%CI(1.05,17.57),P=0.04]等方面均优于传统手法,差异有显著性意义;③虽然机器人辅助技术需时更长[95%CI(12.58,42.33),P=0.000 3],但是并不增加手术并发症的发生[95%CI(0.75,3.71),P=0.21];④提示在行单髁置换时,机器人辅助技术的假体定位准确率更高,且并未增加并发症的发生率,是一种较传统手法更为理想的手术方式。以上结论尚需更大样本、更高质量的随机对照研究加以验证。
ORCID: 0000-0001-9375-8838(高阳阳)
中图分类号:

.jpg)