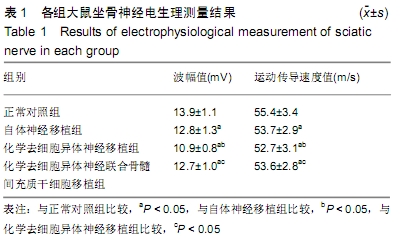
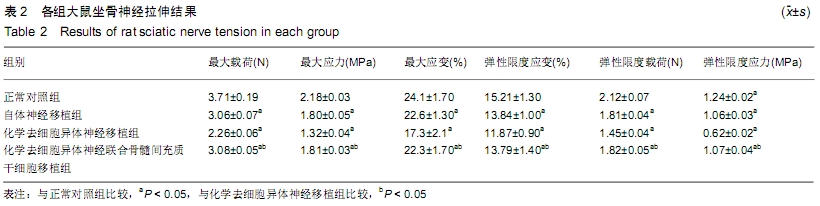
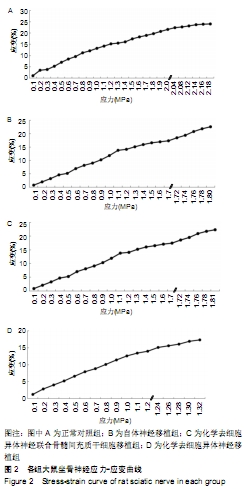
[1] MICKE O, SEEGENSCHMIEDT MH, ADAMIETZ IA, et al. Low-Dose Radiation Therapy for Benign Painful Skeletal Disorders: The Typical Treatment for the Elderly Patient? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017; 98(4):958-963.
[2] LIU Z, ZHU S, LIU L, et al. A magnetically responsive nanocomposite scaffold combined with Schwann cells promotes sciatic nerve regeneration upon exposure to magnetic field. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:7815-7832.
[3] MINTEN MJ, MAHLER E, DEN BROEDER AA, et al. The efficacy and safety of low-dose radiotherapy on pain and functioning in patients with osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Rheumatol Int. 2016;36(1): 133-142.
[4] ZHANG Q, ZHANG ZJ, WANG XH, et al. The prescriptions from Shenghui soup enhanced neurite growth and GAP-43 expression level in PC12 cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016;16:369.
[5] CARRIEL V, GARZÓN I, CAMPOS A, et al. Differential expression of GAP-43 and neurofilament during peripheral nerve regeneration through bio-artificial conduits. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11(2): 553-563.
[6] COONEY DS, WIMMERS EG, IBRAHIM Z, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhance Nerve Regeneration in a Rat Sciatic Nerve Repair and Hindlimb Transplant Model. Sci Rep. 2016;6:31306.
[7] YUE Y, YANG X, ZHANG L, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound upregulates pro-myelination indicators of Schwann cells enhanced by co-culture with adipose-derived stem cells. Cell Prolif. 2016;49(6): 720-728.
[8] HERVERA A, DE VIRGILIIS F, PALMISANO I, et al. Reactive oxygen species regulate axonal regeneration through the release of exosomal NADPH oxidase 2 complexes into injured axons. Nat Cell Biol. 2018; 20(3):307-319.
[9] XU B, ZHANG Y, DU XF, et al. Neurons secrete miR-132-containing exosomes to regulate brain vascular integrity. Cell Res. 2017;27(7): 882-897.
[10] NIELSEN EØ, CHEN L, HANSEN JO, et al. Optimizing Osteogenic Differentiation of Ovine Adipose-Derived Stem Cells by Osteogenic Induction Medium and FGFb, BMP2, or NELL1 In Vitro. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:9781393.
[11] 林耀发,宗海洋,胡显腾,等.大鼠坐骨神经损伤后 Spastin 表达变化的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2017, 31(1):80-84.
[12] 付秀美,杨海艳,王荣良,等.脂肪源性干细胞促进大鼠受损坐骨神经传导及脊髓脑源性神经营养因子和睫状神经营养因子的表达[J].解剖学杂志, 2017,40(1):11-15.
[13] 袁婷,邵志成,欧婷,等.电针治疗对大鼠坐骨神经损伤功能修复的作用[J].中国医学物理学杂志, 2017,34(1):105-108.
