| [1] Hoffmann TK, Schuler PJ, Laban S, et al. Response evaluation in head and neck oncology: definition and prediction. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2017;79(1):14-23.[2] Maruyama T, Nishihara K, Saio M, et al. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease in the regional lymph nodes with node metastasis in a patient with tongue cancer: a case report and literature review. Oncol Lett. 2017; 14(1):257-263.[3] Van den Brekel M, Castelijns J, Snow G. The size of lymph nodes in the neck on sonograms as a radiologic criterion for metastasis: how reliable is it? A JNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998;19:695-700.[4] Kim SH, Oh SN, Choi HS, et al. USPIO enhanced lymph node MRI using 3D multi-echo GRE in a rabbit model. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2016;11(6):544-549.[5] Lahaye MJ, Engelen SM, Kessels AG, et al. USPIO-enhanced MR imaging for nodal staging in patients with primary rectal cancer:predictive criteria. Radiology. 2008;246(3):804-811.[6] Crott R, Lawson G, Nollevaux MC, et al. Comprehensive cost analysis of sentinel node biopsy in solid head and neck tumors using a time-driven activity-based costing approach. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;273(9):2621-2628.[7] Werner JA. Untersuchungen zum Lymphgef äβsystem der oberen Luft-und Speisewege. Aachen: Shaker. 1995.[8] Kim SH, Oh SN, Choi HS, et al. Ultra-small superparamagnetic iron oxide mediated magnetic hyperthermia in treatment of neck lymph node metastasis in rabbit pyriform sinus VX2 carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(10):8035-8040.[9] Payabvash S, Meric K.,Cayci Z. Differentiation of benign from malignant cervical lymph nodes in patients with head and neck cancer using PET/CT imaging.Clin Imaging. 2016;40(1):101-105.[10] Dunne AA, Plehn S, Schulz S, et al. Lymph node tepography of the head and neck in New Zealand white rabbits. Lab Anim. 2003;37: 37-43.[11] 李文晋,牛金亮,朱莉,等.头颈部不同部位肿瘤动物模型的建立及生长转移特性比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(5):748-753. [12] Van den Brekel MW, Stel HV, Castelijns JA, et al. Cervical lymph node metastases:assessing of radiological criteria. Radiology. 1990;177(2):379-384.[13] Steinkamp HJ, Hosten N, Richter C, et al. Enlarged cervical lymph nodes at helical CT. Radiology. 1994;191(3):795-798.[14] Iannessi A. Ouvrier MJ. Thariat J, et al. Imaging in head and neck cancers. Bull Cancer. 2014;101(5):469-480.[15] Sun J, Li B, Li CJ, et al. Computed tomography versus magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosing cervical lymph node metastasis of head and neck cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther. 2015;8:1291-1313.[16] Eida S, Sumi M, Yonetsu K, et al. Combination of helical CT and Doppler sonography in the follow-up of patients with clinical N0 stage neck disease and oral cancer. AJNR. 2003;24(3):312-318.[17] 李文晋,牛金亮,金慧兰,等.头颈部肿瘤颈部淋巴结隐匿性转移的病理实验研究[J].中国药物与临床,2012,12(12):1533-1535. [18] Poant? L, Pop S, Cosgarea M, et al. The role of contrast enhanced ultrasound in the assessment of superficial lymph nodes. Rom J Intern Med, 2012;50(3):189-193.[19] Manca G, Vanzi E, Rubello D, et al. (18)F-FDG PET/CT quantification in head and neck squamous cell cancer: principles, technical issues and clinical applications. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.2016;43(7):1360-1375. [20] Lu L, Li Y, Li W. The role of intravoxel incoherent motion MRI in predicting early treatment response to chemoradiation for metastatic lymph nodes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Adv Ther. 2016;33(7):1158-1168.[21] 蓝美红,牛金亮,李文晋,等.相对表观弥散系数与钆喷替酸葡甲胺增强MRI诊断兔头颈转移淋巴结的对比研究[J].中国中西医结合影像学杂志, 2012,10(2):105-108.[22] Triantafyllou M, Studer UE, Birkhäuser FD, et al. Ultrasmall superparamagnetic particles of iron oxide allow for the detection of metastases in normal sized pelvic lymph nodes of patients with bladder and/or prostate cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49(3):616-624.[23] Froehlich JM, Triantafyllou M, Fleischmann A, et al. Does quantification of USPIO uptake-related signal loss allow differentiation of benign and malignant normal-sized pelvic lymph nodes? Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2012;7(3):346-355.[24] Schramm N. Macrophage imaging for differentiation between infectious spondylitis/spondylodiscitis and sterile vertebral inflammation: new options for the use of USPIO-enhanced MRI beyond lymph node characterization. Radiology. 2010;50(3): 205-207.[25] Wu L, Cao Y, Liao C, et al. Diagnostic performance of USPIO-enhanced MRI for lymph- node metastases in different body regions: a meta-analysis. Eur J Radiol. 2011;80(2):582-589.[26] Choi SH, Kim KH, Moon WK, et al. Comparison of lymph node metastases assessment with the use of USPIO-enhanced MR imaging at 1.5 T versus 3.0 T in a rabbit model. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;31(1):134-141.[27] Bandini M, Gandaglia G, Fossati N, et al. An Explanatory Case on the Limitations of Lymph Node Staging in Recurrent Prostate Cance. Urol Case Rep. 2017;12:34-36.[28] Kawai Y, Sumi M, Nakamura T. Turbo short tau inversion recovery imaging for metastatic node screening in patients with head and neck cancer. Am J Neuroradiol. 2006;27(6):1283-1287.[29] Smits LP, Coolen BF, Panno MD, et al. Noninvasive differentiation between hepatic steatosis and steatohepatitis with mr imaging enhanced with USPIOs in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a proof-of-concept study. Radiology. 2016;278(3):782-791.[30] Seyfer P, Pagenstecher A, Mandic R, et al. Cancer and inflammation: differentiation by USPIO-enhanced MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014;39(3):665-672.[31] Liang L, Luo X, Lian Z, et al. Lymph node metastasis in head and neck squamous carcinoma: efficacy of intravoxel incoherent motion magnetic resonance imaging for the differential diagnosis. Eur J Radiol. 2017;90:159-165. |
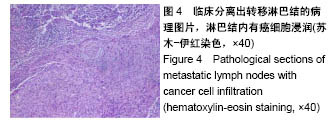
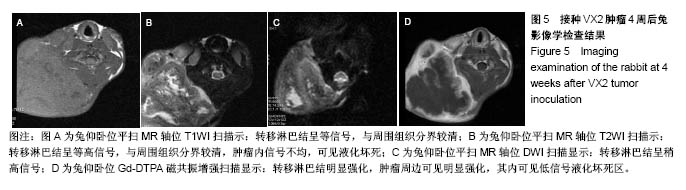
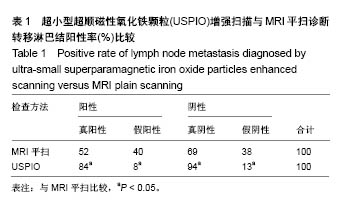
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)