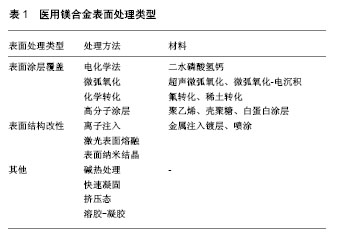
| [1] Gepreel AH, Niinomi M. Biocompatibility of Ti-alloys for long-term implantation. J Mech Behav Biomed. 2013;20(4):407-415. [2] 王艳娜.生物医用AZ31B镁合金表面改性及性能研究[D].沈阳:沈阳建筑大学,2011.[3] 苏颖超.镁合金及复合材料表面钙磷膜层的制备与腐蚀降解行为研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2016.[4] Neděla O, Slepi?ka P, Švor?ík V, et al. Surface Modification of Polymer Substrates for Biomedical Applications. Materials. 2017; 10(10):1115.[5] 齐峥嵘.微弧氧化表面处理的ZK60镁合金在大鼠体内的降解行为及生物相容性研究[D].北京:中国人民解放军军医进修学院,2013.[6] Xu L, Pan F, Yu G, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the surface bioactivity of a calcium phosphate coated magnesium alloy. Biomaterials. 2009;30(8):1512-1523. [7] Surmeneva MA, Tyurin AI, Mukhametkaliyev TM, et al. Enhancement of the mechanical properties of AZ31 magnesium alloy via nanostructured hydroxyapatite thin films fabricated via radio-frequency magnetron sputtering. J Mech Behav Biomed. 2015;46:127-136.[8] 龚沛,王欣宇,郭洁.仿生法制备纯镁/羟基磷灰石复合涂层的研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2008,5(4):39-42.[9] 林锐,刘朝辉,王飞,等.镁合金表面改性技术现状研究[J].表面技术, 2016,45(4):124-131. [10] Li X, Liu X, Wu S, et al. Design of Magnesium Alloys with Controllable Degradation for Biomedical Implants: from Bulk to Surface. Acta Biomater. 2016;45:2-30.[11] Walker J, Shadanbaz S, Kirkland NT, et al. Magnesium alloys: Predicting in vivo corrosion with in vitro immersion testing. J Biomed Mater Res B. 2012;100B(4):1134-1141.[12] Marques IS, Alfaro MF, Cruz NC, et al. Tribocorrosion behavior of biofunctional titanium oxide films produced by micro-arc oxidation: synergism and mechanisms. J Mech Behav Biomed. 2016;60:8.[13] Echever R, Monica, Galvis O, et al. Osseointegration improvement by plasma electrolytic oxidation of modified titanium alloys surfaces. J Mater Sci-Mater M. 2015;26(2):72.[14] 曲立杰.镁合金表面超声微弧氧化生物涂层的组织结构与性能[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2015.[15] 慕伟意,李争显,杜继红,等.镁合金的应用及其表面处理研究进展[J].表面技术,2011,40(2):86-91.[16] Drynda A, Hassel T, Bach FW, et al. In vitro and in vivo corrosion properties of new iron–manganese alloys designed for cardiovascular applications. J Biomed Mater Res B. 2015;103(3): 649-660.[17] Martinez Sanchez AH, Luthringer BJ, Feyerabend F, et al. Mg and Mg alloys: how comparable are in vitro and in vivo corrosion rates? A review. Acta Biomater. 2015;13:16-31.[18] 颜廷亭.AZ31B镁合金的生物医用表面改性研究[D].南京:南京理工大学, 2010.[19] Yeung KWK, Wong KHM. Biodegradable metallic materials for orthopaedic implantations: a review. IOS Press. 2012. [20] Jain A, Kunduru KR, Basu A, et al. Injectable formulations of poly(lactic acid) and its copolymers in clinical use. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2016;107:213. [21] Golshirazi A, Kharaziha M, Golozar M. Polyethylenimine/Kappa Carrageenan: Micro-arc Oxidation Coating for Passivation of Magnesium Alloy. Carbohyd Polym. 