[14] 于光明,王伟,张力,等.硫酸软骨素酶ABC-PLGA缓释微球处理去细胞同种异体神经移植修复大鼠坐骨神经[J].解放军医学院学报, 2014,35(8): 858-862.
[15] JENSEN JN, BRENNER MJ, TUNG TH, et al. Effect of FK506 on peripheral nerve regeneration through long grafts in inbred swine. Ann Plast Surg. 2005;54(4):420-427.
[16] 许扬滨,胡军,江长青,等.用去细胞同种异体神经构建猕猴组织工程化神经的实验研究[J].中华显微外科杂志, 2005,28(2):136-138.
[17] HU J, ZHU QT, LIU XL, et al. Repair of extended peripheral nerve lesions in rhesus monkeys using acellular allogenic nerve grafts implanted with autologous mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Neurol. 2007; 204(2):658-666.
[18] XIANG F, WEI D, YANG Y, et al. Tissue-engineered nerve graft with tetramethylpyrazine for repair of sciatic nerve defects in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2017;638:114-120.
[19] 马信龙,杨召,李秀兰,等.脱细胞周围神经的生物力学特性研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(11): 1293-1297.
[20] 杨召,马信龙,李秀兰,等.不同脱细胞方法对周围神经生物力学性能的影响[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2011,30(1):155-159.
[21] 杨昱,彭江,杨启友.采用多重标记物示踪化学去细胞异体神经修复大鼠面神经缺损[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(4):659-662.
[22] SONDELL M, LUNDBORG G, KANJE M. Regeneration of the rat sciatic nerve into allografts made acellular through chemical extraction. Brain Res. 1998;795(1-2):44-54.
[23] ZHANG ZJ, LI YJ, LIU XG, et al. Human umbilical cord blood stem cells and brain-derived neurotrophic factor for optic nerve injury: a biomechanical evaluation. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(7):1134-1138.
[24] WANG Y, LI ZW, LUO M, et al. Biological conduits combining bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular matrix to treat long-segment sciatic nerve defects. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(6): 965-971.
[25] JIN H, YANG Q, JI F, et al. Human amniotic epithelial cell transplantation for the repair of injured brachial plexus nerve: evaluation of nerve viscoelastic properties. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(2):260-265.
[26] SONDELL M, LUNDBORG G, KANJE M. Regeneration of the rat sciatic nerve into allografts made acellular through chemical extraction. Brain Res. 1998;795(1-2):44-54.
[27] HUDSON TW, LIU SY, SCHMIDT CE. Engineering an improved acellular nerve graft via optimized chemical processing. Tissue Eng. 2004;10(9-10):1346-1358.
[28] LIN W, CHEN X, WANG X, et al. Adult rat bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into Schwann cell-like cells in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2008;44(1-2):31-40.
[29] ZHENG W, HONMOU O, MIYATA K, et al. Therapeutic benefits of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow after global cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2010;1310:8-16.
[30] 李晓晓,张博爱,李俊,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对慢性脑缺血大鼠认知功能及海马CAl区Eph B2的影响[J].中风与神经疾病杂志, 2013,30(2): 104-107.
[31] WANG J, DING F, GU Y, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote cell proliferation and neurotrophic function of Schwann cells in vitro and in vivo. Brain Res. 2009;1262:7-15.
[32] CRIGLER L, ROBEY RC, ASAWACHAICHARN A, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell subpopulations express a variety of neuro-regulatory molecules and promote neuronal cell survival and neuritogenesis. Exp Neurol. 2006;198(1):54-64.
[33] KEILHOFF G, STANG F, GOIHL A, et al.Transdifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells as alternative therapy in supporting nerve regeneration and myelination. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2006;26(7-8): 1235-1252.
[34] ZHAO K, LOU R, HUANG F, et al. Immunomodulation effects of mesenchymal stromal cells on acute graft-versus-host disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21(1):97-104.
[35] COPLAND IB, QAYED M, GARCIA MA, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Patients with Acute and Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease Deploy Normal Phenotype, Differentiation Plasticity, and Immune-Suppressive Activity. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21(5):934-940.
|