| [1] Altman GH,Diaz F,Jakuba C,et al.Silk-based biomaterials. Biomaterials.2003;24(3):401-416.[2] Rockwood DN,Preda RC,Yücel T,et al.Materials fabrication from Bombyx mori silk fibroin. Nat Protoc.2011;6(10):1612.[3] Tzur-Balter A,Shatsberg Z,Beckerman M,et al.Mechanism of erosion of nanostructured porous silicon drug carriers in neoplastic tissues.Nat Commun.2015;6:6208.[4] Sun H,Luo C,Yang G,et al.Anatomical evaluation of the modified posterolateral approach for posterolateral tibial plateau fracture.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23(7):809-818.[5] Sivolella S,Brunello G,Ferrarese N,et al.Nanostructured guidance for peripheral nerve injuries: a review with a perspective in the oral and maxillofacial area.Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(2):3088-3117.[6] Engelberg I,Kohn J.Physico-mechanical properties of degradable polymers used in medical applications: a comparative study. Biomaterials.1991;12(3):292-304.[7] Sung H,Meredith C,Johnson C,et al.The effect of scaffold degradation rate on three-dimensional cell growth and angiogenesis. Biomaterials. 2004;25(26):5735-5742. [8] Font Tellado S,Balmayor ER,Van Griensven M.Strategies to engineer tendon/ligament-to-bone interface: Biomaterials, cells and growth factors.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;94:126-140.[9] Bedi A,Maak T,Walsh C,et al.Cytokines in rotator cuff degeneration and repair.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(2):218-227.[10] Zamani F,Amani-Tehran M,Latifi M,et al.The influence of surface nanoroughness of electrospun PLGA nanofibrous scaffold on nerve cell adhesion and proliferation.Journal of materials science. Mater Med. 2013;24(6):1551-1560.[11] Gao S,Yuan Z,Guo W,et al.Comparison of glutaraldehyde and carbodiimides to crosslink tissue engineering scaffolds fabricated by decellularized porcine menisci.Mater Sci Eng C. 2017;71:891-900.[12] Agrawal CM,Ray RB.Biodegradable polymeric scaffolds for musculoskeletal tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;55(2): 141-150.[13] Chou Y,Yeh W,Chao C,et al.Enhancement of tendon-bone healing via the combination of biodegradable collagen-loaded nanofibrous membranes and a three-dimensional printed bone-anchoring bolt.Int J Nanomed.2016;11:4173-4186.[14] Park S,Gil ES,Kim HJ,et al.Relationships between degradability of silk scaffolds and osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 2010;31(24):6162-6172.[15] Chandrasekaran AR,Venugopal J,Sundarrajan S,et al.Fabrication of a nanofibrous scaffold with improved bioactivity for culture of human dermal fibroblasts for skin regeneration.Biomedical materials (Bristol, England). 2011;6(1):15001.[16] Ma Z,Kotaki M,Yong T,et al.Surface engineering of electrospun polyethylene terephthalate (PET)nanofibers towards development of a new material for blood vessel engineering. Biomaterials. 2005;26(15): 2527-2536.[17] 李鹏昊,刘舒云,王亚洁,等.电纺聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物/Ⅰ型胶原-聚己内酯双层膜预防腱周粘连的相关研究[J].中国医药生物技术, 2017, 12(4):289-296.[18] Orr SB,Chainani A,Hippensteel KJ,et al.Aligned multilayered electrospun scaffolds for rotator cuff tendon tissue engineering.Acta Biomaterialia.2015;24:117-126.