中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (34): 5486-5491.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1953
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
包裹罗哌卡因聚乙二醇/聚乳酸微球植入坐骨神经周围的缓释性能与组织相容性
吴 波1,李祥奎2,王 华1,文之远1
- 1四川现代医院麻醉科,四川省成都市 610041;2四川省医学科学院四川省人民医院麻醉科,四川省成都市 610072
Sustained-release properties and histocompatibility of ropivacaine-coated polyethylene glycol/polylactic acid microspheres implanted around the sciatic nerve
Wu Bo1, Li Xiangkui2, Wang Hua1, Wen Zhiyuan1
- 1Department of Anesthesiology, Modern Hospital of Sichuan, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Anesthesiology, Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences & Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu 610072, Chengdu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
微球技术:是近年发展起来的一种新型给药技术,其中微球直径为1-40 pm,是将药物分散或吸附在高分子、聚合物基质中而形成的微粒分散体系,其具有生物相容性,可被生物降解,尤其在临床肿瘤治疗中具有显著优势。
聚乙二醇/聚乳酸缓释载体材料的优点:提高药物包封率与载药量;通过调整复合物组成比例或是相对分子质量可调控微球的降解速度,进而调控药物释放速率;可降低药物突释效应,延长药物作用时间,达到缓释效果;聚乳酸为疏水性材料,降解产物呈酸性,但是聚乙二醇为亲水性材料,采用聚乙二醇对聚乳酸表面进行修饰,可中和其酸性环境,改善材料的亲水性能;改善药物体内分布情况,降低药物毒性,提高药效。
背景:研究组采用乳化溶剂挥发O/W法制备了包裹罗哌卡因的聚乙二醇/聚乳酸微球,体外实验显示其具有良好的药效学与缓释性能。
目的:进一步观察包裹罗哌卡因的聚乙二醇/聚乳酸微球的体内缓释性能与组织相容性。
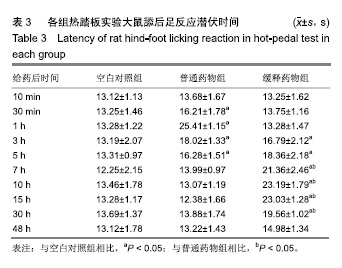
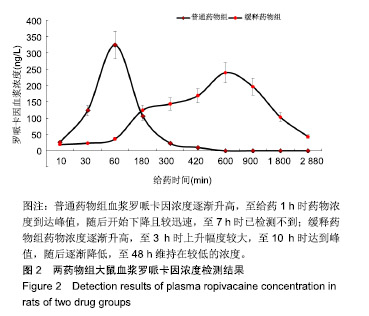
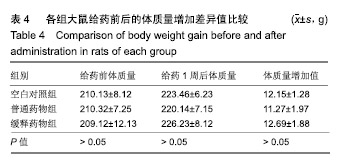
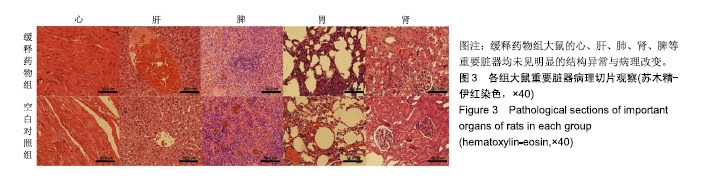
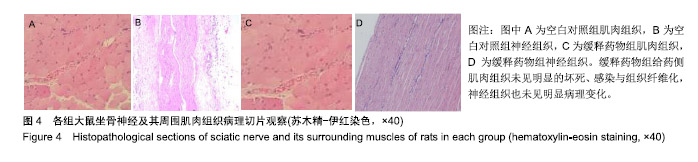
方法:采用乳化溶剂挥发O/W法制备包裹罗哌卡因的聚乙二醇/聚乳酸微球。将150只雄性Wistar大鼠(由四川省医学科学院四川省人民医院实验动物研究所提供)随机分3组处理:空白对照组(n=50)一侧坐骨神经周围间隙植入未包裹罗哌卡因的聚乙二醇/聚乳酸微球,普通药物组(n=50)一侧坐骨神经周围间隙注射盐酸罗哌卡因,缓释药物组一侧坐骨神经周围间隙植入包裹罗哌卡因的聚乙二醇/聚乳酸微球,普通药物组与缓释药物组的罗哌卡因剂量相同。给药后10,30 min及1,3,5,7,10,15,30,48 h,利用热踏板实验评估大鼠坐骨神经感觉阻滞情况,提尾实验观察大鼠坐骨神经运动阻滞情况,高效液相色谱分析血浆中罗哌卡因浓度;术后1周,检测各组大鼠体质量变化,组织学观察坐骨神经组织与其周围肌肉组织及心、肝、肺、肾、脾等重要脏器的病理变化。实验已获得四川省医学科学院四川省人民医院实验动物研究所伦理委员会批准。
结果与结论:①普通药物组给药后30 min后出现坐骨神经感觉与运动阻滞,7 h时感觉阻滞消失,10 h时神经阻滞消失;缓释药物组给药后3 h出现坐骨神经感觉与运动阻滞,48 h时神经阻滞消失;②普通药物组血浆罗哌卡因浓度逐渐升高,至给药1 h时药物浓度到达峰值,随后开始下降且较迅速,至7 h时已检测不到;缓释药物组药物浓度逐渐升高,至3 h时上升幅度较大,至10 h时达到峰值,随后逐渐降低,至48 h维持在较低的浓度;③缓释药物组大鼠未出现呼吸抑制、惊厥、窒息或死亡等中毒表现,切口均正常愈合,大鼠体质量增加值未受影响,心、肝、肺、肾、脾等重要脏器均未见明显的结构异常与病理改变,给药侧肌肉组织未见明显的坏死、感染与组织纤维化,神经组织也未见明显病理变化;③结果表明,包裹罗哌卡因的聚乙二醇/聚乳酸微球具有良好的动物体内缓释性能与组织相容性。
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)