2017;167:185.[22] Xu G, Shen X, Dai L, et al. Reduced bacteria adhesion on octenidine loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles coating on titanium substrates. Mat Sci Eng C. 2017;70:386-395.[23] Ostrowski N, Lee B, Enick N, et al. Corrosion protection and improved cytocompatibility of biodegradable polymeric layer-by-layer coatings on AZ31 magnesium alloys. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(10): 8704-8713.[24] 曾荣昌,刘丽君,骆凯捷,等.AZ31镁合金表面层层组装PSS/GS膜的体外耐蚀与抗菌性能(英文)[J].中国有色金属学报(英文版),2015,25(12): 4028-4039.[25] Agarwal S, Curtin J, Duffy B, et al. Biodegradable magnesium alloys for orthopaedic applications: a review on corrosion, biocompatibility and surface modifications. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater. 2016;68:948.[26] Lu Y, Wan P, Zhang B, et al. Research on the corrosion resistance and formation of double-layer calcium phosphate coating on AZ31 obtained at varied temperatures. Mat Sci Eng C. 2014;43(43): 264-271.[27] Qiao X, Russell S J, Yang X, et al. Compositional and in Vitro Evaluation of Nonwoven Type I Collagen/Poly-dl-lactic Acid Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. J Funct Biomater. 2015;6(3):667-686.[28] Wang ZL, Yan YH, Tao W, et al. Poly (L-lactic acid)/Hydroxyapatite/ Collagen Composite Coatings on AZ31 Magnesium Alloy for Biomedical Application. P I Mech Eng H. 2013;227(10):1094.[29] 张春怀.医用镁合金的腐蚀行为及高分子修饰研究[D].天津:天津大学, 2007.[30] 唐荻.激光+碱热处理的医用Mg--4.0Zn--1.5Sr合金的降解及生物相容性研究[D].沈阳:东北大学,2014.[31] Ho YH, Vora HD, Dahotre NB. Laser surface modification of AZ31B Mg alloy for bio-wettability. J Biomater Appl. 2015;29(7):915-928.[32] 高正源,潘复生,汤爱涛,等.AZ31镁合金表面纳米A12O3涂层的耐蚀耐磨性能研究[J].功能材料,2013,44(8):1069-1072.[33] Vimbela GV, Ngo SM, Fraze C, et al. Anti bacterial properties and toxicity from metallic nanomaterials. Int J Nanomed. 2017;12: 3941-3965.[34] 张佳.新型Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr合金在模拟体液中的降解行为研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2010.[35] 张晶.Mg-Zn-Zr合金的表面处理及其内外腐蚀降解性能研究[D].天津:天津理工大学,2014.[36] 谢兴文,黄晋,李宁,等.镁及镁合金植入体在骨科临床中的应用与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(39):7317-7321.[37] 钱琳灵.表面处理对医用镁合金降解性能的影响研究[D].南京:东南大学,2016.[38] 龚才华.表面有机改性镁基生物材料的制备及生物相容性研究[D].重庆:重庆大学,2016.[39] Zhao S, Chen Y, Liu B, et al. A Dual-task Design of Corrosion-controlling and Osteo-compatible Hexamethylenediaminetetrakis-(methylene phosphonic acid) (HDTMPA) Coating on Magnesium for Biodegradable Bone Implants Application. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(5):1640-1652.[40] 彭友霖,周丽丽,周艳红.镁合金作为生物医用植入材料的临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2011,15(42):7923-7926. |
.jpg)
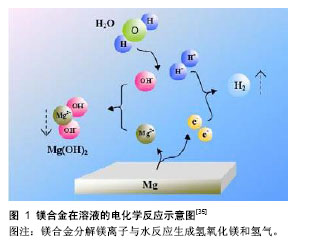
.jpg)