[19] Beason DP,Connizzo BK,Dourte LM,et al.Fiber-aligned polymer scaffolds for rotator cuff repair in a rat model.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(2):245-250. [20] Pham QP,Sharma U,Mikos AG.Electrospun poly(epsilon-caprolactone) microfiber and multilayer nanofiber/microfiber scaffolds: characterization of scaffolds and measurement of cellular infiltration. Biomacromolecules. 2006;7(10):2796-2805.[21] Diseases EI.U.S.Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Recommendations and Reports CONTENTS. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2012;28(11):373-392.[22] Wu XL,Briggs L,Murrell GAC.Intraoperative Determinants of Rotator Cuff Repair Integrity. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40:2771-2776.[23] Alhakim W,Noorani A,Lambert S.Assessment and treatment strategies for rotator cuff tears. Shoulder Elbow.2015;7(2):76.[24] Lorbach O,Baums MH,Kostuj T,et al.Advances in biology and mechanics of rotator cuff repair.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(2):530-541.[25] 李嘉,戴海峰,刘莎莎,等.骨膜补片加强修复促进肩袖腱骨愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(30):4847-4751.[26] 刘斌,袁振超,贺聚良,等.肿瘤型肱骨近端假体复合人工补片重建肩关节临床疗效观察[J].实用医学杂志,2017,33(1):164-165.[27] Inui A,Kokubu T,Mifune Y,et al.Regeneration of rotator cuff tear using electrospun poly(d,l-Lactide-Co-Glycolide) scaffolds in a rabbit model.Arthroscopy. 2012;28(12):1790-1799.[28] Chainani A,Hippensteel KJ,Kishan A,et al.Multilayered electrospun scaffolds for tendon tissue engineering.Tissue Eng Part A. 2013; 19(23-24):2594-2604.[29] Zhao S,Zhao J,Dong S,et al.Biological augmentation of rotator cuff repair using bFGF-loaded electrospun poly(lactide-co-glycolide) fibrous membranes.Int J Nanomedicine.2014;9:2373-2385.[30] Zhao S,Xie X,Pan G,et al.Healing improvement after rotator cuff repair using gelatin-grafted poly(L-lactide) electrospun fibrous membranes.J Surg Res.2015;193(1):33-42.[31] Hakimi O,Mouthuy PA,Zargar N,et al.A layered electrospun and woven surgical scaffold to enhance endogenous tendon repair.Acta Biomaterialia.2015;26:124-135.[32] Orr SB,Chainani A,Hippensteel KJ,et al.Aligned multilayered electrospun scaffolds for rotator cuff tendon tissue engineering.Acta Biomater2015;24:117-126.[33] Li Z,Song L,Huang X,et al.Tough and VEGF-releasing scaffolds composed of artificial silk fibroin mats and a natural acellular matrix. RSC Adv.2015;5(22):16748-16758.[34] Chou Y,Yeh W,Chao C,et al.Enhancement of tendon–bone healing via the combination of biodegradable collagen-loaded nanofibrous membranes and a three-dimensional printed bone-anchoring bolt.Int J Nanomedicine.2016;11:4173-4186. [35] Li X,Cheng R,Sun Z,et al.Flexible bipolar nanofibrous membranes for improving gradient microstructure in tendon-to-bone healing.Acta Biomaterialia.2017;61:204-216.[36] 任士友,江长青,张文涛.不同肩袖补片特点:应用强度、降解速率及酸性降解物的调控[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(30):4876-4881. |
.jpg)


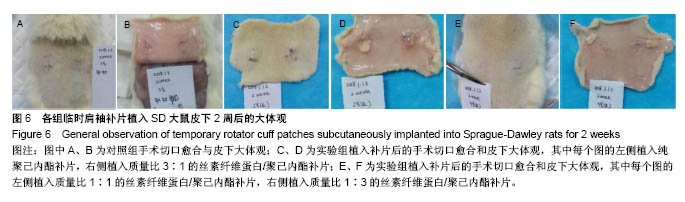
.jpg)
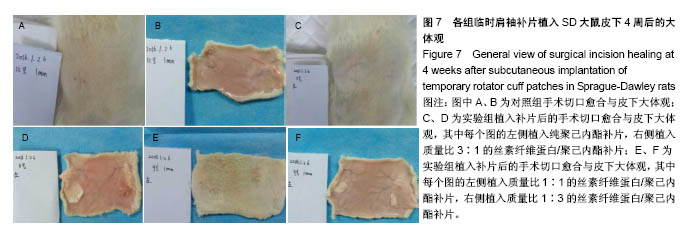
.jpg)
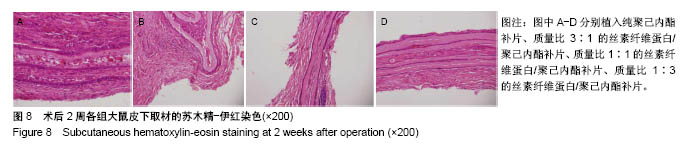
.jpg)
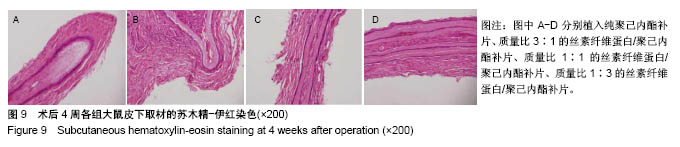
.jpg)